Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: While racial disparities in clinical outcomes for RA patients (pts) receiving bDMARDs or csDMARDs have been described,1 there remains a paucity of data on racial differences in response to advanced therapies. Here, we evaluate impact of race on tofacitinib efficacy and safety in RA pts.
Methods: This post hoc analysis used pooled data from 8 Phase (P)2, 6 P3, and 1 P3b/4 RCTs of pts treated with tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID, adalimumab (ADA; 40 mg Q2W), or placebo (PBO), stratified by self-reported pt race (White, Black, Asian, Other) at baseline (BL) visit. Efficacy outcomes at Month (M)3 were: ACR20/50/70 and CDAI/DAS28‑4(ESR) LDA (scores ≤ 10 and ≤ 3.2, respectively) rates, and least squares (LS) mean change from BL (∆) in DAS28(ESR) and HAQ-DI. Incidence rates (IRs; unique pts with events/100 pt-yrs) were estimated for adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, discontinuations due to AEs, and all-cause mortality.
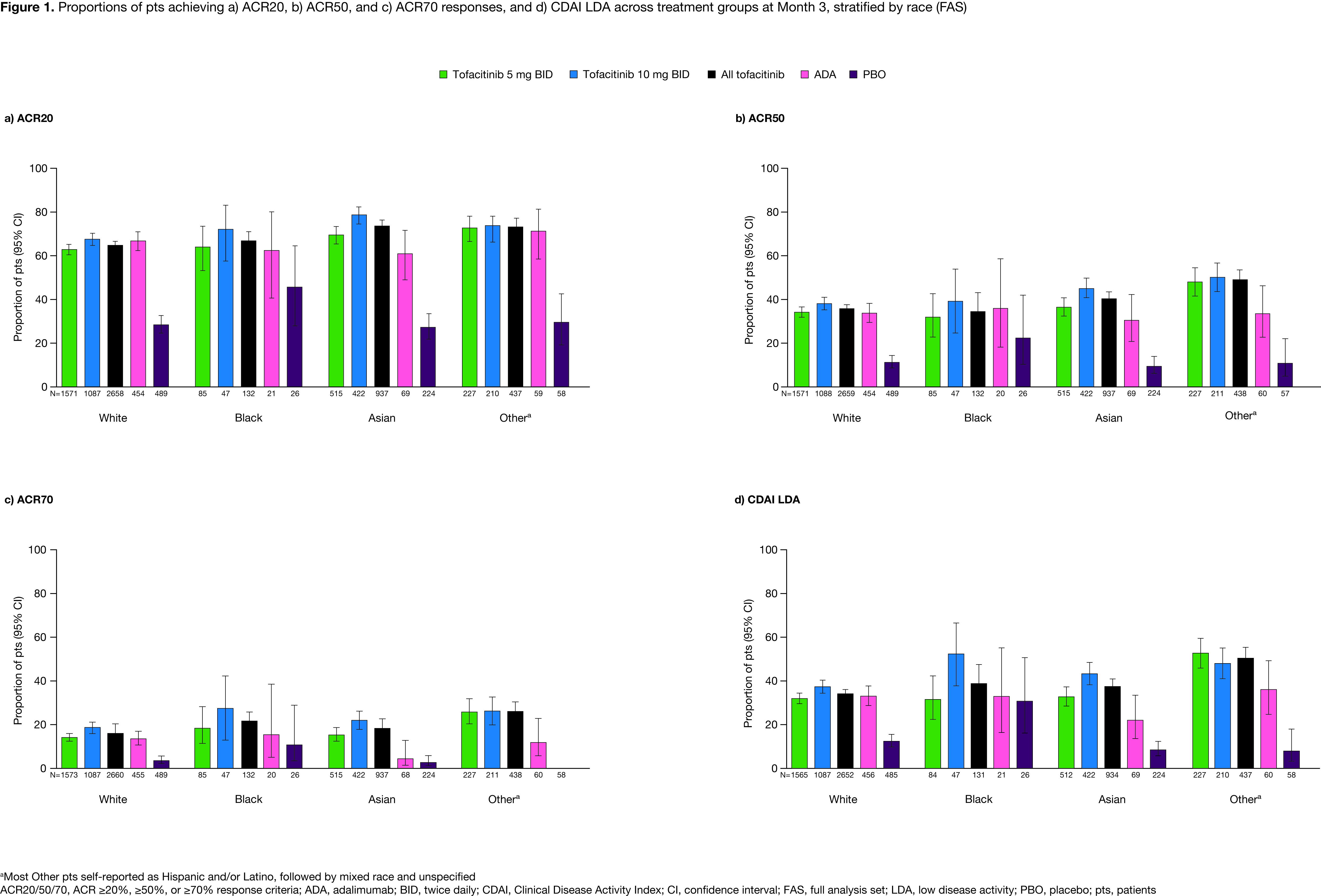
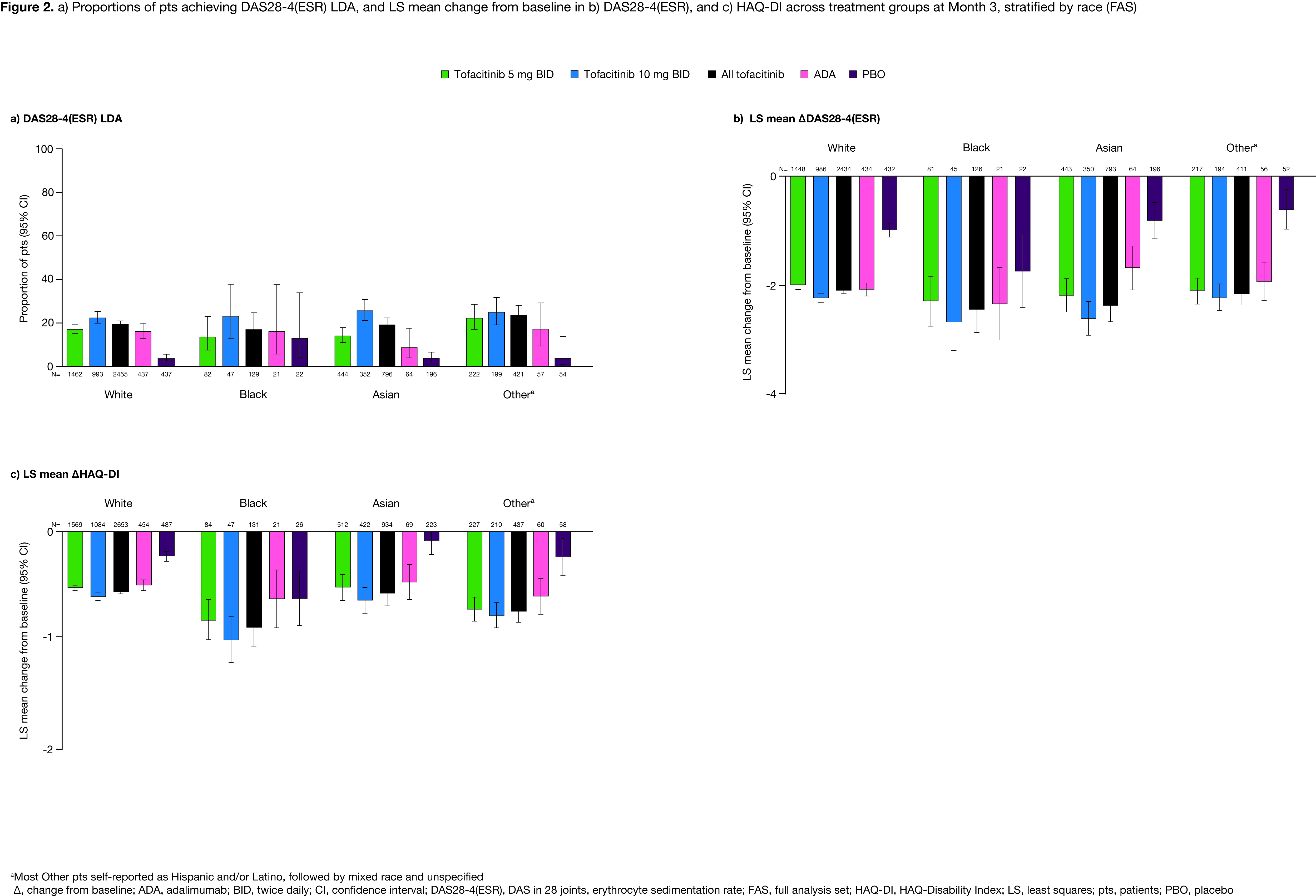
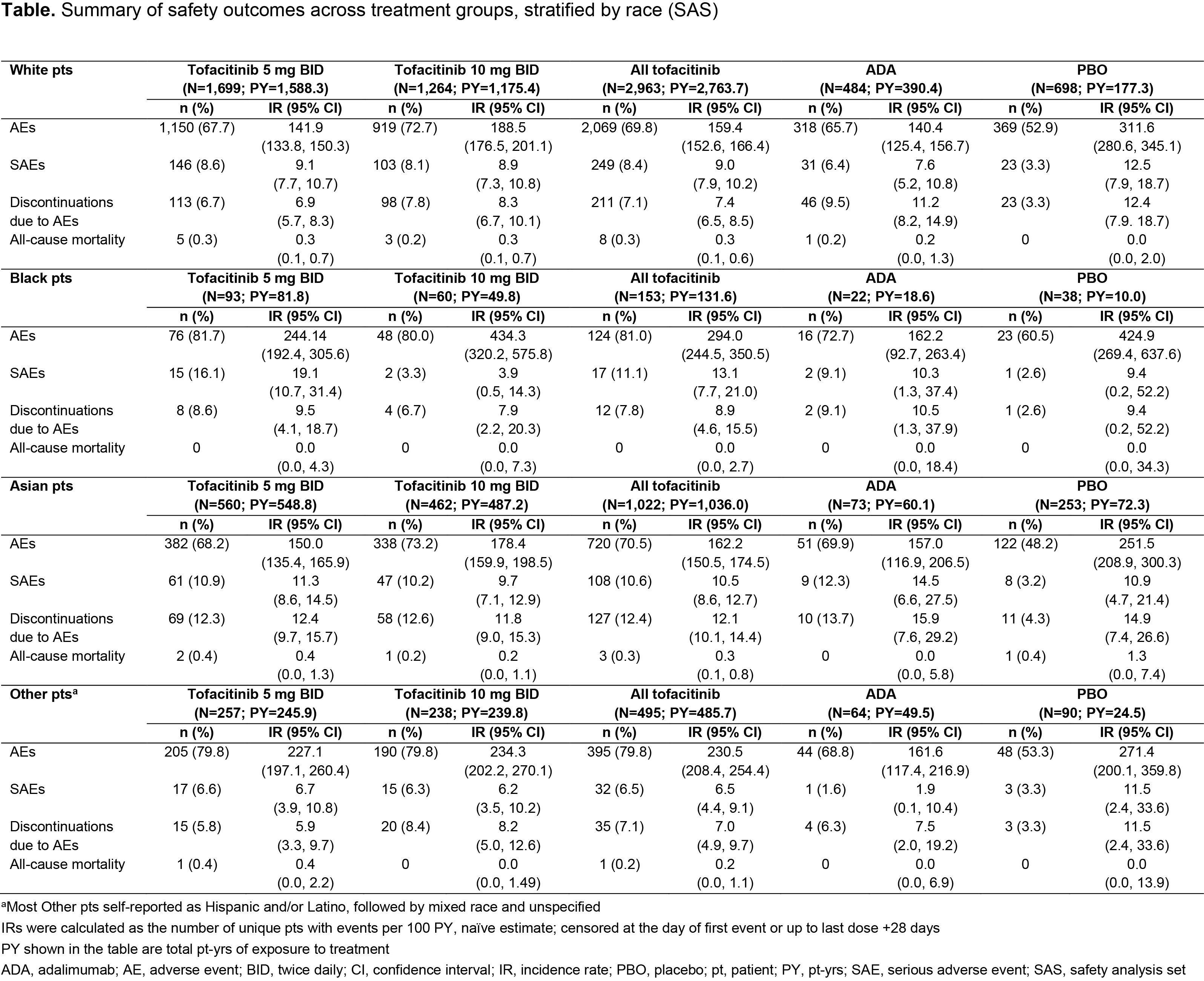
Results: 6,355 pts were included (White, n=4,145; Black, n=213; Asian, n=1,348; Other, n=649). BL characteristics were generally similar across treatment/racial groups, excepting higher rates of prior bDMARD exposure in White/Black vs Asian/Other pts. Across treatment arms, White, Black, Asian, and Other pts most commonly enrolled from Europe (40.9%), North America (68.1%), East/South Asia (97.9%), and Latin America (80.6%), respectively; most Other pts self-reported as Hispanic and/or Latino, followed by mixed race and unspecified. At M3, ACR20/50/70 and CDAI LDA rates were mostly higher in Other vs White pts with tofacitinib, similar across racial groups with ADA, and numerically higher in Black vs White/Asian/Other pts with PBO (Figure 1a–d). DAS28‑4(ESR) LDA rates and LS mean ∆DAS28-4(ESR) were broadly similar across racial groups with active treatment, and numerically higher in Black vs White/Asian/Other pts with PBO (Figure 2a–b). Across active treatment arms, LS mean ∆HAQ-DI was generally comparable across racial groups with some numerical differences, and higher in Black vs White/Asian pts with PBO (Figure 2c). Safety outcomes were broadly similar across treatment arms, with some higher IRs for AEs seen with Black/Other vs White/Asian pts (Table).
Conclusion: Across racial groups, tofacitinib efficacy/safety was consistent with previous findings from the tofacitinib RA clinical program, although results should be interpreted with caution due to low pt numbers in some groups. Noting this limitation, some trends in efficacy outcomes were seen between racial groups; higher ACR20/50/70 and CDAI LDA rates in Other vs White pts with tofacitinib may be attributable to prior treatment history/regional practice norms. Numerically higher PBO responses in Black vs White/Asian/Other pts may reflect demographic differences, notably country of enrollment, across racial groups participating in RCTs. Safety findings were generally consistent across racial/treatment groups. Future analyses should focus on the impact of socio-economic, cultural, genetic, or practice-based differences that may underpin these results.
1. Greenberg JD et al. Am J Med 2013; 126: 1089-98.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by K Woollcott, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wright G, Mysler E, Chen Y, Kinch C, Yndestad A, Kwok K, Cadatal M, Germino R, Ogdie A. Impact of Race on the Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Patients with RA: A Post Hoc Analysis of Phase 2, 3, and 3b/4 Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-race-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-ra-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-2-3-and-3b-4-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-race-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-ra-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-2-3-and-3b-4-clinical-trials/