Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Human Etiology and Pathogenesis - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, relapsing autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs and is a highly heterogeneous condition, with wide variations in the presentation and severity of disease and the biological markers identified [1]. We analyzed multi-modal biomarker (mRNA, miRNA, cytokines and autoantibodies) data from ~100 clinically annotated SLE patients under standard of care from a single clinical center (Northwell Rheumatology Clinic) along with ~100 NHVs to identify key dysregulated and co-dysregulated markers in SLE.
Methods: To address the issue of heterogeneity, we applied 2 approaches namely outlier analysis [2] followed by market basket analysis [3] to identify dysregulated and co-dysregulated markers in this multi-modal biomarker rich dataset. We also used pathway analysis and knowledge databases to assess the biological relevance of these markers.
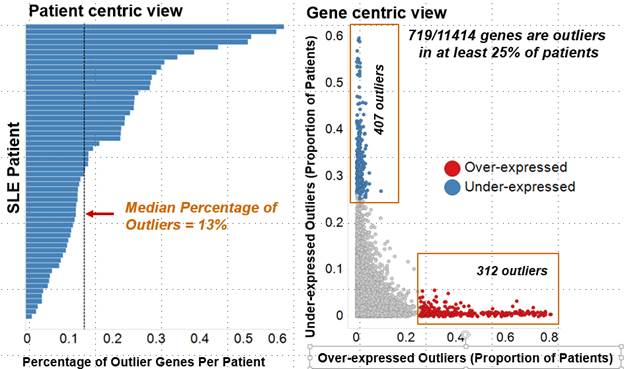
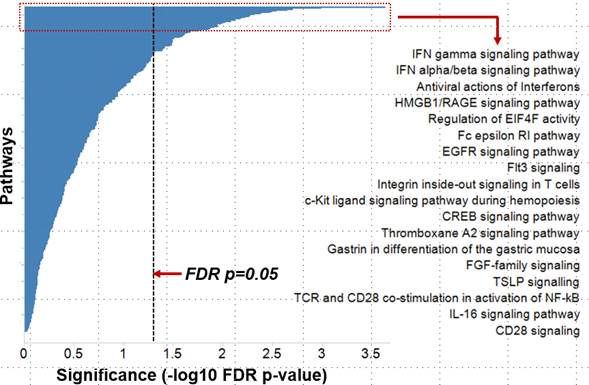
Results: For the whole blood transcriptomic data, on an average, 13% genes were found to be dysregulated in an SLE patient and ~ 6% of genes were found to be dysregulated in at least 25% of SLE patients (Fig.1). Percentage of outlier genes showed weak correlation with SLEDAI scores . Pathway analysis of outlier genes showed an enrichment for IFN signaling pathways (Fig. 2). Market basket analysis identified several high-confidence (>0.8) co-dysregulated associations across a wide proportion of patients. The IFN genes formed the most promiscuous associations. The high-confidence associations were further prioritized based on multi-modality (e.g. miRNA:mRNA) and opposing regulation.
Conclusion: Several key dysregulated markers were identified in SLE patients using outlier analysis, which might have been otherwise missed by traditional ANOVA-based approaches because of the heterogeneity in patients. Furthermore, the market basket analysis identified several co-dysregulated markers in patient sub-populations which might be missed by traditional co-expression analysis that requires co-dysregulation across all patients. These markers can be drivers and potential patient stratification biomarkers of SLE and might also help to understand the pathophysiology of this heterogeneous and complex disease.
References:
1. Merrill JT et al. A 2014 update on the management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2014.
2. Macdonald, J. W. et al. "COPA–cancer Outlier Profile Analysis." Bioinformatics: 2950-951 (2006)
3. Hahsler, M. et al. "Arules – A Computational Environment for Mining Association Rules and Frequent Item Sets." J. Stat. Soft. 14.15 (2005)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hu YS, Bandyopadhyay S, Carman J, Manjarrez-Orduño N, Jiang C, Suchard S, Menard L, habte S, kansal S, jayaswal V, Furie RA, Nadler SG. Identifying Dysregulated and Co-Dysregulated Markers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Using Multi-Modal Biomarker Data from a Large Pre-Clinical Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identifying-dysregulated-and-co-dysregulated-markers-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-using-multi-modal-biomarker-data-from-a-large-pre-clinical-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identifying-dysregulated-and-co-dysregulated-markers-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-using-multi-modal-biomarker-data-from-a-large-pre-clinical-study/