Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a polyarticular autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized for pain, joint edema and functional limitation. Some items in evaluation could be affected by other medical conditions. Hand osteoarthritis can coexist with RA but its effect is unknown. The aim of our study was to describe the impact of hand osteoarthritis on rheumatoid arthritis pain, disease activity and health status.
Methods:
We performed a descriptive and transversal study comparing patients with RA with and without hand osteoarthritis. A total of 41 patients per group were calculated to find a difference of 20mm in visual analogue scale (VAS) of pain. Demographic characteristics were registered as well as disease characteristics, treatment, disease activity, patient and physician global assessment, function disability (HAQ-DI score) and quality of life; quality of sleep, depression and anxiety diagnosis were also analyzed.
Results:
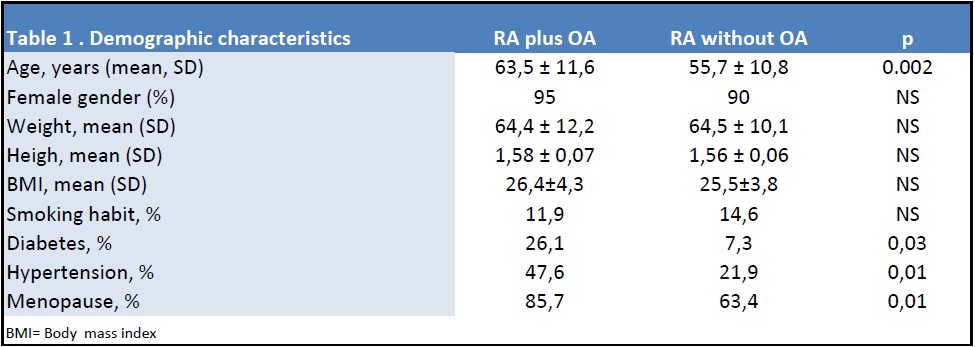
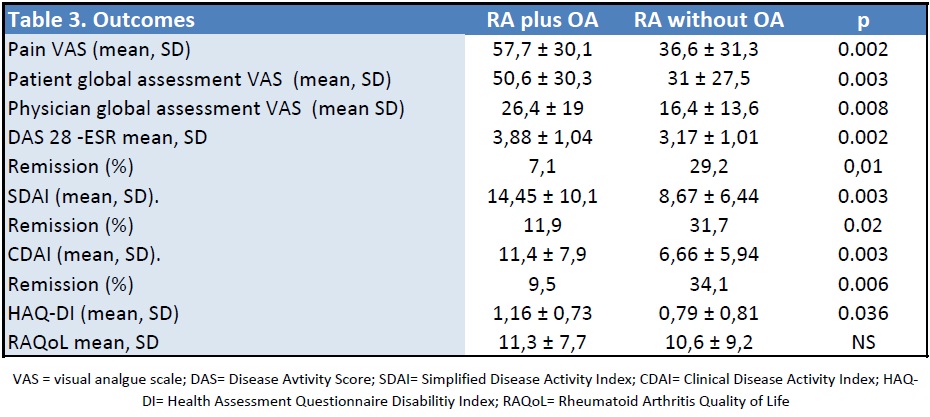
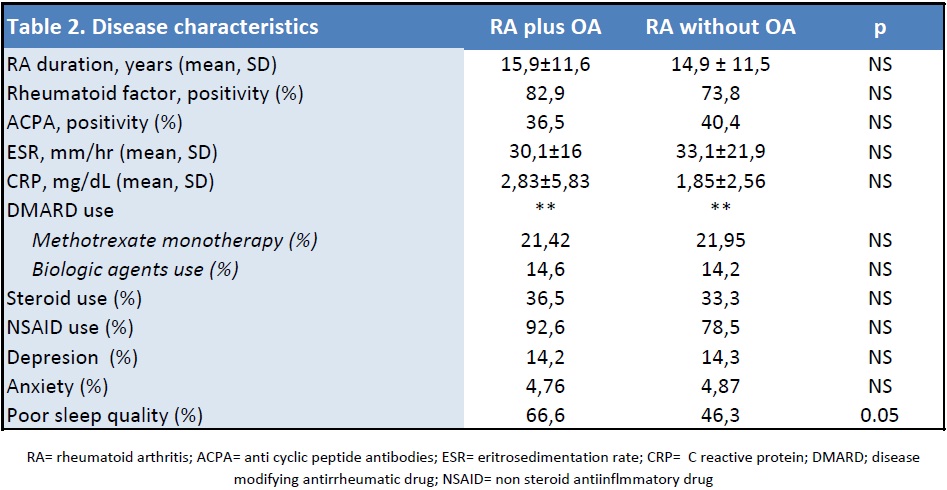
We included 83 patient; 42 RA patients with hand OA and 41 without; demographic characteristics were similar but patients with OA were older than controls (63,5 ± 11,6 vs 55,7 ± 10,8; p=0.002). Comorbities were more prevalent among patients with osteoarthritis. (Table 1). Characteristics of the disease (RA) were similar among the groups (Table 2); there were no differences on treatment strategies (methotrexate monotherapy, steroids and biologic use); although NSAID use was more frequent among patients with hand osteoarthritis (92.6% vs 78.5%) it was not significant. Depression and anxiety prevalence were similar but self-reported quality of sleep was poorer in patients with OA. Patients with OA reported more intensity of pain, resulted in worse global assessment (patient and physician reported), higher activity (DAS 28, SDAI and CDAI), showed more disability but interestingly, reported similar quality of life scores (Table 3). Patients without hand OA were more probable to achieve remission compared with patients with this condition [OR 4,09 (IC 95% 1,2 – 13,46)].
Conclusion:
Although it might be regarded as a benign condition, osteoarthritis of the hand exerts a great impact over patients with rheumatoid arthritis, affecting the possibility of achieving response to treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Espinosa Ortega HF, Arce Salinas CA, Ruiz Medrano E. Impact of Osteoarthritis of the Hand on Disease Activity Scores and Health Status in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-osteoarthritis-of-the-hand-on-disease-activity-scores-and-health-status-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-osteoarthritis-of-the-hand-on-disease-activity-scores-and-health-status-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/