Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In 2023, Spain approved the inactivated varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine in individuals over 50 years of age with immunosuppressive conditions, including rheumatology patients due to both immune system alterations and immunosuppressive therapies. It is anticipated that the proportion of vaccinated patients will increase in the coming years, resulting in fewer herpetic events and associated complications.Our objective is to describe a population of rheumatology patients eligible for VZV vaccination and to analyze vaccination uptake and incidence of herpetic events.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, observational, descriptive study of patients followed at a tertiary care Rheumatology Department. Between January 2021 and June 2024, patients were referred for vaccination prior to initiating biologic, targeted synthetic, or immunosuppressive therapy. Demographic and clinical characteristics were recorded. A subanalysis of herpetic events and their incidence before and after the vaccine was performed.
Results: 431 patients (66.1% female) were referred for VZV vaccination, most commonly with Rheumatoid Arthritis (34.1%). The mean age at treatment initiation was 51.49 ± 13.81 years (Table 1). The most frequently initiated therapy was anti-TNF agents (25.29%), followed by JAK inhibitors (20.6%).Of these, 171 patients (39.7%) received the VZV vaccine, primarily women with rheumatoid arthritis. Among vaccinated patients, JAK inhibitors were the most commonly initiated treatment (41.52%), with Upadacitinib used in 31 cases. The annual proportion of patients vaccinated against VZV increased from 10.87% in 2021 to 66.67% in 2024 (Figure 1).29 herpetic events occurred in 23 patients, yielding an incidence of 0.06 events per patient over a mean follow-up of 10.81 years. Of these, 21 were women and 8 were receiving JAK inhibitors. Among vaccinated individuals, 22 herpetic events were recorded, with 18 occurring prior to vaccine administration and 4 events reported post-vaccination. The majority of herpetic episodes were cutaneous monometameric (60.7%), followed by multimetameric cutaneous involvement (10.7%). The incidence of herpetic events in the vaccinated group was 0.02 events per patient (2.33% of vaccinated patients). In contrast, the incidence in unvaccinated patients was higher, at 0.05 events per patient (5.8% of the unvaccinated population).
Conclusion: 39.7% of patients referred for pre-biologic varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccination received it, with uptake increasing progressively over the study period. The most frequent treatment initiated were JAK inhibitors. 29 herpetic events were documented in 23 patients, most of which were mild. Among these 23 patients, 18 had been vaccinated, with only 4 herpetic events occurring after vaccine administration. The incidence of herpetic events among unvaccinated patients was 0.05 events per patient, corresponding to 5.8% of that subgroup. In contrast, the incidence in the vaccinated cohort was reduced to 0.02 events per patient, affecting 2.33% of vaccinated individuals. These findings support a potential protective role of VZV vaccination in reducing herpes zoster events in immunocompromised rheumatology patients.
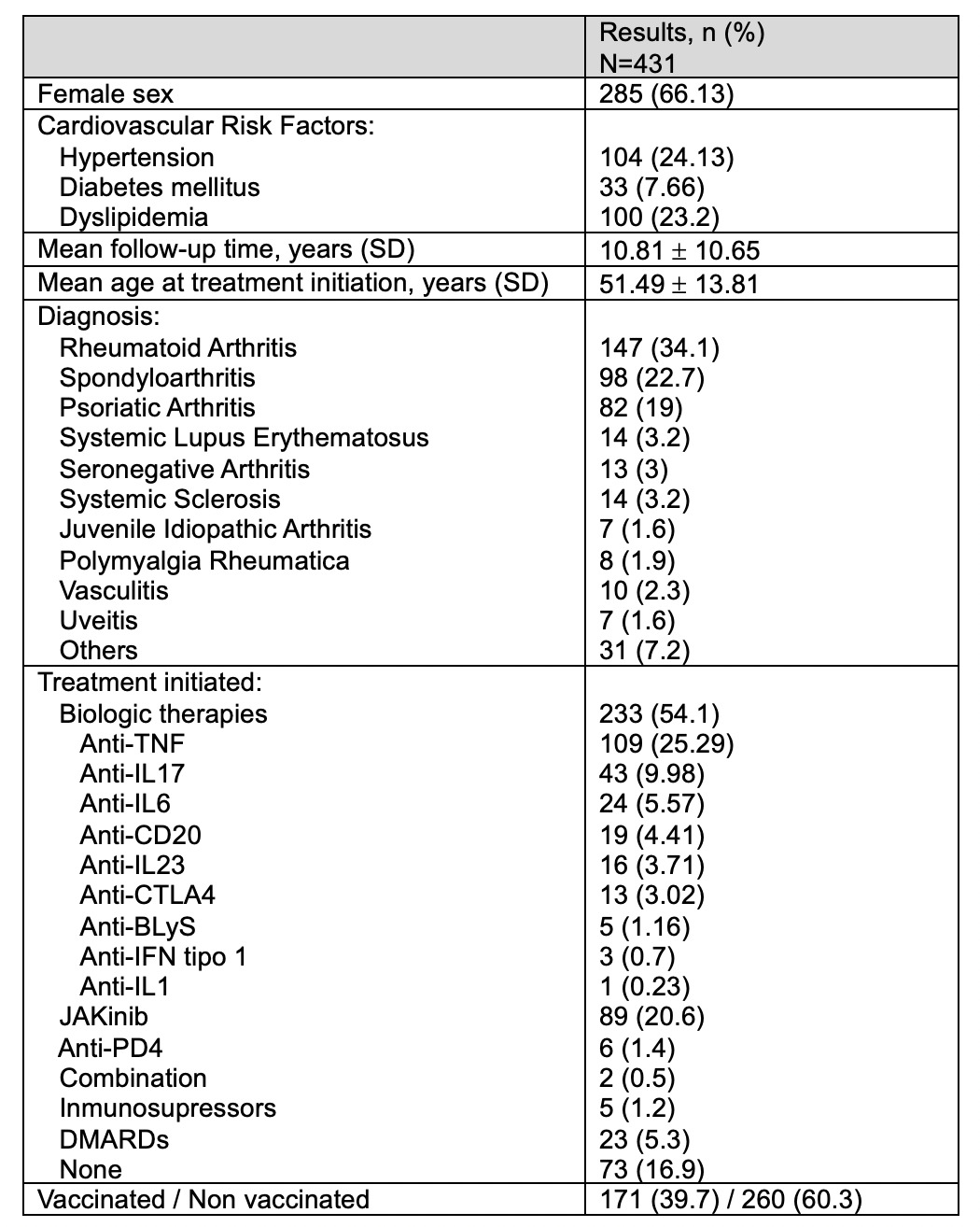 Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients
.jpg) Figure 1. Annual Proportion of Patients Referred to Preventive Medicine Who Received VZV Vaccination.
Figure 1. Annual Proportion of Patients Referred to Preventive Medicine Who Received VZV Vaccination.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mas Sanchez L, GRAU GARCIA E, Valera Ribera C, Muñoz-Martínez P, Ramos Castro D, Torrat Noves A, Villanueva Manes B, Alcántara Álvarez I, Simeo Vinaixa M, Perez Hurtado A, Andrés Román Ivorra J. Implementation of the Varicella Zoster virus vaccine and its Real-World effectiveness [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/implementation-of-the-varicella-zoster-virus-vaccine-and-its-real-world-effectiveness/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/implementation-of-the-varicella-zoster-virus-vaccine-and-its-real-world-effectiveness/
