Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-4:45PM
Background/Purpose: There is a pressing need to identify novel therapeutic targets in lupus nephritis. Multiomic approaches hold great potential for discovery. We integrated urine proteomics and kidney single cell transcriptomics to discover biological processes and biomarkers associated with histologically active LN.
Methods: Urinary proteins (up to 1200) were quantified (RayBiotech Kiloplex) in urine samples from two independent cohorts of SLE patients with lupus nephritis (n=30 and n=144). Samples were collected on the day of (73%) or within 3 weeks (27%) of kidney biopsy in SLE patients with proteinuria > 500mg/d. The NIH Activity Index was determined by a renal pathologist at each site. Intrarenal expression of candidate biomarkers was evaluated using single cell transcriptomics of renal biopsies from patients with active lupus nephritis (n=24).
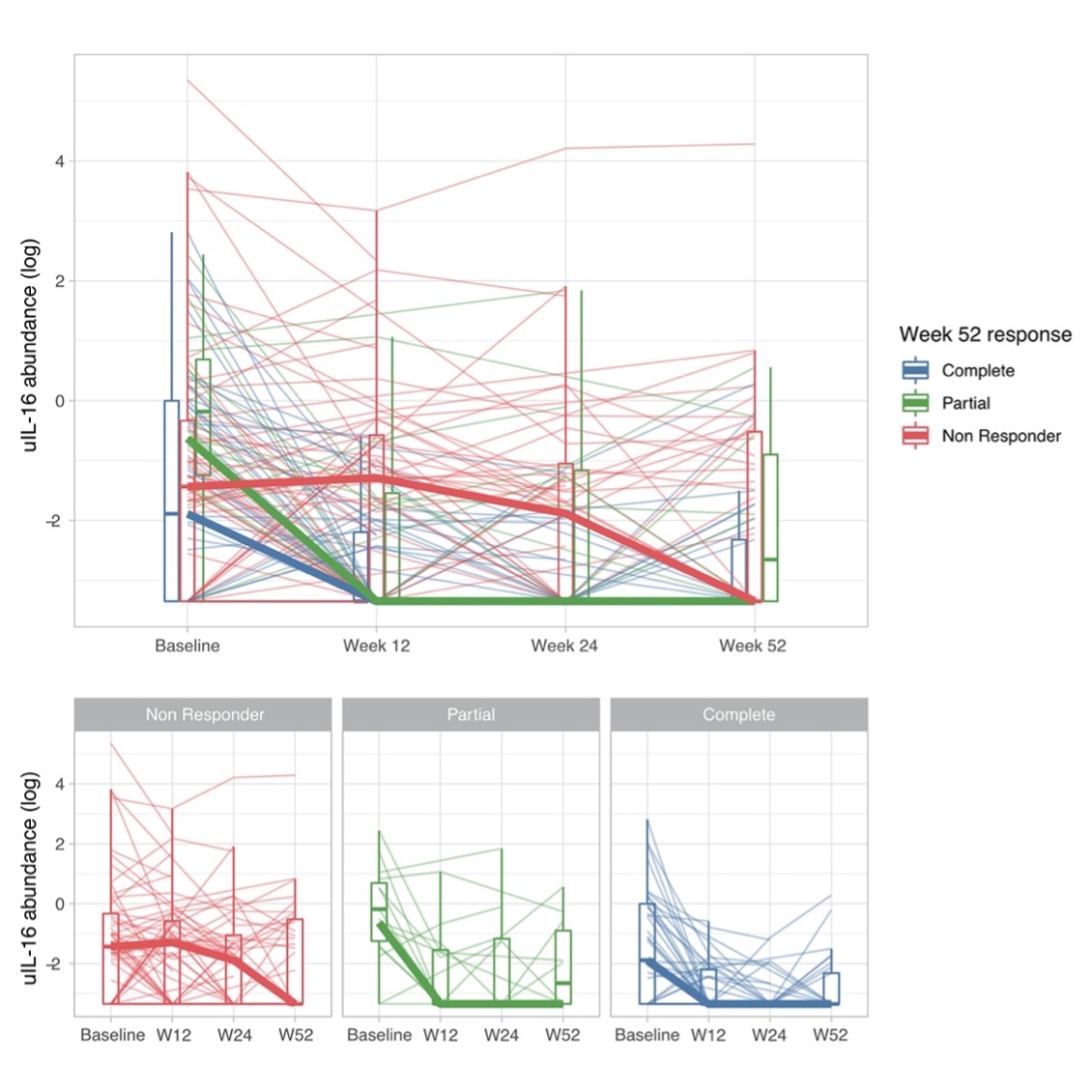
Results: A total of 174 patients were included: 127 (73%) had a proliferative histological class (III or IV +/- V), 47 (27%) pure membranous (V). Urinary IL-16 showed the strongest positive correlation with histological activity (NIH Activity Index) in two independent cohorts (r=0.69, p=9∙10-5; r=0.49, p=3∙10-10; Figure 1). Response to treatment was paralleled by an early reduction of urinary IL-16 (Figure 2). Single cell RNA sequencing independently demonstrated that IL16 is the second most widely expressed cytokine by most infiltrating immune cells in lupus nephritis kidneys (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Urine proteomics can profoundly change the diagnosis and management of lupus nephritis by noninvasively monitor active intrarenal biological pathways. These findings implicate IL-16, a proinflammatory chemokine, in lupus nephritis pathogenesis designating it as a potentially treatable target and biomarker.
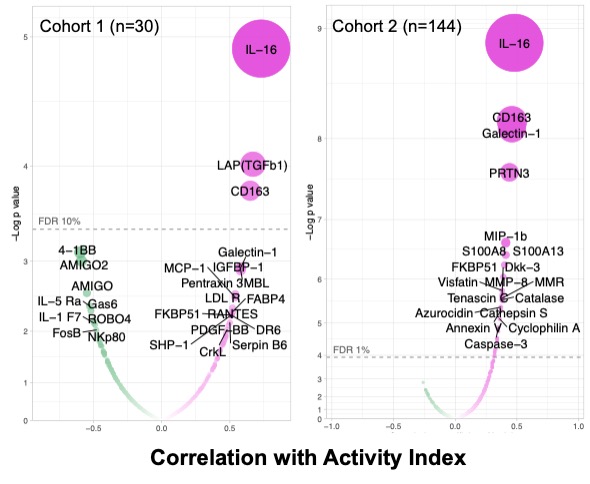 Figure 1. Urinary biomarkers associated with the LN NIH Activity Index. Volcano plots displaying Spearman correlation coefficient for 1000 (left) and 1200 (right) urinary biomarkers with LN histological activity. FDR = false discovery rate.
Figure 1. Urinary biomarkers associated with the LN NIH Activity Index. Volcano plots displaying Spearman correlation coefficient for 1000 (left) and 1200 (right) urinary biomarkers with LN histological activity. FDR = false discovery rate.
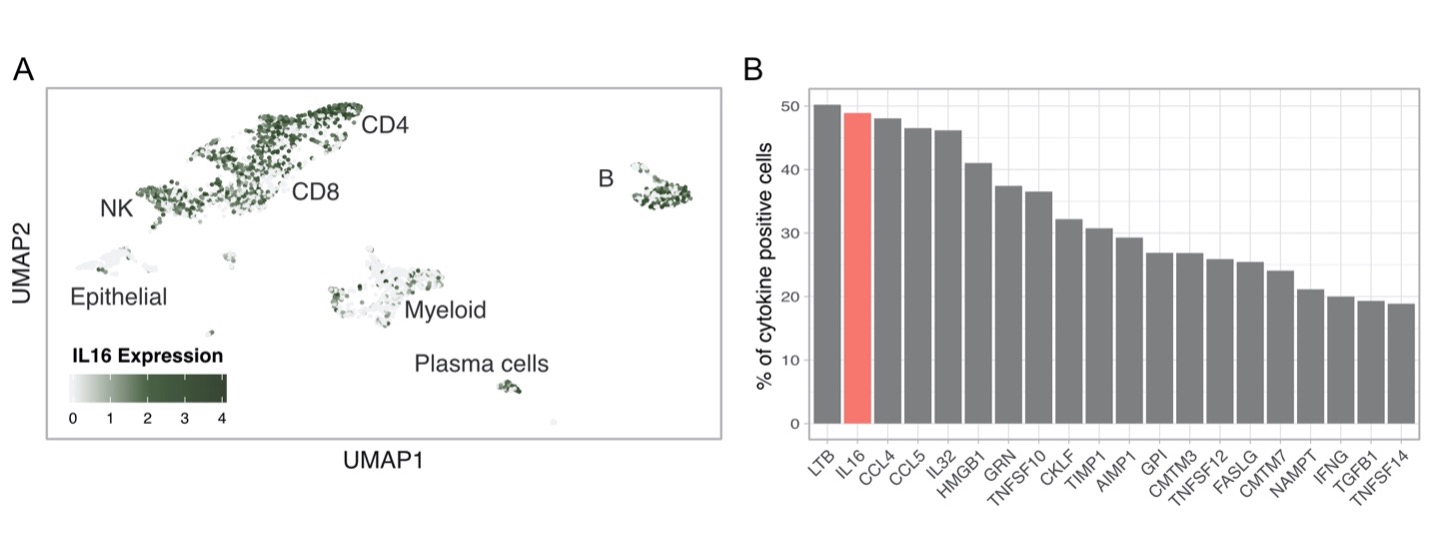 Figure 3. Intrarenal expression of IL16 based on single cell RNA sequencing of lupus nephritis kidney biopsies. (A) UMAP plot showing IL16 expression by all kidney infiltrating immune cells. (B) Percentage of cytokine positive cells across all kidney infiltrating immune cells. The bar plot shows the top 25 cytokines out of a comprehensive list of 236 obtained from the “Cytokine Registry” (Immport) and the Gene Ontology database.
Figure 3. Intrarenal expression of IL16 based on single cell RNA sequencing of lupus nephritis kidney biopsies. (A) UMAP plot showing IL16 expression by all kidney infiltrating immune cells. (B) Percentage of cytokine positive cells across all kidney infiltrating immune cells. The bar plot shows the top 25 cytokines out of a comprehensive list of 236 obtained from the “Cytokine Registry” (Immport) and the Gene Ontology database.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fava A, Rao D, Mohan C, Zhang T, Rosenberg A, Fenaroli P, Belmont H, Izmirly P, Clancy R, Monroy-Trujillo J, Fine D, Arazi A, Berthier C, Davidson A, James J, Diamond B, Hacohen N, Wofsy D, Raychaudhuri S, (AMP) RA/SLE Network A, Buyon J, Petri M, Accelerating Medicines Partnership in RA/SLE T. IL-16 Is Linked to Lupus Nephritis Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-16-is-linked-to-lupus-nephritis-activity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-16-is-linked-to-lupus-nephritis-activity/