Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:15PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Previously reported results from RESET-RA (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04539964) showed neuroimmune modulation via electrical stimulation of the left vagus nerve using an implantable device to treat RA provided clinical efficacy compared to sham at 3 months. Further improvement was observed in both groups, after sham crossover to stimulation. Vagus nerve stimulation may directly impact bone turnover via release of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) and neurotransmitters that act through ChemR23 receptors, nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and adrenergic receptors on osteoblasts and osteoclasts to reduce RANKL pathways and increase OPG, leading to inhibition of osteoclast activity.To objectively evaluate treatment effect of neuroimmune modulation on joint erosions, we report results from RESET-RA, which employed an OMERACT-validated imaging method using gadolinium-enhanced MRI of the hand and wrist, called RAMRIS (Rheumatoid Arthritis MRI Scoring system).
Methods: Adults with moderate-to-severe, active RA despite prior exposure to one or more biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs (b/tsDMARDs) underwent outpatient surgery to implant the integrated neurostimulator, followed by 1:1 randomization to treatment (stimulation) or sham. MRIs were obtained at baseline, 3 months and 6 months after randomization and evaluated to assess progression of bone erosions. Images were scored centrally by two independent radiologists blinded to treatment allocation, clinical information, and the order in which images were acquired to ensure objective, unbiased scoring. While active synovitis was not required for eligibility, prespecified analyses included an enriched subgroup of patients with erosive phenotype, i.e., patients at higher risk of erosion progression based on active, intra-articular synovitis at baseline (score ≥ 2 on any individual joint, at least 4 joints with a synovitis score of 1, or any joint with osteitis).
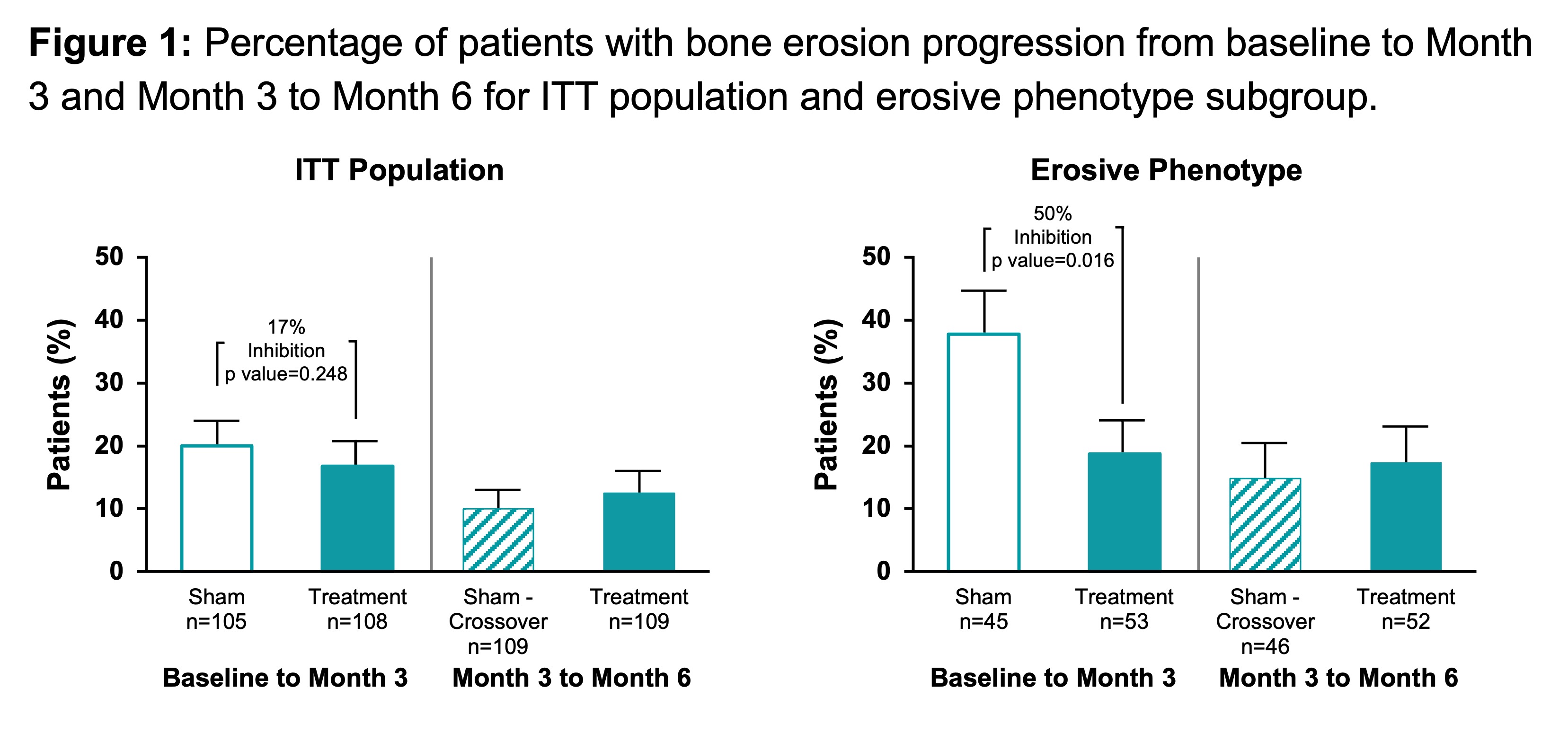
Results: Baseline RAMRIS scores were comparable between treatment and sham for both the ITT population and enriched subgroup. The non-enriched, ITT population showed that at 3 months, treatment had fewer patients with erosion progression ( >0.5 increase in erosion score) compared to sham, but differences were not statistically significant. However, in the enriched subgroup, the proportion of patients with erosion progression at 3 months was significantly lower for treatment (18.9%) compared to sham (37.8%, p=0.0156) (Figure 1). After sham crossed over to treatment and received stimulation for 3 months, the proportion of patients with erosion progression reduced to levels comparable to the treatment group (17.0% treatment, 21.7% sham-crossover, (Figure 1). The cumulative distribution of change in erosion scores also showed greater inhibition of erosion progression with stimulation that was more pronounced in the enriched subgroup (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Neuroimmune modulation using an implantable device is effective in inhibiting progression of structural damage as early as 3 months in adults with active RA and active synovitis at baseline who previously had inadequate response or intolerance to at least one b/tsDMARD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peterfy, MD, PhD C, Tesser J, Levine Y, Evangelista M, Strand V, Weinblatt M, Chernoff D. Impact of Vagus Nerve-Mediated Neuroimmune Modulation on structural joint damage using Gd-MRI RAMRIS imaging in Biologic-Experienced Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-vagus-nerve-mediated-neuroimmune-modulation-on-structural-joint-damage-using-gd-mri-ramris-imaging-in-biologic-experienced-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-vagus-nerve-mediated-neuroimmune-modulation-on-structural-joint-damage-using-gd-mri-ramris-imaging-in-biologic-experienced-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/

.jpg)