Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Comorbidities may affect the efficacy of bDMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Post-hoc analysis of the randomized clinical trial (RCT) data shows that the efficacy of the direct IL-6 inhibitor olokizumab (OKZ) does not depend on the comorbidity burden [1,2]. However, information about the impact of comorbidities on the OKZ effectiveness in routine clinical practice is lacking. The study purpose was to determine the impact of comorbidity burden on the OKZ efficacy in RA patients in the real-world data (RWD) study.
Methods: Biologic DMARDs (bDMARD)-naive patients with RA on methotrexate ± glucocorticoids (GC) inefficacy who received OKZ for at least 24 weeks were included in our retrospective RWD study. To assess the impact of comorbid conditions on effectiveness, we used Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index (RDCI). Patients were stratified into two groups based on the baseline RDCI score: “RDCI-L” (RDCI ≤ 1) vs “RDCI-H” (RDCI ≥ 2). The following effectiveness variables were analyzed at Week 24 after treatment initiation: proportion of patients that achieved SDAI ≤ 3.3, CDAI ≤ 2.8 and ≤ 10, DAS28(ESR) ≤ 2.6 and ≤ 3.2. To address the imbalance in baseline parameters across comorbidity groups, an optimal 1:1 propensity score matching algorithm based on logistic regression model was employed. Odds Ratios (ORs) with 95% Confidence Intervals (CIs) were estimated using logistic regression to present the study findings. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: In the general group of patients, 77.9% had comorbidities: сardiovascular diseases – 41.4%, osteoarthritis-24.3%, osteoporosis-16.4%, gastrointestinal diseases-11.5%, diabetes-7.4%, kidney damage-4.2%, lung damage-3.9%.Overall, 222 patients treated with OKZ 64 mg q2w or q4w were included in the analysis (per 111 patients in RDСI-L and RDСI-H groups). The baseline characteristics were similar in both groups and are presented in the Table 1. The median values of baseline RA activity corresponded to high disease activity. There was no significant difference in the effectiveness results between RDСI-L and RDСI-H groups (Table 2), similar proportions of patients achieved low disease activity and remission in both groups (p > 0.05). These findings align with the general trend observed in previous research of OKZ efficacy in relation to comorbidity burden in RCT.
Conclusion: There were no significant differences in effectiveness outcomes in OKZ-treated RA patients with high and low comorbidity burden over 24 observation weeks in the RWD study. Further research may clarify the impact of comorbidities on OKZ outcomes.
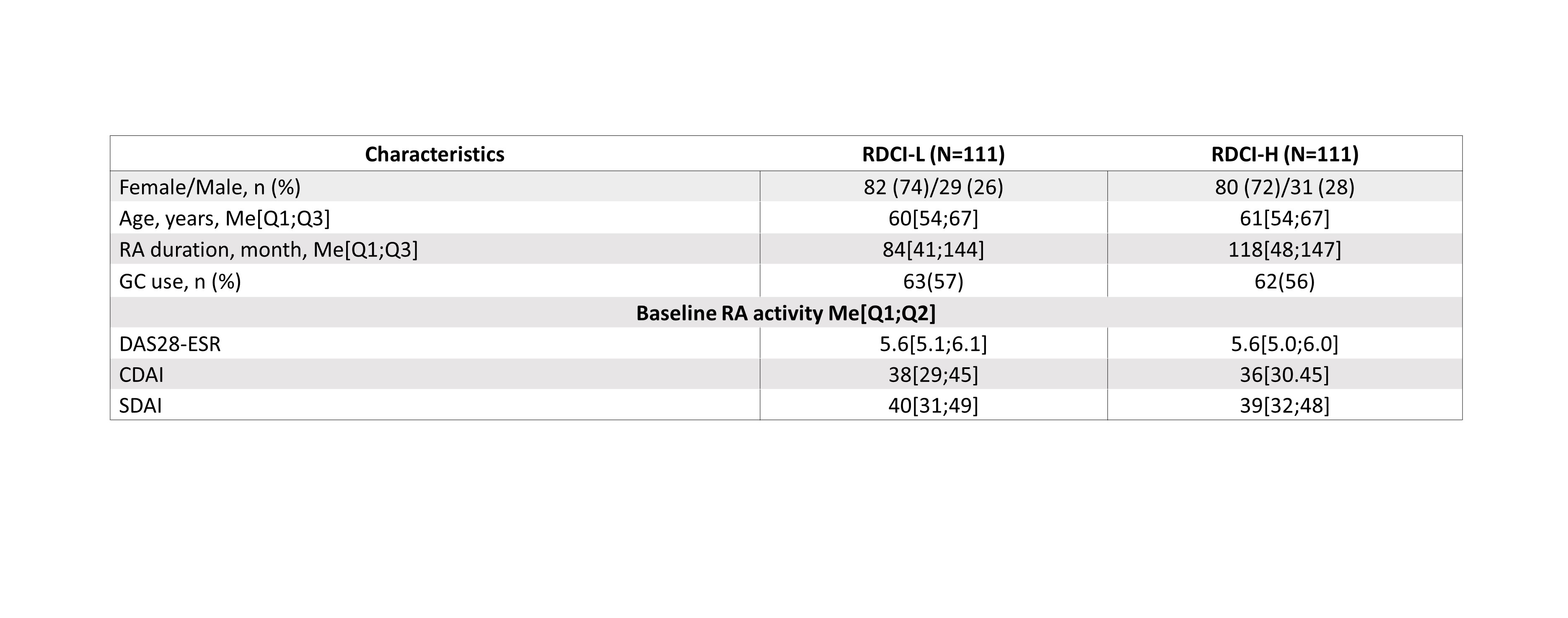 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients in RDCI-L ad RDCI-H
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients in RDCI-L ad RDCI-H
Note: CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; DAS28, The Disease Activity Score 28; GC, corticosteroids; Me, median; n(%), number (percentage) of patients; Q1;Q3, the first and the third quartiles; RDCI, Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index; SDAI, Simplified Disease Activity Index.
.jpg) Table 2. The impact of comorbidities on efficacy in OKZ treated patients (week 24)
Table 2. The impact of comorbidities on efficacy in OKZ treated patients (week 24)
Note: OR > 1 indicates that patients with high comorbidity have higher odds of achieving the outcome compared to those with low comorbidity.
CI, confidence interval;
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Korolev M, Dubikov A, Bukhanova D, Egorova A, Alekseev E, Kuzkina S, Samsonov M. Impact of Comorbidity Burden on the Efficacy of, a Direct Interleukin 6 Inhibitor, Olokizumab: Real World Evidence [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-comorbidity-burden-on-the-efficacy-of-a-direct-interleukin-6-inhibitor-olokizumab-real-world-evidence/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-comorbidity-burden-on-the-efficacy-of-a-direct-interleukin-6-inhibitor-olokizumab-real-world-evidence/
