Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
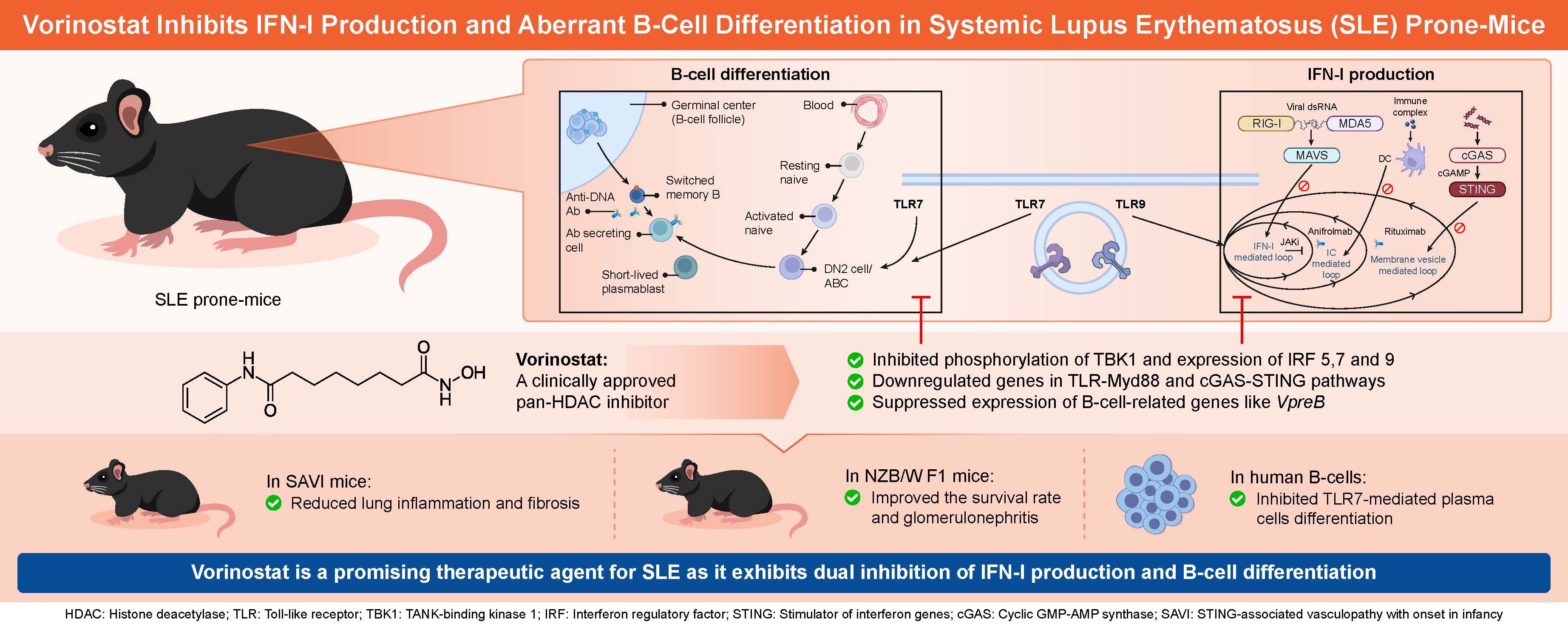
Background/Purpose: This study aimed to identify drugs that can inhibit both type I interferon (IFN-I) production and abnormal B-cell maturation and to elucidate the therapeutic effects of the candidate compounds in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)–prone mice and their underlying molecular mechanisms.
Methods: We identified an inhibitor of IFN-I production from a chemical library of clinically approved drugs. Then, we examined its efficacy in suppressing the expression and phosphorylation of upstream signaling molecules for IFN-I and the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells. We also examined whether it could alleviate disease severity in SLE-prone mice, including STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI) mice and New Zealand Black/White F1 (NZB/W F1) mice.
Results: Vorinostat, a clinically approved pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor, inhibited both IFN-I production and B-cell differentiation. Vorinostat inhibited TBK1 phosphorylation and following IRF3 nuclear translocation, and suppressed the expression of IFN-I–inducing molecules, such as IRF5 and IRF7, and B-cell–related genes, such as VpreB. Vorinostat ameliorated lung inflammation and fibrosis in SAVI mice by decreasing IFN-I. It alleviated the mortality and severity of renal disease in NZB/W F1 mice by suppressing IFN-I induction and B-cell differentiation. It also suppressed Toll-like receptor 7–mediated plasma cell differentiation in human B cells.
Conclusion: Vorinostat simultaneously suppresses IFN-I production and B-cell differentiation via inhibiting TBK1 phosphorylation and IFN-I– and B-cell–related gene expression. It should be reevaluated as a therapeutic agent for SLE, as it is expected to benefit patients with SLE in need of more effective and better tolerated therapies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hirayama T, Takamatsu H, Kumanogoh A. Identification of HDAC Inhibitor Targeting Type I Interferon and B-cell Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-hdac-inhibitor-targeting-type-i-interferon-and-b-cell-abnormalities-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-hdac-inhibitor-targeting-type-i-interferon-and-b-cell-abnormalities-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/