Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with gout have impaired health-related quality of life (HRQoL) relating to acute or chronic inflammation from elevated serum uric acid (sUA) levels. SEL-212 is a novel, once-monthly, two‐component infusion therapy of nanoparticles containing sirolimus (SEL-110) followed by pegadricase (SEL‑037, a pegylated uricase) designed to reduce sUA. Results from DISSOLVE I and II (DI and DII) Phase 3 trials demonstrated that SEL-212 significantly improved response rates (sUA <6 mg/dL for ≥80% of treatment period [TP] 6) and mean sUA levels vs placebo in pts with chronic refractory gout. Post hoc analyses were conducted in pts who received the first 3 (F3D) or 6 doses (F6D) of SEL-212, to assess effects on physical and mental functioning, daily activities and pain.
Methods: DI (US) and DII (global) were randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of pts with ≥3 gout flares within 18 months prior to screening or ≥1 tophus or a current diagnosis of gouty arthritis, in whom oral urate lowering therapy failed to normalize sUA and control symptoms, and naïve to uricase-based therapy. Pts received high- or low-dose (HD or LD) SEL‑212 (consisting of SEL-110 [0.15 or 0.1 mg/kg] plus SEL-037 [0.2 mg/kg]) or placebo on Day 0 (D0) for each of the six 28-day TPs. Patient reported outcomes (PROs: 36‑item Short Form survey [SF‑36], Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index [HAQ-DI] and pain visual analogue scale [VAS]) were assessed at baseline, TP4 D0 and TP6 D28. Analyses were performed using pooled data from DI and DII and reported as least squares mean [standard error].
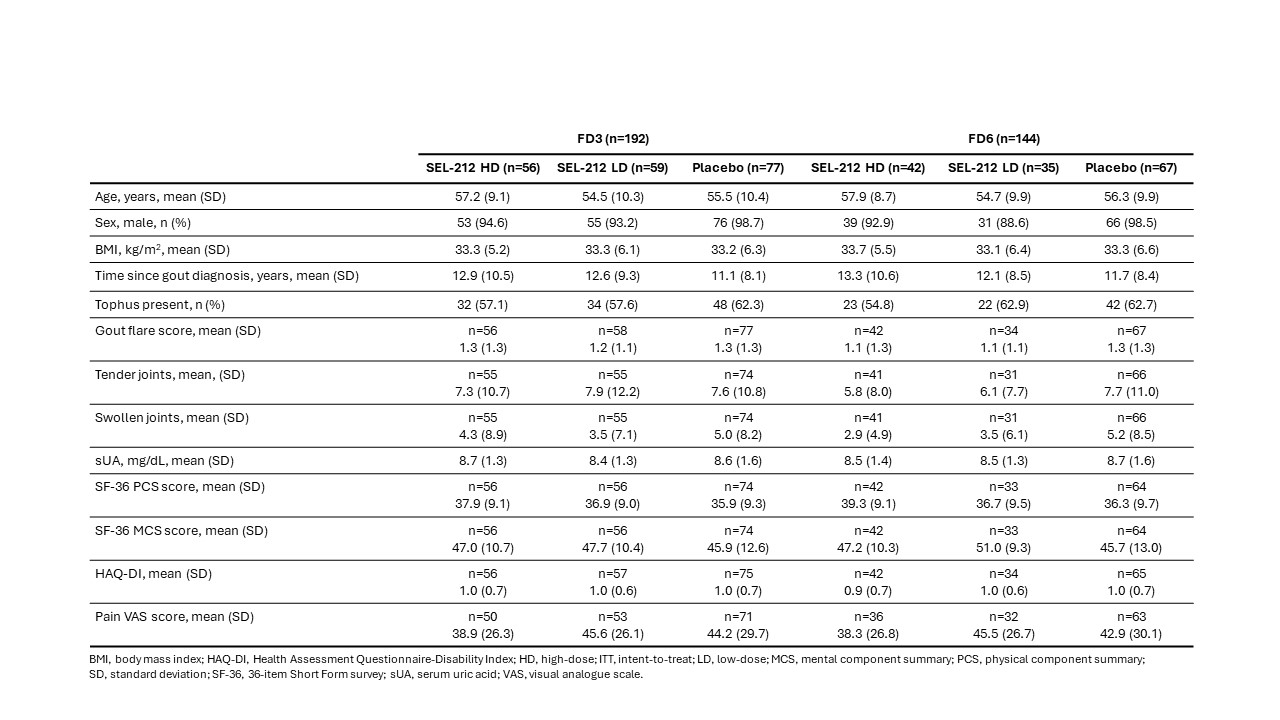
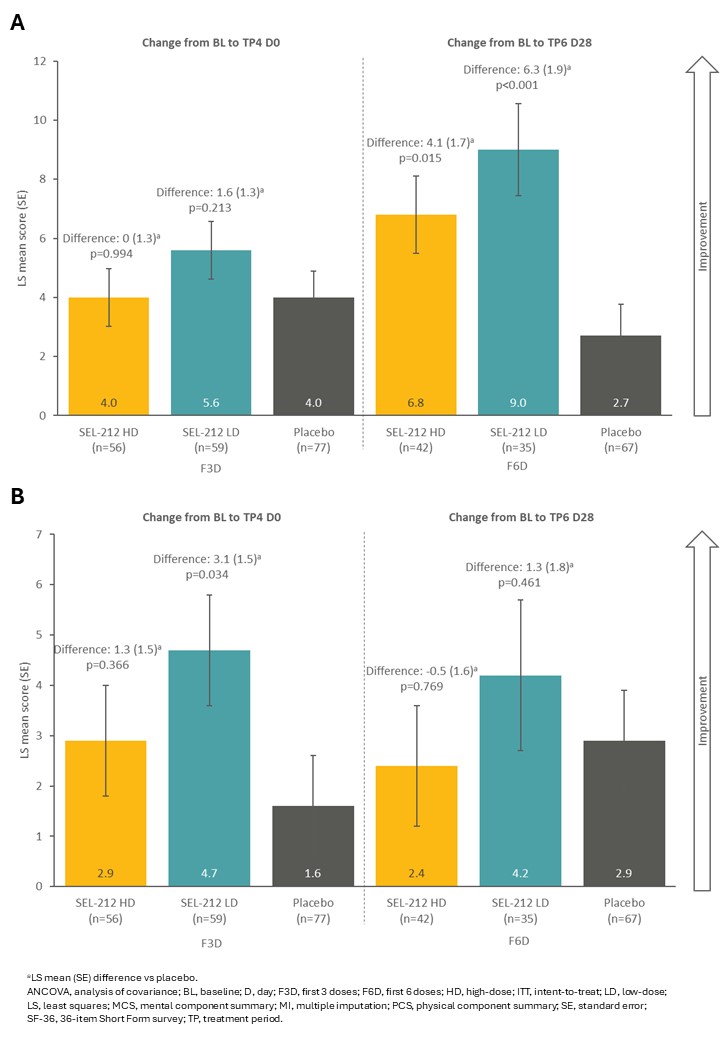
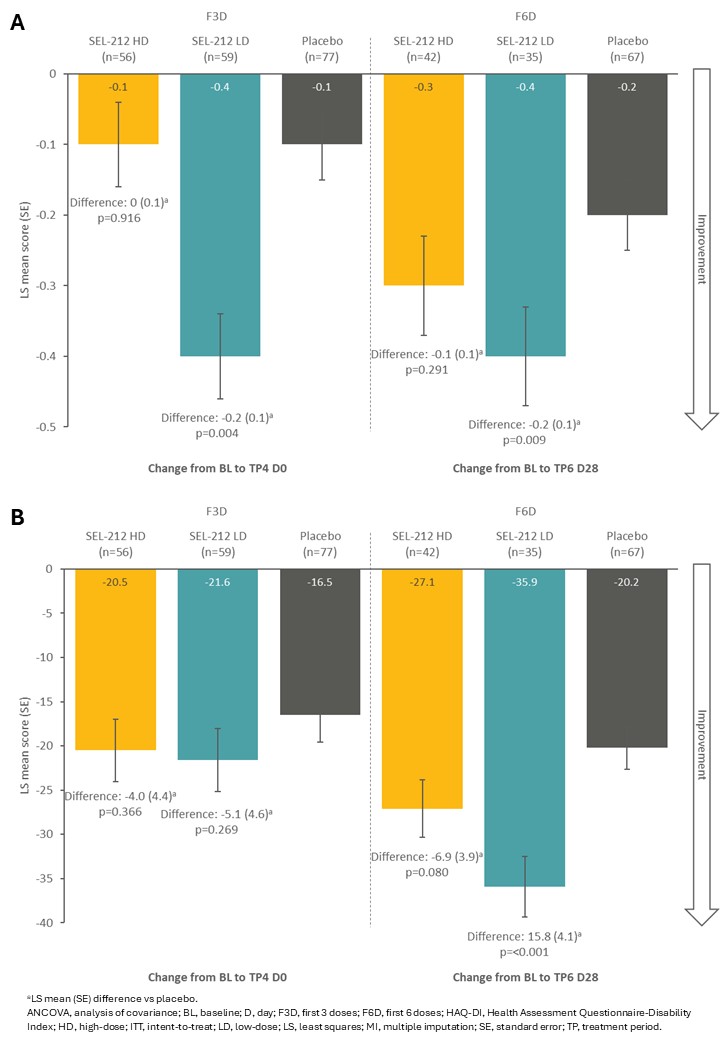
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar in the intent-to-treat and F3D/F6D populations and across treatment arms for the F3D/F6D subgroups (Table 1). Change from baseline in SF-36 physical component summary score was improved to a greater extent with SEL-212 LD (5.6 [0.1]) vs placebo (4.0 [0.9]) in the F3D subgroup, and further improved with SEL‑212 LD (9.0 [1.6]) and SEL-212 HD (6.8 [1.3]) vs placebo (2.7 [1.1]) in the F6D subgroup (Fig 1A). Change from baseline in SF-36 mental component summary score was improved to a greater extent with SEL-212 LD (4.7 [1.1]) and SEL-212 HD (2.9 [1.1]) vs placebo (1.6 [1.0]) in the F3D subgroup, while an improvement was observed for SEL-212 LD (4.2 [1.5]) vs placebo (2.9 [1.0]) in the F6D subgroup (Fig 1B). In the F3D subgroup, change from baseline in HAQ-DI was improved with SEL‑212 LD (-0.4 [0.1]) vs placebo (-0.1 [0.1]) (Fig 2A). In the F6D subgroup, change from baseline in HAQ‑DI was improved with SEL-212 LD (-0.4 [0.1]) and SEL-212 HD (-0.3 [0.1]) vs placebo (-0.2 [0.1]) (Fig 2A). Similar data were reported for pain VAS score, with a trend for improved outcomes observed in the F6D vs FD3 subgroup (Fig 2B).
Conclusion: Clinically meaningful changes in PROs were reported after 3 doses of SEL-212, which further improved after 3 additional doses, indicating patients reported an incremental HRQoL benefit with prolonged treatment duration. SEL-212 improved clinical and HRQoL outcomes, including functional ability, mental health and pain, in adults with refractory gout, which is likely reflective of improved urate lowering with this novel agent.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Khanna P, Kivitz A, Kragh N, Falk A, Azeem R, Santin-Janin H, Baraf H. Improvements in Patient-Reported Outcomes After Treatment with SEL-212 in Adults with Refractory Gout: Results from Two Randomized Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-patient-reported-outcomes-after-treatment-with-sel-212-in-adults-with-refractory-gout-results-from-two-randomized-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-patient-reported-outcomes-after-treatment-with-sel-212-in-adults-with-refractory-gout-results-from-two-randomized-phase-3-trials/