Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1776–1795) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is an inflammatory arthritis and shares several clinical features with Osteoarthritis (OA), the most common form of arthritis. This often leads to challenges in correctly diagnosing these diseases. Synovial Fluid (SF) from joints of arthritis patients contain a rich population of pathogenic modulators, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), making it a good source to study disease biomarkers. In this study, we aimed to 1) identify differentially expressed miRNA in SF of PsA and OA patients, and 2) identify differentially expressed miRNA driven pathways.
Methods: Synovial fluid aspirated from knees of 12 PsA (sex: 8M, 4F; age (years): (median, range) = (45 (19-64)) and 12 OA patients (sex: 6M, 6F, age: (median, range) = (60 (43-74)) was used for miRNA sequencing using Illumina NextSeq 550. Linear modelling with empirical Bayes moderation (using the Limma R package) was used for assessing differential expression of miRNAs. Gene targets and enriched pathways targeted by significant miRNAs were identified by using integrative tools miRDIP and pathDIP set to a very high confidence class. For validation, SF samples from additional 35 PsA and 37 OA patients were retrieved. Total RNA including miRNA was extracted from these samples, and 5 selected candidate miRNAs were validated using quantitative RT-PCR. ΔΔCt method was used to calculate fold change. Differentially expressed miRNAs were defined as those with a two-fold change in expression (-1.0 ≥ log2FC ≥ 1.0; p-value < 0.05).
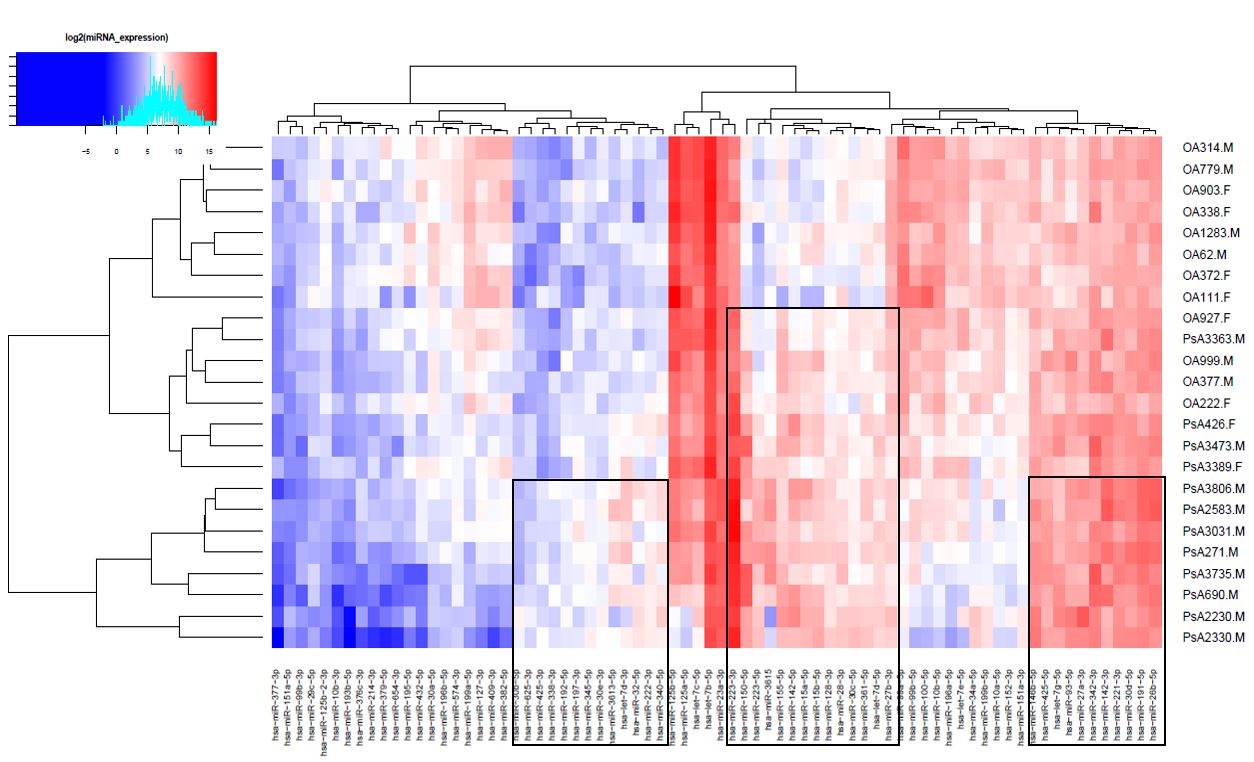
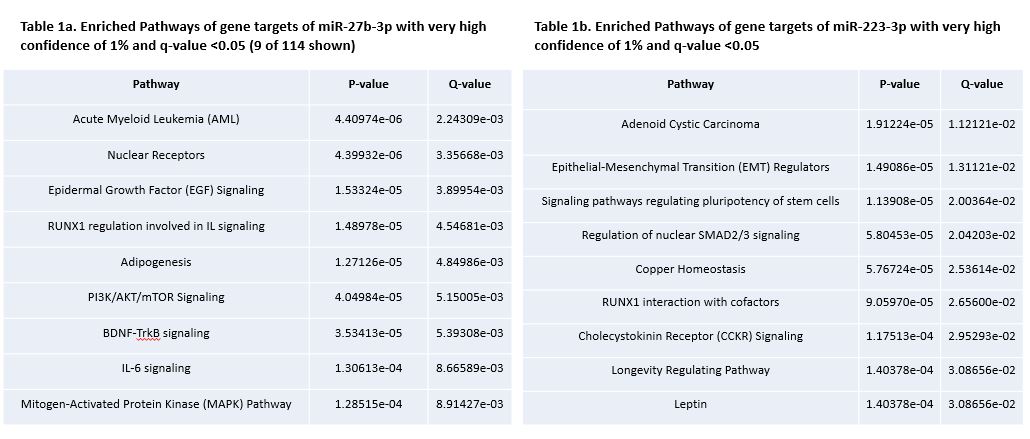
Results: After miRNA sequencing, 51 miRNAs were found to be significantly differentially expressed between PsA and OA (FDR adjusted p-value less than 0.05) (Fig. 1). QKI (RNA binding protein), OTUD4 (TLR signalling regulator), and NFAT5 (osmotic stress response regulator) in PsA, and, CELF2 (mRNA processor), NFAT5, and ACVR2B (TGFβ receptor) in OA, were the highest ranked gene targets of significant miRNAs.Figure 2 shows the signalling cascade that include genes targeted by miRNAs upregulated in PsA and OA. Pathways such as mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and WNT signalling were included which have also been previously demonstrated to be associated with PsA and OA. On qRT-PCR, 2 out of 5 miRNAs; miR-27b-3p (log2FC= -2.391, p-value < 0.05), and miR-223-3p (log2FC= 2.830, p-value < 0.05), were significantly dysregulated in SF of PsA patients compared to OA patients. Analysis using miRDIP and pathDIP revealed 195 gene targets and 114 enriched pathways for miR-27b-3p (Table 1a), and 223 gene targets and 9 enriched pathways for miR-223-3p (Table 1b).
Conclusion: Several miRNAs are deregulated between PsA and OA. miR-27b-3p, and miR-223-3p were validated in an independent cohort of patients. Identification of gene targets and enriched pathways further support the validated findings. Additional analysis of the remaining significant miRNAs will provide valuable pathogenetic insights and may identify diagnostic signature of PsA vs OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ganatra D, Samman A, Nasri D, Rahmati S, Cruz Correa O, Machhar R, Gandhi R, Kapoor M, Chandran V. Identifying Synovial Fluid Micro-RNA Signature That Distinguishes Psoriatic Arthritis from Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identifying-synovial-fluid-micro-rna-signature-that-distinguishes-psoriatic-arthritis-from-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identifying-synovial-fluid-micro-rna-signature-that-distinguishes-psoriatic-arthritis-from-osteoarthritis/