Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s Disease (SjD) exhibits heterogeneity in clinical manifestations and underlying biology. This heterogeneity complicates drug development, with no targeted therapy approved to date. Identifying molecular biomarkers to stratify SjD into homogeneous patient subgroups can increase drug development success.
This study uses a deep learning foundation model for immune-mediated and inflammatory diseases (IMID); the model was applied to SjD cohorts to identify new transcriptomic biomarkers predictive of disease activity.
Methods: Patient’s blood transcriptomic data were fetched from 3 SjD cohorts (ASSESS, TRACTISS, and PRECISESADS) in NECESSITY, a European H2020 IMI2 project. Patients met the AECG 2002 classification criteria.
A machine learning model was developed on RNA data to predict individual patients’ disease activity defined using ESSDAI, a 12-domain composite score grading specific-organ involvement. We then focused on the biological and hematological domains as they rely on objective blood measurements; the organ systems were considered involved if the patient’s ESSDAI domain was > 0.
We leveraged a proprietary deep learning foundation model for gene expression – a 50 million parameters Transformer pretrained on bulk RNAseq from 21k IMID blood samples. The model was fine-tuned on ASSESS and TRACTISS data to predict organ involvement; PRECISESADS served as external validation. State-of-the art QA/QC, normalization, and binning of gene expression levels – adapted to each cohort’s RNA technology – were applied to ensure data quality & interoperability across datasets. The 1,200 most variable genes on the training set were selected as predictive features. Algorithm performance was measured using the AUROC.
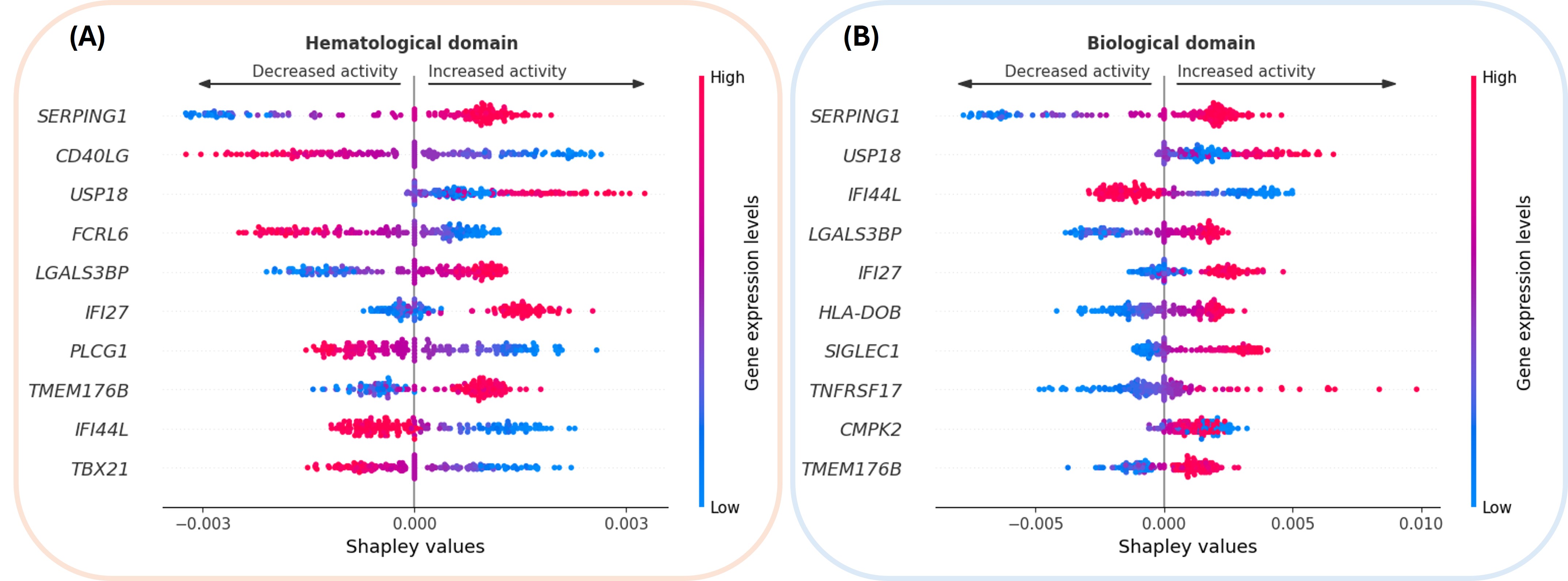
Molecular biomarkers were identified by computing Shapley values on the validation set to quantify gene importance.
Results: The dataset included 363 patients from ASSESS, 133 from TRACTISS, and 172 from PRECISESADS.
No marker was found associated with overall disease activity assessed by ESSDAI yet, so we focused on markers for specific ESSDAI domains. In the validation set, the model achieved an AUROC of 0.66 (95% CI 0.55 to 0.75) and 0.67 (95% CI 0.59 to 0.75) for binary assessment of hematological and biological ESSDAI domains, respectively.
Figure 1 depicts genes’ correlation with disease activity. High SERPING1 expression (red) correlates with both biological and hematological domains. CD40LG expression stands out as a key modulator of hematological activity; it likely acts as a proxy for the CD4+ T cell population (correlation p=2.7e-4) and thus inversely correlates with lymphopenia, a criterion of hematological activity. The interferon pathway genes (IFI44L, IFI27, SIGLEC1, CMPK2) are present in both domains, emphasizing once again the role of interferon signaling in SjD [1].
Conclusion: This study identifies RNA biomarkers predictive of disease activity in specific ESSDAI domains. These biomarkers can serve to stratify SjD, further improving the development of investigational drugs.
1. Verstappen et al. A leading role for interferon as a treatment target in Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol 19, 468–469 (2023).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jara-Mikolajczak A, Abessera Z, Rethoret-Pasty M, Mazuir E, Bruley A, Ng W, Alarcon-Riquelme M, Bombardieri M, Bowman S, Pontarini E, Gottenberg J, Mariette X, LAIGLE L, Duquesne J, Moigeon P, Bouget V. Identification of Molecular Biomarkers for Sjögren’s Disease Stratification via a Deep Learning Foundation Model Dedicated to Immune-Mediated and Inflammatory Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-molecular-biomarkers-for-sjogrens-disease-stratification-via-a-deep-learning-foundation-model-dedicated-to-immune-mediated-and-inflammatory-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-molecular-biomarkers-for-sjogrens-disease-stratification-via-a-deep-learning-foundation-model-dedicated-to-immune-mediated-and-inflammatory-disease/