Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: This study aims to evaluate the impact of comorbidities on disease activity and functional disability in patients with RA treated with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs).
Methods: We analyzed longitudinal data of 2,127 patients in a nationwide cohort of RA receiving bDMARD in South Korea (KOBIO-RA). Patients were enrolled at the time of starting bDMARD and followed up yearly thereafter. In this study, follow-up was censored when initial bDMARD was discontinued or at seventh visit, whichever came first. Functional status was assessed using Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3). In each follow-up visit, we assessed whether the patient attained the minimal clinically important difference (MCID, defined as a 3.6-point decrease from baseline) in RAPID3 and low disease activity (LDA) based on Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI). Effect of comorbidities on these responses was analyzed using generalized estimating equations (GEE).
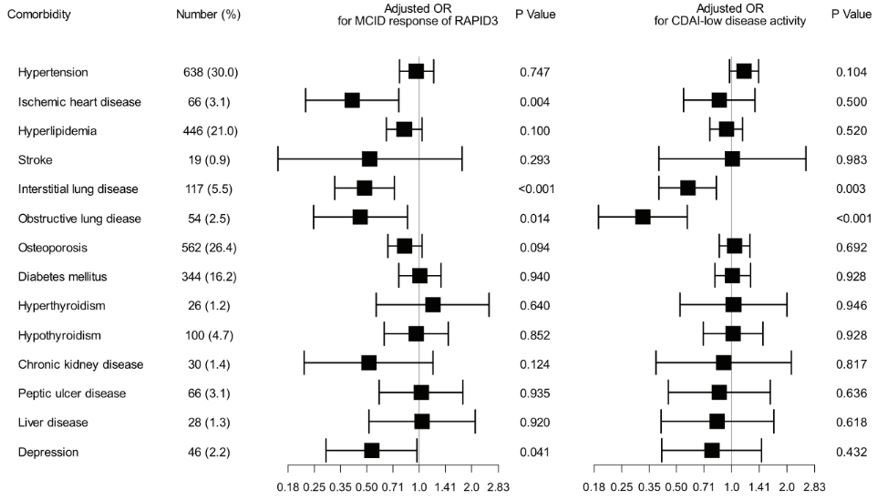
Results: At baseline, the mean (SD) disease activity was 15.25 (5.67) for RAPID3 and 26.85 (11.15) for CDAI. During the follow-up encompassing 5244 1-year intervals, 3489 (66.5%) and 3788 (74.0%) intervals achieved the MCID-RAPID3 and CDAI-LDA, respectively. Ischemic heart disease (adjusted OR 0.41 [0.22-0.76]), interstitial lung disease (adjusted OR 0.49 [0.33-0.72]), obstructive lung disease (adjusted OR 0.46 [0.25-0.85]), and depression (adjusted OR 0.56 [0.29-0.97]) were associated with poor RAPID3 response (Figure). Other comorbidities did not significantly influence the functional status. Presence of comorbidities was not associated with disease activity of RA except for pulmonary disease. Patients with interstitial lung disease or obstructive lung disease showed a significantly less likelihood of achieving CDAI-LDA (adjusted OR 0.58 [0.40-0.83] and 0.33 [0.19-0.57], respectively).
Conclusion: Pulmonary diseases were associated with higher patient reported functional index and disease activity in RA, while ischemic heart disease and depression were associated function index independent of the disease activity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim J, Shin K, Lee E, Park J. Impact of Comorbidity on Disease Activity and Functional Status in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Biologic DMARDs, a Longitudinal Analysis of the KOBIO-RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-comorbidity-on-disease-activity-and-functional-status-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-biologic-dmards-a-longitudinal-analysis-of-the-kobio-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-comorbidity-on-disease-activity-and-functional-status-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-biologic-dmards-a-longitudinal-analysis-of-the-kobio-ra/