Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatology patients are particularly vulnerable to pneumococcal infection due to both their underlying disease and immunosuppressive therapy. Thus, quality improvement metrics include increasing pneumococcal vaccination rate in rheumatology patients. Our goal was to implement a nurse driven protocol to increase by 10% the pneumococcal conjugate and polysaccharide vaccination rate during a three month period among immunosuppressed patients aged 19-64 years old followed at an academic adult rheumatology clinic.
Methods: Eligible adults aged 19-64 years old were identified in the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) using a search protocol based on pre-set immunosuppressive medication group. We calculated baseline vaccination rate by assessing whether patients had received either the Pneumovax23 (PPSV23) or Prevnar13 (PCV13) or both vaccines from January 1, 2019 – December 31, 2019. We developed a nurse-driven workflow for vaccination implementation in the clinic. Using Center for Disease Control (CDC) guidelines, we created a pneumococcal vaccination protocol (Table 1) and converted it into a university approved Standing Medical Order (SMO) to be used by the nursing staff. We held educational sessions for the nursing staff to review the protocols and workflow. Staff re-training was implemented mid-way through the cycle. Post-intervention pneumococcal vaccination rates were calculated on a monthly basis.
Results: Baseline rate of both PCV13 and PPSV23 immunization (full immunization) for immunosuppressed rheumatology patients aged 19-64 years in 2019 was 6.6%. Baseline rate of unique patients within the target population who had received any type of immunization in our clinic (either PCV13, PPSV23, or both) was 25.3%.
Average monthly percentage of unvaccinated patients within target population seen in our clinic in 2019 was 73.2%. Percent of eligible patients who had pneumococcal vaccination series initiated, on average per month, in our clinic was 3.9% for 2019.
Start date for the intervention phase of project was January 1, 2020. We obtained post-intervention vaccination data for Jan-March 21, 2020 [a truncated three month time period due to COVID-19 pandemic clinic changes]. While the percentage of initiation of vaccination series continued to be low in Jan and Feb 2020, we achieved 11.4% vaccination rate of previously unvaccinated patients in March 2020 (Figure 1), which represents a nearly three fold increase over baseline vaccination rate.
Conclusion: During a three month cycle of nurse-driven SMO protocol to implement pneumococcal vaccination, we were able to increase our pneumococcal vaccination initiation rate of eligible immunocompromised patients from baseline of 3.9% to 11.4%. Overall vaccination rates of eligible patients remain low, but we anticipate that continued use of a nurse driven protocol will improve this rate. Our study suggests that using a nurse-driven SMO protocol is a useful tool in improving vaccination rate amongst immunocompromised rheumatology patients. The post-intervention data is currently scarce; however, we hope to obtain four months more worth of data after the clinics are anticipated to re-open in June 2020.
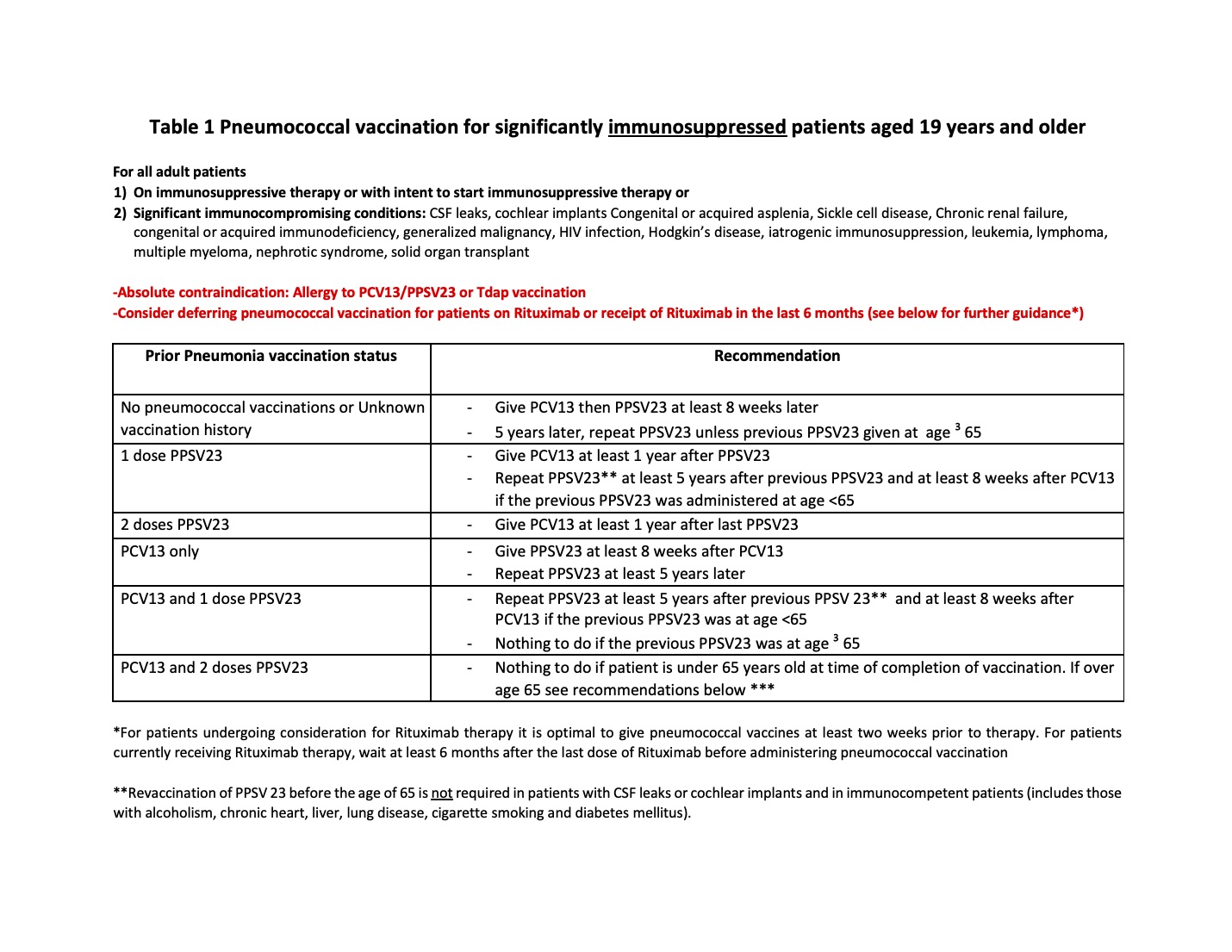 Table1: Pneumococcal Vaccination For Significantly Immunosuppressed Patients Aged 19 Years And Older
Table1: Pneumococcal Vaccination For Significantly Immunosuppressed Patients Aged 19 Years And Older
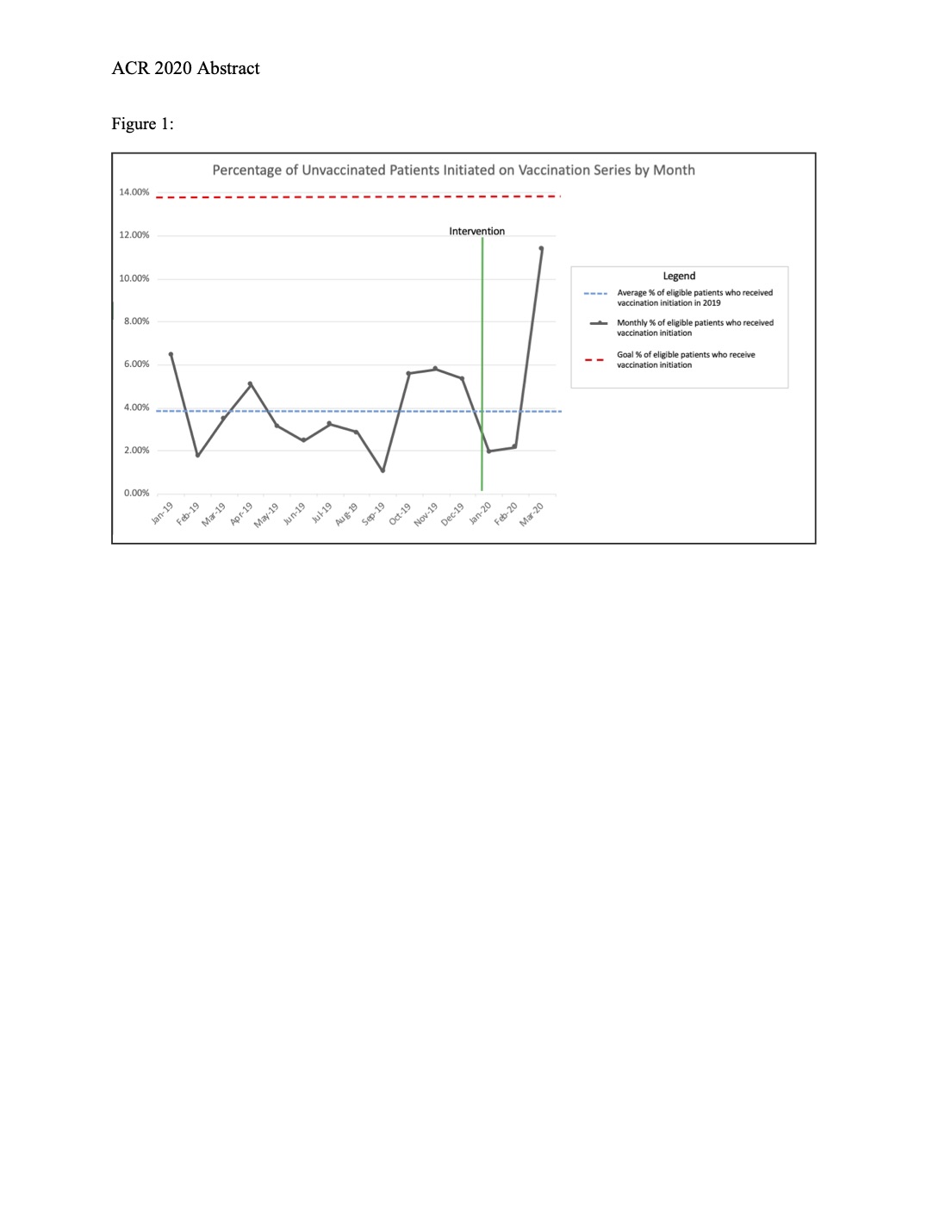 Figure 1: Percentage Of Unvaccinated Patients Initiated On Vaccination Series By Month
Figure 1: Percentage Of Unvaccinated Patients Initiated On Vaccination Series By Month
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Joerns E, Bermas B, Bajaj P, Pokala N, Arasaratnam R, Reisch J, Wang D. Improving Pneumococcal Vaccination Rates Among Immunosuppressed Adults in an Academic Rheumatology Clinic Utilizing a Nurse Driven Protocol [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-pneumococcal-vaccination-rates-among-immunosuppressed-adults-in-an-academic-rheumatology-clinic-utilizing-a-nurse-driven-protocol/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-pneumococcal-vaccination-rates-among-immunosuppressed-adults-in-an-academic-rheumatology-clinic-utilizing-a-nurse-driven-protocol/
