Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1082–1099) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a key treatment for patients with lupus and other rheumatic diseases. To minimize the risk of retinal toxicity, the American College of Ophthalmology (ACO) guidelines published in 2016 recommends using a maximum HCQ daily dose of ≤5mg/kg of actual body weight and to begin annual retinopathy screening after 5 years of HCQ use with automated visual fields plus optical coherence tomography (OCT). The aim of this quality improvement project was to assess if an educational intervention could improve the adherence to ACO dosing recommendations and retinal toxicity monitoring in a large VA Medical Center.
Methods: Patients above 18 years old with a connective tissue disorder diagnosis and who were actively using HCQ were evaluated. HCQ dosing above 5 mg/kg, and eye screening status were reviewed. Two different interventions were implemented twelve months apart: 1) An educational intervention using a personal email with the ACO guidelines was sent to each provider with patients requiring screening testing or HCQ dose adjustment. 2) Second intervention using a “system alert” in the medical record with the correct HCQ dosing and annual OCT was created as a reminder when prescribing or renewing HCQ. Changes in compliance from pre- to post-interventions were assessed.
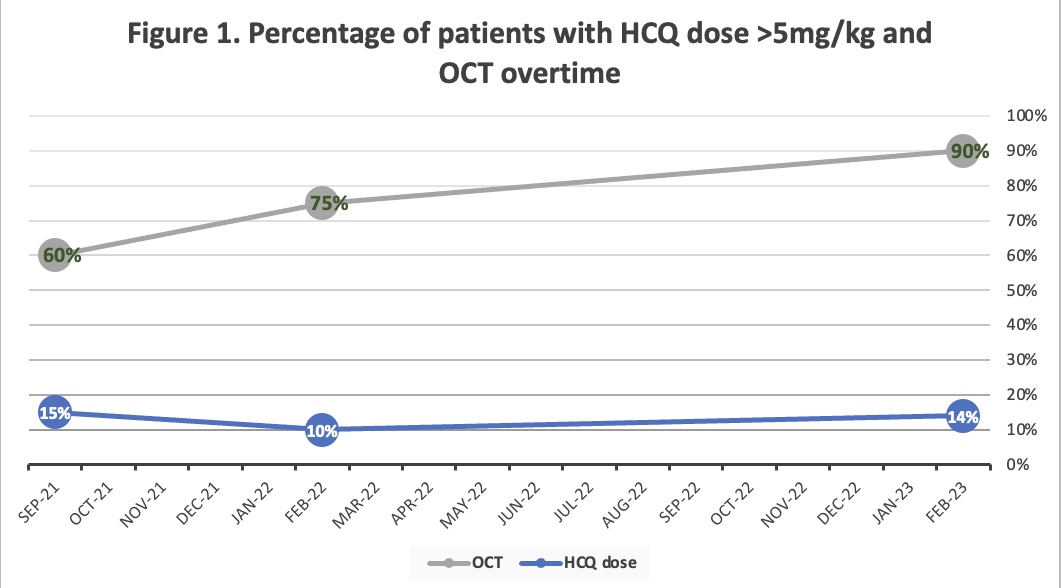
Results: A total of 258 patients with an active HCQ prescription were included. Forty patients (15%) had a HCQ dose above 5mg/kg. Among this group, HCQ was mainly prescribed by a Rheumatologist (35/40).From the forty patients with HCQ dose above 5mg/kg, 24 (60%) had at least one OCT screening. After the first intervention, the number of patients who required HCQ dose adjustment went down by 5% (15% vs 10%). Most of the patients who required HCQ dose adjustment were receiving a HCQ dose between 5-5.9 mg/kg (60%). More patients had an updated OCT (75% post vs 60% pre). After the second intervention, the number of patients who required HCQ dose adjustment went up by 4%. However, more patients had an updated OCT (90% post vs 75% pre) (Figure).
Conclusion: Educational interventions, including the review of guidelines, or system alerts on different medical records were associated with a notable improvement in retinal toxicity screening but had modest or no effect on adherence to ACO HCQ dosing recommendations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salgado Guerrero M, Gaffo A. Improving Hydroxychloroquine Dosing and Eye Screening Compliance in Patients with Connective Tissue Disorder [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-hydroxychloroquine-dosing-and-eye-screening-compliance-in-patients-with-connective-tissue-disorder/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-hydroxychloroquine-dosing-and-eye-screening-compliance-in-patients-with-connective-tissue-disorder/