Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1052–1081) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have changed the landscape of treatment for many cancers. However, most cancer clinical trials for ICI excluded patients with pre-existing autoimmune diseases (PAD). Efficacy and safety data on the use of ICI in patients with rheumatic PAD (Rh-PAD) is limited to retrospective case series and reports, and many do not differentiate between Rh-PAD and non-rheumatic PAD. In one study of a large French retrospective cohort, patients on immunosuppression (IS) at baseline had poorer tumor outcomes (1).
Objectives: To explore the impact of baseline IS on the safety and efficacy of ICI in patients with Rh-PAD using data from the CanRIO retrospective and prospective cohorts.
Methods: We evaluated patients with Rh-PAD treated with at least one dose of ICI, including CTLA-4, PD-1, or PDL-1 inhibitors. 45 patients were recruited prospectively between Jan 2020 and Apr 2023 across 9 Canadian academic sites and followed at regular intervals as per a standardized study protocol. 57 patients were retrospectively recruited using data extracted from patients referred to rheumatology specialists between Jan 2013 and Jun 2022 across 10 Canadian sites. We used logistic regression to compare the occurrence and severity of flares and de-novo immune-related adverse events (irAE), as well as tumor response, between patients on baseline IS and not on baseline IS.
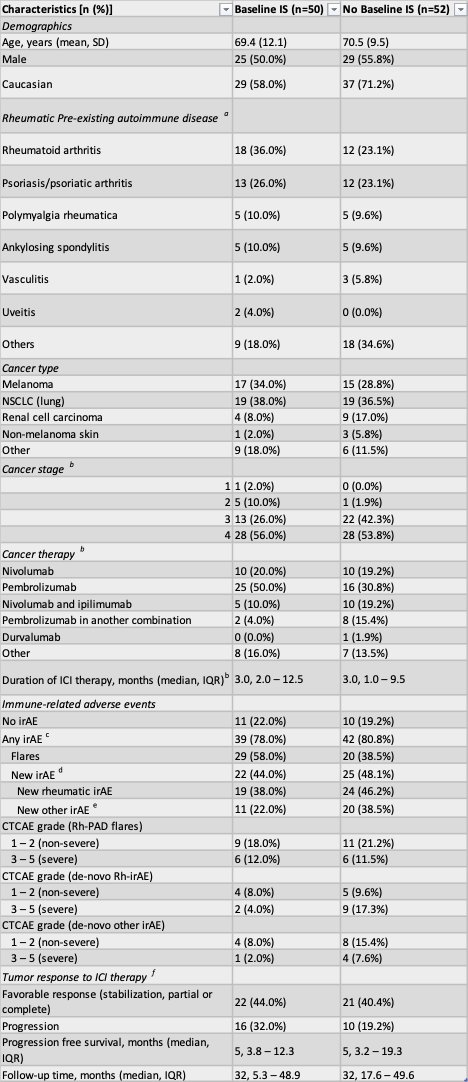
Results: One hundred and two patients with Rh-PADs were followed for a median of 32 months; 50 were on baseline IS prior to ICI start, and 52 were not. The most common Rh-PADs were rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (Table 1).
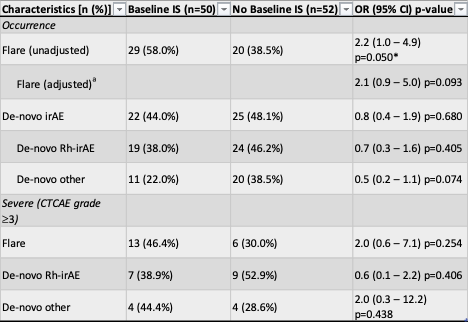
Cancer type, cancer stage, ICI type, and ICI exposure time were similar in both groups (Table 1). The flare rate of patients on baseline IS was 58%, compared to only 38% in the group without baseline IS (adjusted OR=2.1; 95% CI = 0.9-5.0; p=0.09). There were no statistically significant differences in the risk of a severe flare (CTCAE grade ≥3) (p = 0.3), development of a de-novo Rh-irAE (p = 0.4) or a severe de-novo Rh-irAE (p = 0.4) (Tables 1 & 2). Tumor follow-up data was available for 38 of the 50 patients on baseline IS and 37 of the 52 patients without baseline IS. The rate of tumor progression was 42% (16 of 38) in the IS group and 27% (10 of 37) in the no IS group (HR=1.4; 95% CI = 0.6-3.1; p=0.437) but there was no difference in progression free survival between groups.
Conclusion: Early data from patients with Rh-PAD in the multicenter prospective and retrospective CanRIO cohorts suggest that 1) ICI can be effective for cancer treatment in patients with Rh-PAD, and should be offered as indicated; 2) Baseline IS does not seem to protect from flares of Rh-PAD; 3) Baseline IS does not seem to change the risk of developing de-novo irAE, nor the severity of flares/de-novo irAEs; 4) There was a non-significant trend towards baseline IS increasing the hazard of tumor progression but no difference in progression free survival between groups.
[1] Tison A, et al. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with cancer and preexisting autoimmune disease: A nationwide, Multicenter Cohort Study. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2019;71(12):2100–11.
a 3 patients who were on baseline IS had more than one Rh-PAD; 1 patient who was not on baseline IS had more than one Rh-PAD
b Missing data for 3 patients in the baseline IS group and 1 patient in the no baseline IS group
c 13 patients on baseline IS experienced a flare of their Rh-PAD and a de-novo irAE; 3 patients not on baseline IS experienced a flare of Rh.PAD and de-novo irAEs
d 5 patients on baseline IS experienced both de-novo Rh-irAE and other irAEs; 12 patients not on baseline IS experienced de-novo Rh-irAE and other irAEs
e Including skin, endocrinological (other than thyroid), heart and eyes
f Missing tumor response information for 7 patients on baseline IS and 5 in no baseline IS
a Adjusted for Rheumatic Pre-existing autoimmune disease
(*) Indicates significance at p 0.05. OR calculated using logistic regression
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gonzalez Arreola L, Ye C, Hudson M, Roberts J, Pope J, Appleton T, Hoa S, Fifi-Mah A, Maltez N, Saltman A, Himmel M, Colmegna I, Ladouceur A, Obrzut A, Tan J, Moon D, Nevskaya T, Schmidt E, Cho L, Toban N, Jamal S. Impact of Immunosuppression on the Safety and Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatic Autoimmune Disease: Experience from the Canadian Research Group of Rheumatology in Immuno-Oncology (CanRIO) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-immunosuppression-on-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-immune-checkpoint-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatic-autoimmune-disease-experience-from-the-canadian-research-group-of-rheumatology-in-imm/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-immunosuppression-on-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-immune-checkpoint-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatic-autoimmune-disease-experience-from-the-canadian-research-group-of-rheumatology-in-imm/