Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Clinical pharmacists (CPs) embedded within outpatient clinics have revolutionized the impact of provided services and have the potential to improve various aspects of clinical care including patient and provider satisfaction, adherence to medications, long-term disease remission, and increased access to care. There are limited studies on the value of CPs in specialty areas including rheumatology and gastroenterology (GI). CPs were integrated into the rheumatology and GI clinics at University of Texas Southwestern (UTSW) Medical Center starting October 2022. The IMPACT Study’s objective was to measure the impact of CP integration in the rheumatology and GI clinics.
Methods: CPs were embedded into the rheumatology and GI Clinics in October 2022. The CPs worked with key stakeholders to develop a workflow process for the CPs to order new biologic medications under a drug therapy management agreement. CPs would meet with patients to order new biologic medications and assist with various medication needs.
The pre-intervention period was January 2022 to June 2022. The post-intervention period was from January 2023 to June 2023. We performed a retrospective chart review to measure the time from biologic medication ordered (BMO) to prior authorization (PA) decision and BMO to biologic medication dispensed (BMD) by UTSW Specialty Pharmacy. The data was analyzed utilizing a non-parametric Wilcoxon test. Rheumatology and GI clinicians were surveyed via Microsoft Forms to assess provider satisfaction with CPs.
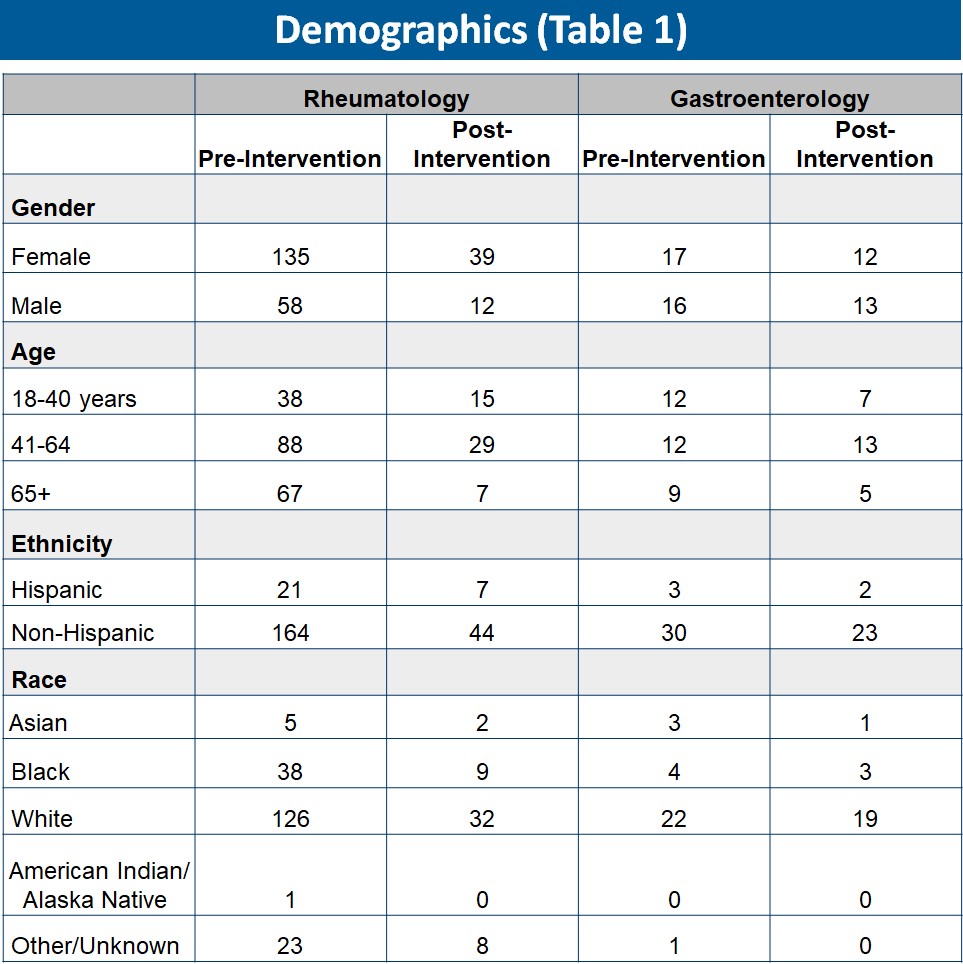
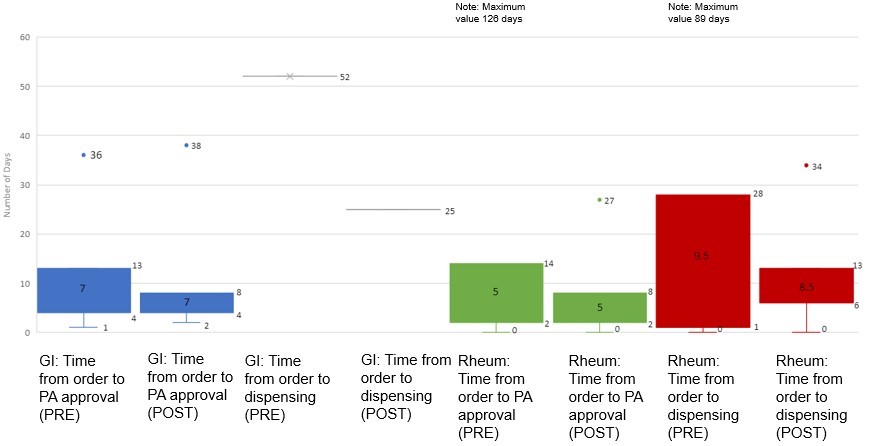
Results: The sample size in the pre vs post intervention time frames for the rheumatology clinic were significantly different as shown in the demographics Table 1 (193 vs 51 patients). For the GI clinic, the sample sizes were similar. In the pre and post intervention GI clinics, the 75th percentile time from BMO to PA decision improved from 13 days to 8 days (Figure 1). The median time was 7 days each (p-value=0.5206). In the pre and post intervention rheumatology clinic, the 75th percentile time from BMO to PA decision improved from 14 days to 8 days. The median time was 5 days each (p-value=0.1327). The 75th percentile time from BMO to BMD in the pre and post intervention rheumatology clinics improved from 28 days to 13 days, while the median time was 9.5 and 8.5 days respectively (p-value=0.8372).
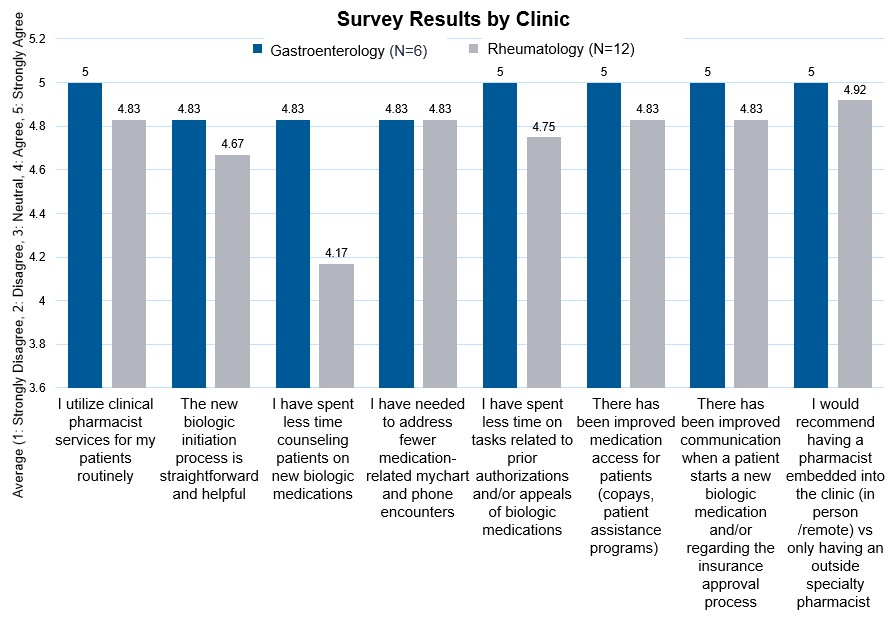
Survey questions discussed the benefit of CPs in various roles (Figure 2). Mean provider responses ranged from 4.17-5 for all questions (4=agree, 5=strongly agree).
Conclusion: After embedding CPs in the rheumatology and GI clinics, there was no statistically significant improvement in median time. However, we observed consistent improvement in the 75th percentile times for BMO to PA decision and BMD times, suggesting that the benefit of embedding CPs lies in reducing severe delays of patients initiating biologic medications. The new workflow process decreased the variance in time to initiate biologics and PA decision from pre to post intervention, suggesting that the intervention of embedding a CP helped to standardize the biologic medication process and reduce outliers. In addition, provider surveys demonstrated unanimous satisfaction with CP integration in all clinical domains.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mittal S, Dara P, Dhamankar O, Cordova N, Mohiuddin S, Zamir A, Blackwell J, Mofor P, Alvarez C, Kalra A, Zhang S, Syed N, Bajaj P. IMPACT (Impact of eMbedded Pharmacists in an Academic Center sTudy) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-impact-of-embedded-pharmacists-in-an-academic-center-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-impact-of-embedded-pharmacists-in-an-academic-center-study/