Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The adjuvanted recombinant glycoprotein E (gE) herpes zoster vaccine (RZV) received expanded approval for use in 2021 for adults receiving immunosuppression. Despite approval, little clinical or immunogencitiy data exist of RZV in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who are at high risk of herpes zoster (HZ). Further, it is unclear if biologics and other immunosuppressive therapies used in RA could diminish vaccine response. Accordingly, we evaluated the immunogenicity of RZV in RA patients using the T-cell co-stimulatory inhibitor abatacept.
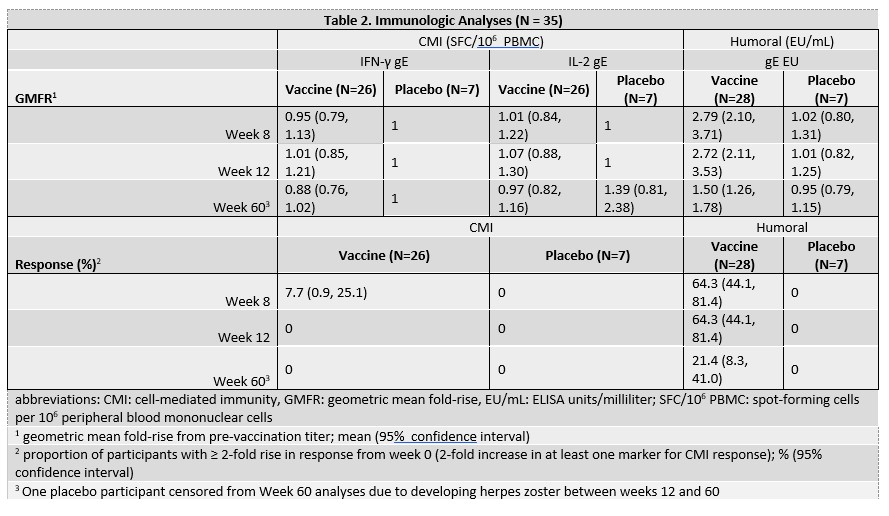
Methods: 70 participants aged ≥ 18 years with RA taking abatacept were randomized 4:1 to receive RZV or placebo at entry and then at week 8. Blood collected at weeks 0, 8, 12, and 60 was used to measure gE-specific cell-mediated immunity (CMI) by IFNg & IL2 dual-color FLUOROSPOT and IgG antibodies by ELISA. We defined a CMI response as ≥ 2-fold increase in IFN-γ or IL-2 spot forming cells (SFC) at week 12 and humoral response as ≥2-fold increase in IgG titer at week ≥8. Immunologic analyses are ongoing. Immunologic data for the first 35 participants are presented here and will be updated to incorporate all 70 participants for the conference.
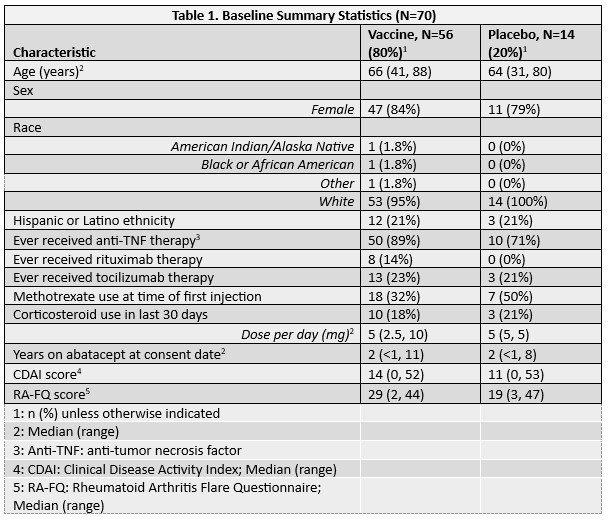
Results: The 70 participants enrolled had median age 65 years (range, 31-88 years); 13 (19%) used corticosteroids within 30 days of week 0; and 25 (60%) were using methotrexate (MTX) at week 0 (Table 1). Of the 35 participants included in the preliminary immunogenicity analyses, one participant in the placebo arm developed HZ between weeks 12 and 60 and was censored from the week 60 analyses. No other participants developed HZ during the study. All 35 participants were included in the humoral immunity analysis, and 33 (94.3%) in the CMI analysis, with 2 excluded due to missing week 0 CMI measurements. At week 12, no participants in the vaccine arm achieved a ≥2-fold increase in either CMI marker. In contrast, 64.3% (95% CI 44.1, 81.4) developed ≥2-fold increase in anti-gE antibodies with geometric mean fold-rise (GMFR) of 2.72 (95% CI 2.1, 3.5) (Table 2). At week 60, only 21.4% (95% CI 8.30, 41.0) maintained a ≥2-fold antibody increase compared to week 0. In a subgroup analysis of the vaccine arm stratified by MTX use at week 0, CMI responses were nil for both groups and humoral responses were similar at week 12 (MTX use: 63.6% (95% CI: 30.8-89.1); no MTX use: 64.7% (95% CI: 38.3, 85.8). There were no responses in the placebo group.
Conclusion: In this phase 2 study, people with RA who received RZV while using abatacept had poor vaccine responses, including a notable absence of CMI responses. Antibody responses to RZV were lower in magnitude and frequency than those previously described. These results raise the possibility that RZV may not confer adequate protection against HZ in people with RA taking abatacept. Future studies should assess whether holding abatacept around the time of vaccination would enhance vaccine immunogenicity. Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03604406).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Winthrop K, Hawkins J, Weinberg A, Siegel S, Baxter J, Garth K, Huffstutter J, Loveless J, gharib S, Reddy S, Sinha J, Moreta E, Ridley D, Messaoudi I, Curtis J. Immunogenicity of the Recombinant Zoster Vaccine in People with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Abatacept [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunogenicity-of-the-recombinant-zoster-vaccine-in-people-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-abatacept/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunogenicity-of-the-recombinant-zoster-vaccine-in-people-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-abatacept/