Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression are extremely prevalent amongst patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study we sought to assess the impact of treatment with tocilizumab (TCZ), an IL-6 antagonist, upon anxiety and depressive symptoms in a cohort of RA patients.
Methods: This study was part of a larger, multi-center study performed at 13 medical centers in Israel between January 2014 and July 2015. Study participants were adults diagnosed with RA who received a weekly subcutaneous injection of tocilizumab for 24 weeks. We used the Hamilton Depression (HDRS) and Anxiety (HAMA) scores in order to assess the severity of depression and anxiety respectively. RA disease activity indices and depression and anxiety levels were assessed at baseline, 4 weeks and study completion. Patients whose anxiety and/or depression levels decreased significantly, e.g., a decrease ≥ 25% in anxiety and/or depression levels between baseline and study end, were compared with patients for whom they did not. Logistic regression identified factors associated with significant decrease, in addition we assessed correlations between levels of depression and anxiety with scores reflecting the disease activity of the rheumatoid disease.
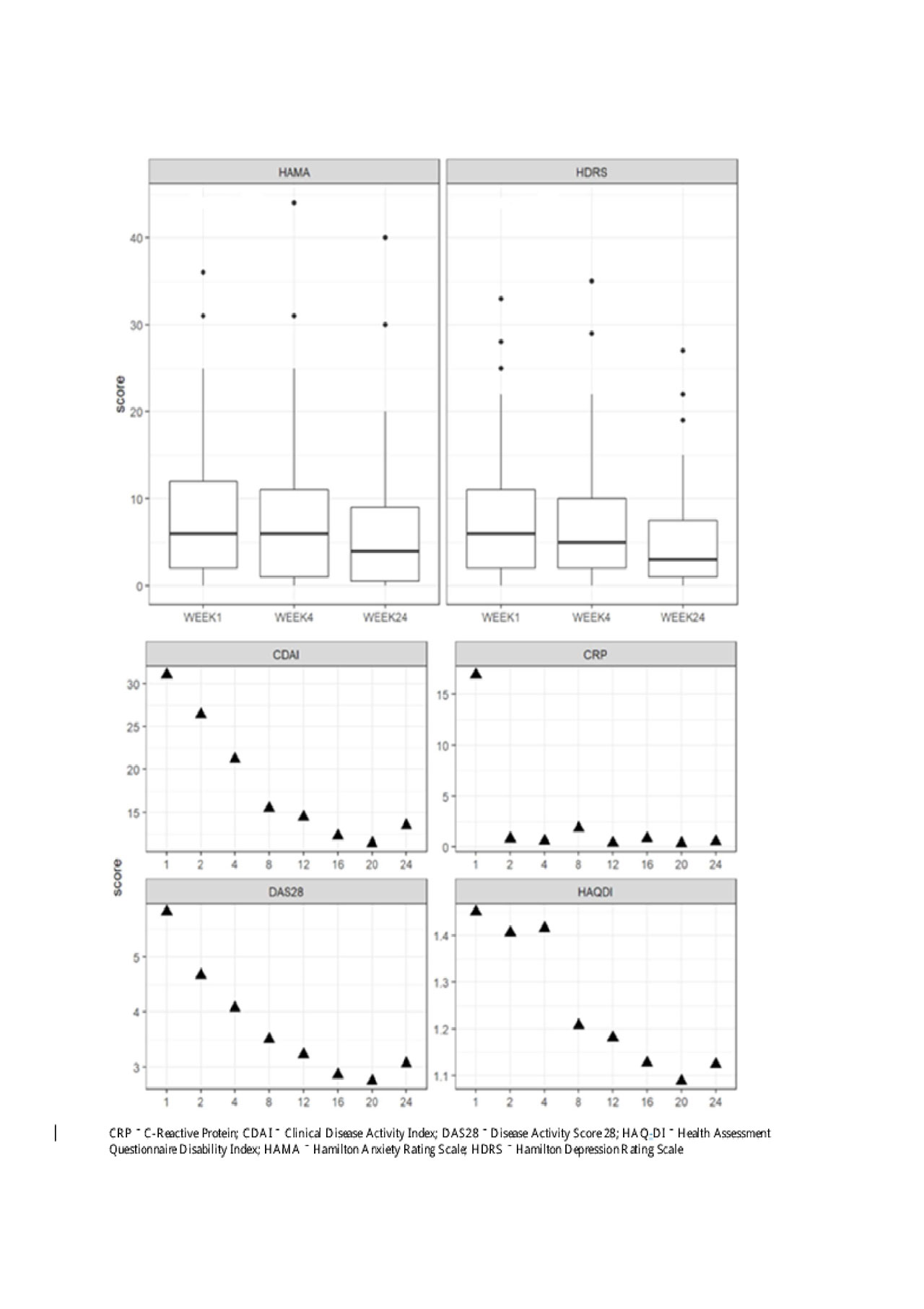
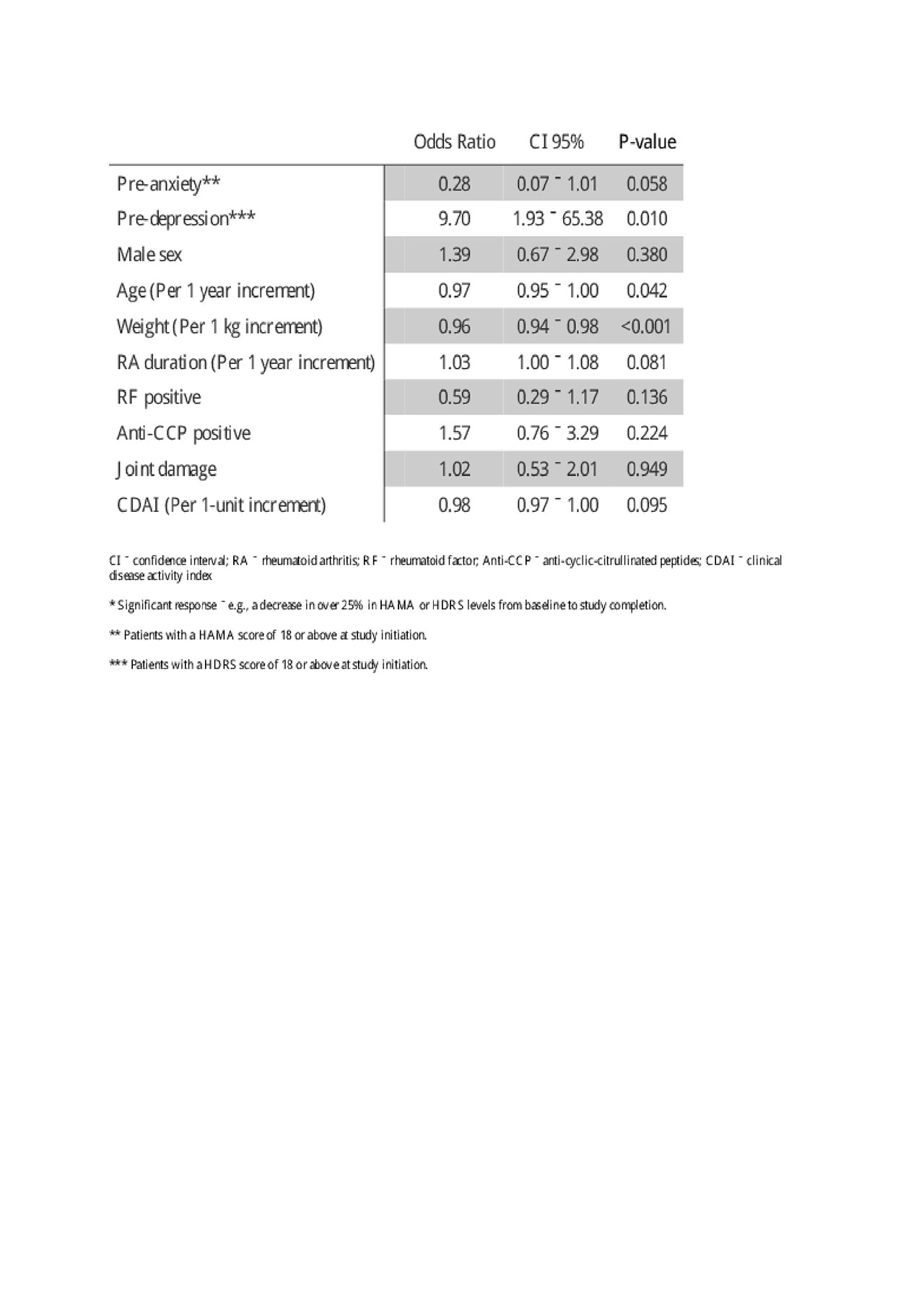
Results: Ultimately, 91 patients were included in the study. The mean age was 54 years and the majority were female (79%). The mean score in all disease activity indices as well as depression and anxiety levels decreased dramatically from baseline to study completion. Sixty patients (66%) demonstrated a significant decrease in anxiety and/or depression levels. When logistic regression was performed, an HDRS score indicative of depression at study baseline demonstrated an independent association with a significant psychiatric response whilst older age and increased weight were negatively associated. Older age and increased weight were negatively associated with a significant decrease. The following correlations were observed with the HAMA and HDRA scores respectively; HAQ-DI (r=0.4, 0.42), DAS28 (r=0.29, 0.32) and CDAI (0.28 and 0.33), all of them were statistically significant (p< 0.01).
Conclusion: This study has demonstrated a favorable impact of TCZ therapy on parameters reflecting depression and anxiety severity in patients with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tiosano S, Yavne Y, Watad A, Langevitz P, Lidar M, Feld J, Tishler M, Aamar S, Elkayam O, Balbir-Gurman A, Molad Y, Ehrlich S, Amital D, AMITAL H. Impact of Tocilizumab on Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tocilizumab-on-anxiety-and-depression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tocilizumab-on-anxiety-and-depression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/