Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The spectrum of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) includes many diseases that were thought to be confined to a single organ, as the retroperitoneal fibrosis. Many patients identified with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis (IRF) could be reclassified as IgG4-RD, due to immunohistochemistry techniques. Classification criteria have not been uniform during last years and IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis frequency is unknown in our country. We aim to describe IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis (IgG4-RF) frequency using last published criteria and compare clinical, histopathologic and radiologic features with non-Ig4-RF
Methods:
A dynamic retrospective cohort involving 16 adults with histopathological diagnosis of IRF at Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires since january 2010 to february 2020 was studied. Pathology slides were reviewed, and immunohistochemistry for IgG4 and IgG was performed and assessed for each case. 2019 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/ European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) classification criteria were used to identify IgG4-RD cases. Mann Whitney U test and the Fisher exact test were used to compare continuous and categorical variables respectively
Results: 8 (50%) patients met criteria for IgG4-RF. The median age was similar in the two subsets (61 years old in IgG4-RF versus 54, p = 0.2) and both had male predominance. 3 patients presented other manifestations of IgG4-RD in IgG4-RF group. None had either high serum IgG4 levels or eosinophilia. All of the IgG4-RF had infrarenal and circumferential retroperitoneal extension along the aorta on computed tomography but there were not significant differences with non-IgG4-RF (p= 0.4 and 0.1). Hydronephrosis, renal failure and requirement of renal replacement therapy did not differ between groups. Corticosteroids were mostly used as drug therapy, followed by azathioprine but most of the patients did not receive specific treatment. 7 (87.5%) patients needed surgical or endoscopic intervention in each group. 7 patients in each subset were admitted to hospital with a similar median number of hospitalizations (3 in IgG4-RF versus 2, p=0.07). All of Ig4-RF patients had a dense lymphocytic infiltrate and storiform fibrosis (p=0.01) and 75% presented eosinophils (p=0.04). IgG4+ cells/hpf and IgG4/IgG ratio were significantly higher than patients with non-Ig4-RF (p = 0.01 and 0.03, respectively)
Conclusion: Half of patients in our IRF retrospective cohort met criteria of IgG4-RF, first data in our region. ACR/EULAR new criteria may be helpful in order to homogenize the identification of Ig4-RD. These findings may motivate further evaluation of this condition, increasing early recognition, accurate treatment and integral follow-up
 Figure 1. Overview of patient selection
Figure 1. Overview of patient selection
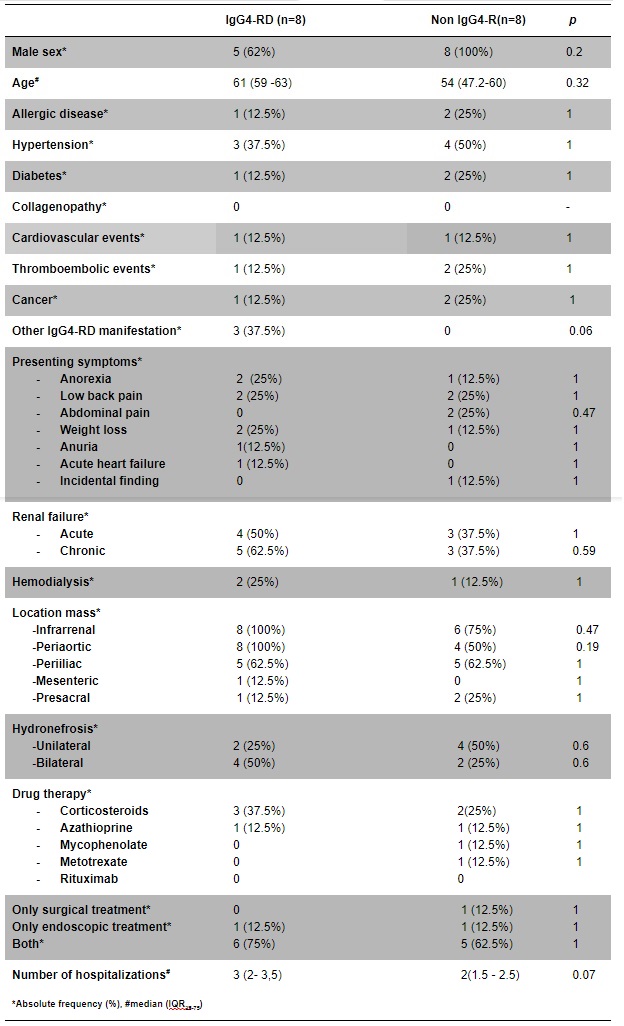 Table 1. Clinical and radiologic features of IgG4- related and non – IgG4- related retroperitoneal fibrosis
Table 1. Clinical and radiologic features of IgG4- related and non – IgG4- related retroperitoneal fibrosis
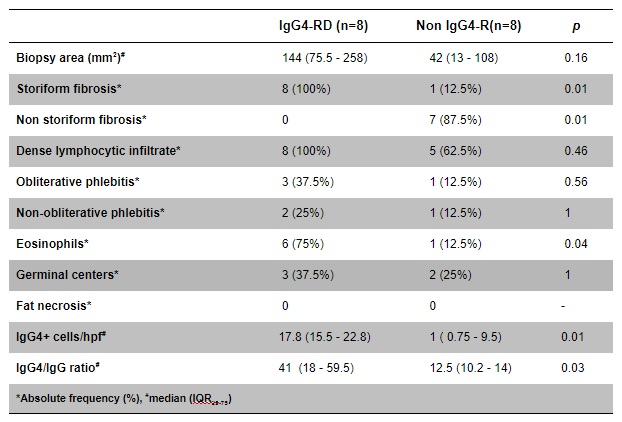 Table 2. Histopathological features of IgG4- related and non – IgG4- related retroperitoneal fibrosis
Table 2. Histopathological features of IgG4- related and non – IgG4- related retroperitoneal fibrosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Angarola E, Jauk F, Peuchot V, Orlova M, Valeo M, Pollan J, Garcia Rivello H. IgG4-related Retroperitoneal Fibrosis. Retrospective Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg4-related-retroperitoneal-fibrosis-retrospective-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg4-related-retroperitoneal-fibrosis-retrospective-cohort/
