Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Type I interferon (IFN) plays a role in the pathogenesis of dermatomyositis (DM) and correlates with measures of disease activity. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) serves as an intracellular sensor of dsRNA present in viral infections, and DM patients with anti-MDA5 antibodies have high levels of IFN and a similar pathophysiology to certain viral infections such as SARS-CoV2, including risk of sometimes life-threatening interstitial lung disease (ILD). Interferon alpha inducible protein 27 (IFI27) is an IFN-inducible protein involved in IFN-induced cell apoptosis, proliferation, and immune responses. Unlike other IFN-inducible genes, IFI27 appears to be a more specific marker of viral respiratory infections, and its regulation pattern is distinct from other IFN-inducible genes.1 We sought to better understand the biological relevance of IFI27 in DM with anti-MDA5 antibodies.
Methods: Stranded RNA sequencing was performed on whole blood samples from DM patients seen at the Stanford Rheumatologic Dermatology outpatient clinic. IFI27 expression levels (FPKM) were natural log-transformed to normalize the distribution. Type 1 IFN score was calculated as previously described Associations between IFI27 expression, Type 1 IFN score and selected clinical features were assessed using Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for binary variables and Spearman’s correlation for continuous variables.
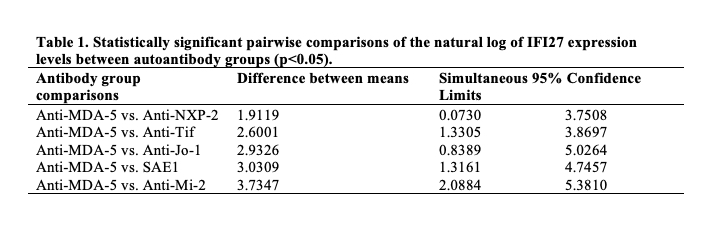
Results: Our data set consisted of blood samples from 201 adult DM patients. The median disease duration at baseline blood collection was 1.8 years (range 0.1–39.4 years). We found that IFI27 expression was 2.5 times higher in the anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) autoantibody group (p< 0.05), compared to all other autoantibody types (Table 1). IFI27 expression showed no significant associations with demographic factors (age, gender, ethnicity), medication use (prednisone, DMARD, IVIG), or CK levels. However, elevated IFI27 expression characterized patients with interstitial lung disease (p=0.007) and cutaneous ulcers (p=0.001) compared to those without these features, and correlated more strongly with these features that Type I IFN scores. In contrast, while IFI27 was correlated with Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Activity and Severity Index activity (CDASI-A) score (R=0.35, p< 0.0001) and muscle strength (R=-0.34, p< 0.0001), it correlated less strongly than IFN score (R=0.52, p< 0.0001) and (R=0.37, p< 0.0001), respectively.
Conclusion: IFI27 expression exhibits distinct clinical correlations compared to composite IFN scores, correlating more strongly with ILD than the Type 1 IFN score. We hypothesize that IFI27 may reflect an underlying vascular pathogenesis within dermatomyositis phenotypes, evidenced by its association with cutaneous ulcers.
References:
1. Tang BM, Shojaei M, Parnell GP, et al. A novel immune biomarker IFI27 discriminates between influenza and bacteria in patients with suspected respiratory infection. The European respiratory journal. 2017;49(6):1602098-1602098. doi:https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.02098-2016
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leeolou M, Chung L, Sarin K, fiorentino d. IFI27 Is Differentially Upregulated in Anti-MDA5 Dermatomyositis and Correlates with the Presence of Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ifi27-is-differentially-upregulated-in-anti-mda5-dermatomyositis-and-correlates-with-the-presence-of-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ifi27-is-differentially-upregulated-in-anti-mda5-dermatomyositis-and-correlates-with-the-presence-of-interstitial-lung-disease/