Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Currently available diagnostic tests for inflammatory arthritis lack sufficient sensitivity and specificity, often requiring the integration of clinical manifestations with physician expertise for accurate diagnosis. Urine is a noninvasive and easily accessible specimen that represents a promising diagnostic tool. This study aimed to identify novel urinary proteomic biomarkers in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and evaluate their associations with clinical parameters and disease activity.
Methods: Urine protein profiling was performed on samples from 20 patients with AS and 10 control subjects, each with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), gout, or healthy controls (HC), using label-free quantitative proteomics. Differentially expressed proteins were identified using MaxQuant and the UniProt database (fold change ≥ 1.5, p < 0.05). Selected proteins were validated by Western blot analysis and further assessed by ELISA in an independent cohort of 75 AS patients and 37 HC. Associations between protein levels and clinical parameters, including BASDAI and ASDAS-CRP, were also analyzed.
Results: Urine proteins were analyzed by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry, identifying 1,975 proteins. Among them, AMY1A, SDC1, and PIK3IP1 were selected as candidate biomarkers based on high-fold changes and statistical significance. Western blot analysis confirmed significantly higher expression of these proteins in AS patients compared to those with RA, gout, and HC, supporting the proteomic findings (Figure 1). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis demonstrated good diagnostic performance, with the individual area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.812 (AMY1A), 0.875 (SDC1), and 0.852 (PIK3IP1). Notably, the combination of all three markers yielded an improved AUC of 0.973, indicating enhanced diagnostic accuracy with multiplexed analysis. In the validation cohort, ELISA assay confirmed that PIK3IP1 and SDC1 levels were significantly elevated in AS patients (p = 0.0082 and 0.0179, respectively), whereas AMY1A showed no significant difference (p = 0.7058) (Figure 2). No significant correlations were found between the three biomarkers and disease activity indices such as BASDAI or ASDAS-CRP. However, AMY1A levels were related to a history of enthesitis, and PIK3IP1 levels were associated with underlying hypertension (Table 1).
Conclusion: AMY1A, SDC1, and PIK3IP1 were identified as potential urinary biomarkers for AS. Among them, PIK3IP1 and SDC1 showed significantly higher levels in AS patients and demonstrated good diagnostic performance. While these markers were not associated with disease activity scores, these results suggest their potential utility in AS diagnosis.
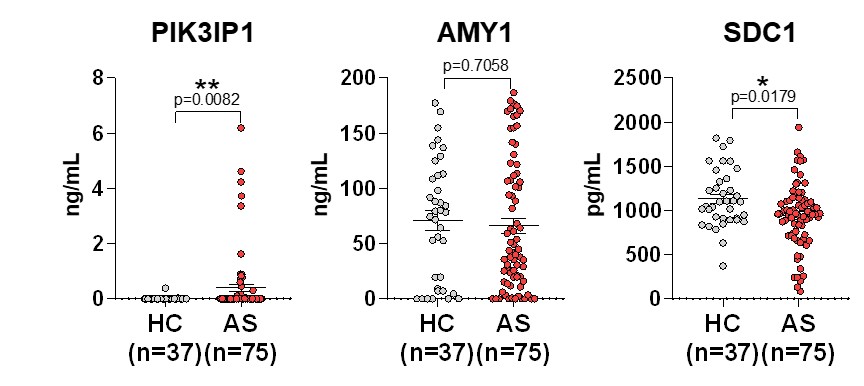 Figure 1. Verification of PIK3IP1, AMY1A and SDC1 in urine by western blot. Western blot analysis in the urine sample set: A; Ankylosing spodylitis (n=20), R; Rheumatoid arthritis (n=10), G; Gout (n=10), H; Healthy controls (n=10). THP-1 was used as an input amount control
Figure 1. Verification of PIK3IP1, AMY1A and SDC1 in urine by western blot. Western blot analysis in the urine sample set: A; Ankylosing spodylitis (n=20), R; Rheumatoid arthritis (n=10), G; Gout (n=10), H; Healthy controls (n=10). THP-1 was used as an input amount control
.jpg) Figure 2. Validation of PIK3IP1, AMY1A and SDC1 in urine by ELISA assay. ELISA assay in the urine sample set: Ankylosing spondylitis (n=75), Healthy controls (n=37).
Figure 2. Validation of PIK3IP1, AMY1A and SDC1 in urine by ELISA assay. ELISA assay in the urine sample set: Ankylosing spondylitis (n=75), Healthy controls (n=37).
.jpg) Table 1. Correlation analysis between urinary levels of AMY1A, SDC1, and PIK3IP1 and clinical variables in AS patients. AS; Ankylosing spondylitis, BMI; Body mass index, ESR; Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP; C-reactive protein, BASDAI; Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, ASDAS-CRP; Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score – C-reactive protein, NSAID; Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug, csDMARD; Conventional synthetic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug, bDMARD; Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug
Table 1. Correlation analysis between urinary levels of AMY1A, SDC1, and PIK3IP1 and clinical variables in AS patients. AS; Ankylosing spondylitis, BMI; Body mass index, ESR; Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP; C-reactive protein, BASDAI; Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, ASDAS-CRP; Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score – C-reactive protein, NSAID; Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug, csDMARD; Conventional synthetic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug, bDMARD; Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Son C, Jang D, Nam S, Oh Y, Jo S, Kim J, Kim T. Identification of Urine Proteomic Biomarkers Associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-urine-proteomic-biomarkers-associated-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-urine-proteomic-biomarkers-associated-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/
