Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: This systematic literature review and meta-analysis aimed to better estimate the effect of oral supplementation with polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA; omega (n)-3 and n-6) on inflammatory rheumatic disease (IRD) activity in terms of duration, dose, type and source.
Methods: The literature was searched in PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane Library databases up to October 2020. Studies were reviewed in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. The effect of PUFA supplementation on disease activity was expressed as the standardized mean difference. Metaregression and subgroup analyses involved type of IRD, Jadad score, PUFA source (animal or vegetable) and doses.
Results: We obtained 43 references; 31 randomized controlled studies compared the effects of PUFA and placebo on disease activity (732 IRD patients receiving PUFA supplementation and 732 receiving placebo, most with rheumatoid arthritis). We found a significant improvement in pain, swollen and tender joint count, Disease Activity Score in 28 joints, and Health Assessment Questionnaire score in IRD patients receiving PUFA supplementation as compared with controls, with a significant decrease in erythrocyte sedimentation rate but not C-reactive protein level. Although meta-regression revealed no difference by IRD type or source or dose of PUFA supplementation, subgroup analysis revealed more parameters significantly improved with animal- than vegetable-derived PUFAs and 3-to 6-month supplementation. Most studies examined high-dose supplementation ( >2 g/day).
Conclusion: PUFA consumption, especially omega-3 from animal source >2 g/day, may improve IRD activity and might be an adjuvant therapy in rheumatoid arthritis.
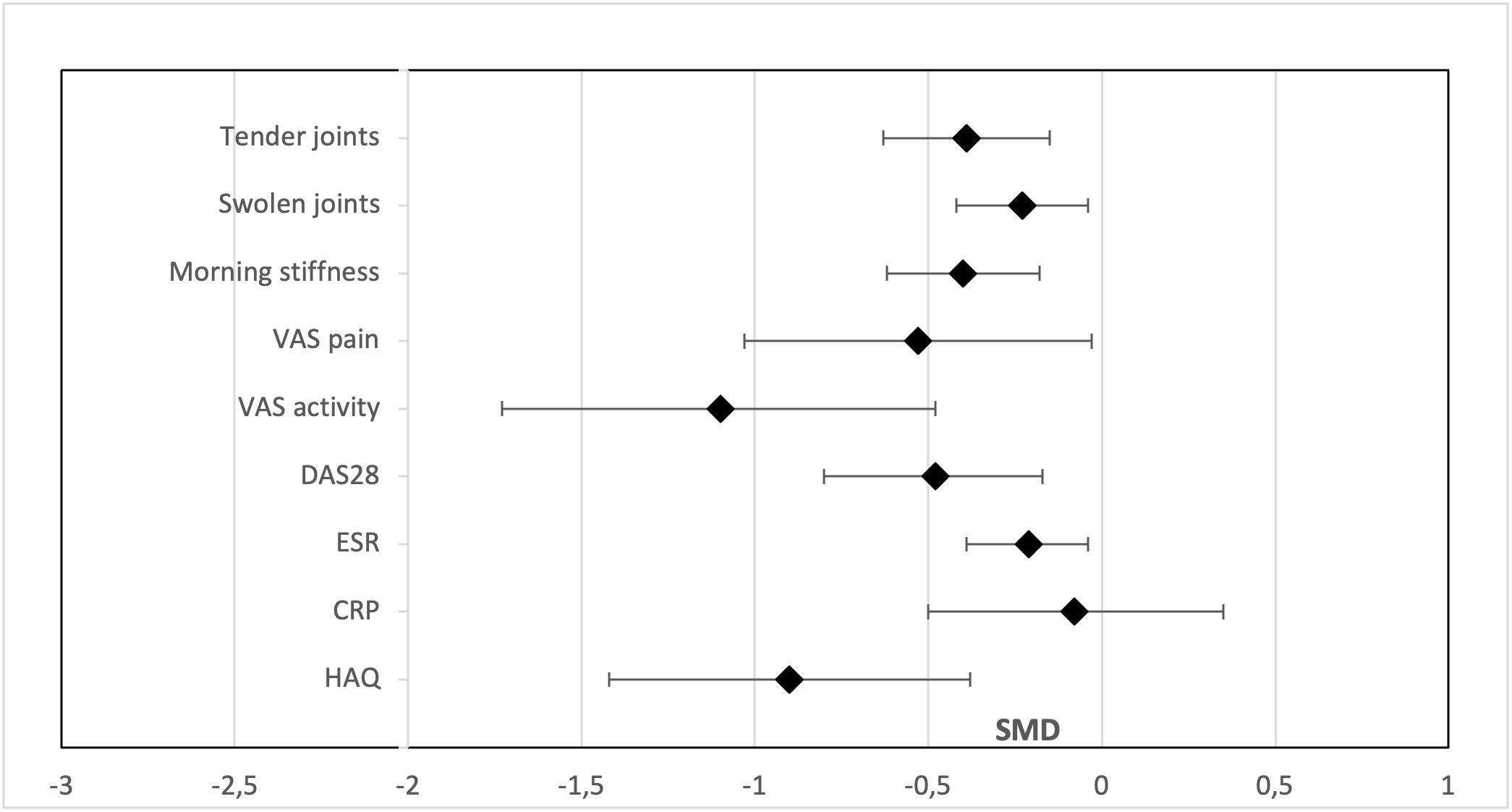 Figure 1. Overall effect of oral PUFA supplementation as compared with controls on parameters of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Data are standardized mean difference (SMD) (95% confidence interval [CI]). VAS= visual analog scale; DAS28= Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; ESR= erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP= C-reactive protein; HAQ= Health Assessment Questionnaire
Figure 1. Overall effect of oral PUFA supplementation as compared with controls on parameters of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Data are standardized mean difference (SMD) (95% confidence interval [CI]). VAS= visual analog scale; DAS28= Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; ESR= erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP= C-reactive protein; HAQ= Health Assessment Questionnaire
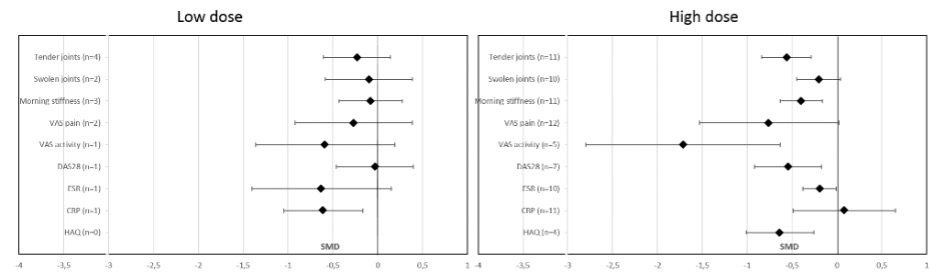
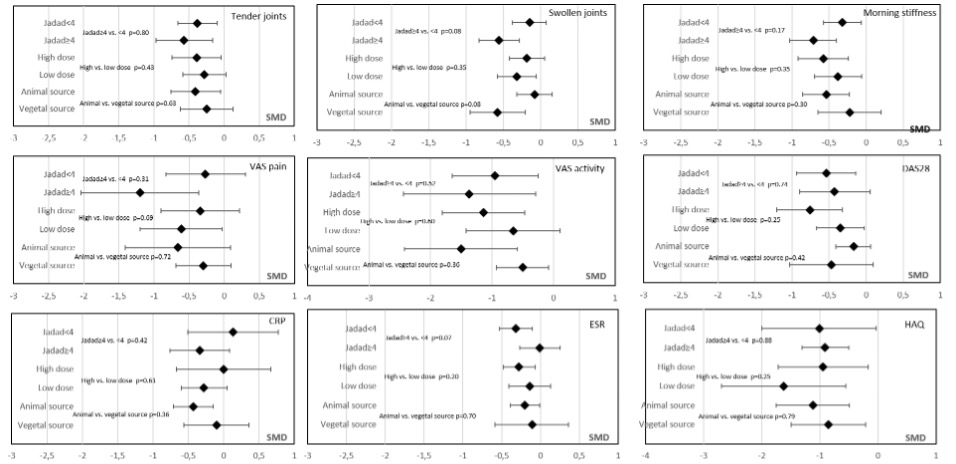 Figure 2. Meta-regression analysis of effect of oral PUFA supplementation as compared with controls on parameters of RA Data are standardized mean difference (SMD) (95% CI). VAS= visual analog scale; DAS28= Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; ESR= erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP= C-reactive protein; HAQ= Health Assessment Questionnaire
Figure 2. Meta-regression analysis of effect of oral PUFA supplementation as compared with controls on parameters of RA Data are standardized mean difference (SMD) (95% CI). VAS= visual analog scale; DAS28= Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; ESR= erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP= C-reactive protein; HAQ= Health Assessment Questionnaire
Data are standardized mean difference (SMD) (95% CI).
VAS= visual analog scale; DAS28= Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; ESR= erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP= C-reactive protein; HAQ= Health Assessment Questionnaire
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sigaux J, Mathieu S, N guyen Y, Sanchez P, LETAROUILLY J, Soubrier M, czernichow s, FLIPO R, Sellam J, Daïen C. Impact of Type, Dose and Duration of Oral Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Disease Activity in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-type-dose-and-duration-of-oral-polyunsaturated-fatty-acid-supplementation-on-disease-activity-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-systematic-literature-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-type-dose-and-duration-of-oral-polyunsaturated-fatty-acid-supplementation-on-disease-activity-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-systematic-literature-review-and-meta-analysis/