Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Muscle inflammation is a major clinical manifestation in patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM). Phenotypes of PM/DM patients, especially those with interstitial lung diseases, are known to be classified through different subsets of autoantibodies, however, there are few studies evaluating muscle inflammation by serum biomarkers. The aim of this study is to identify serum biomarkers associated with muscle inflammation in PM/DM patients.
Methods: This study is a cross-sectional study. The study subjects were initially screened from 150 PM/DM patients who had visited the Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, and the Department of Respiratory Medicine at Nagasaki University Hospital between August 2008 and June 2021. Inflammation of bilateral thigh muscles was evaluated and scored by two experienced radiologists using the MRI score proposed by Andresson et al (Arthritis Research & Therapy .2017;19:17). Serum biomarkers including cytokines, measured by 43-item bead array, from PM/DM patients as well as healthy subjects (n=101, obtained from annual health check-up at Saza town in Nagasaki prefecture) were examined according the manufactures’ instructions. Cases with no disease activity, complicated by rapidly progressive interstitial lung diseases or malignancy, missing data of MRI or stored serum were excluded. Eventually, 43 patients, whose femoral MRI images were examined at the same time of serum collection, were included in the present study.
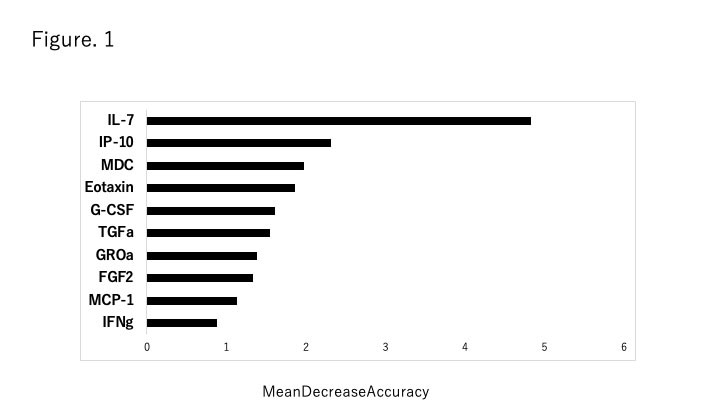
Results: Thirty-eight of the 43 cytokines were found to be suitable for further analysis. RandomForest analysis showed that the most significant cytokine was IL-7 to be ranked by the cytokines for distinguishing the two groups divided by median MRI score (Figure 1). In addition, the serum IL-7 levels in the patients with high MRI score were significantly higher than those in the healthy subjects. The correlation analysis between MRI score with IL-7 showed a correlation coefficient of 0.3551 (p=0.019). In contrast, the distribution of autoantibodies, including anti-synthetase antibodies, did not influence that of MRI score.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that serum IL-7 accurately reflects the status of muscle inflammation of PM/DM patients. Determination of serum IL-7 may represent a biomarker for the prediction of severity of muscle inflammation in patients of PM/DM, based on the scoring of MRI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matsuo H, Shimizu T, Koga T, Oki N, Uetani M, Kawakami A. Identification of Serum Biomarkers Associated with Muscle Inflammation Detected on MRI in Polymyositis/dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-serum-biomarkers-associated-with-muscle-inflammation-detected-on-mri-in-polymyositis-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-serum-biomarkers-associated-with-muscle-inflammation-detected-on-mri-in-polymyositis-dermatomyositis/