Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Fibroblasts exert important homeostatic functions but can also drive disease pathogenesis. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), synovial fibroblasts (SFs) contribute to the joint destruction by producing the osteoclast differentiation factor receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand RANKL as well as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) to induce bone erosion and cartilage damage, respectively. However, the mechanisms underlying the tissue-destructive fibroblast phenotype remain unclear.
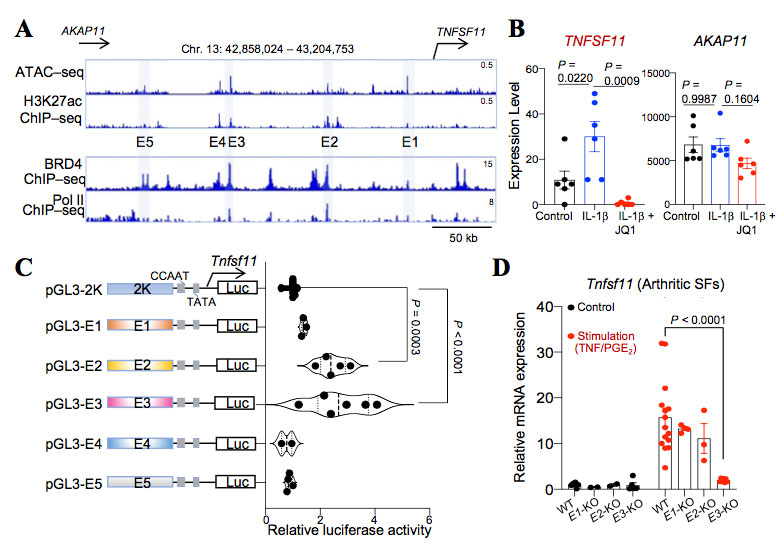
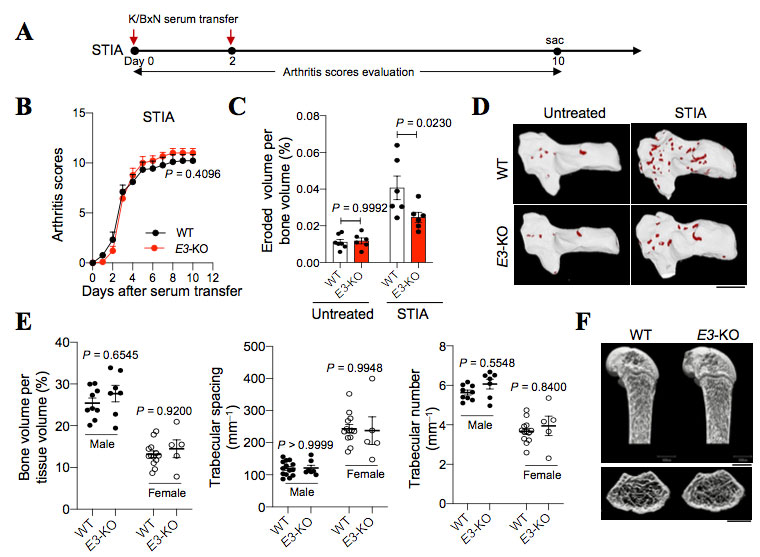
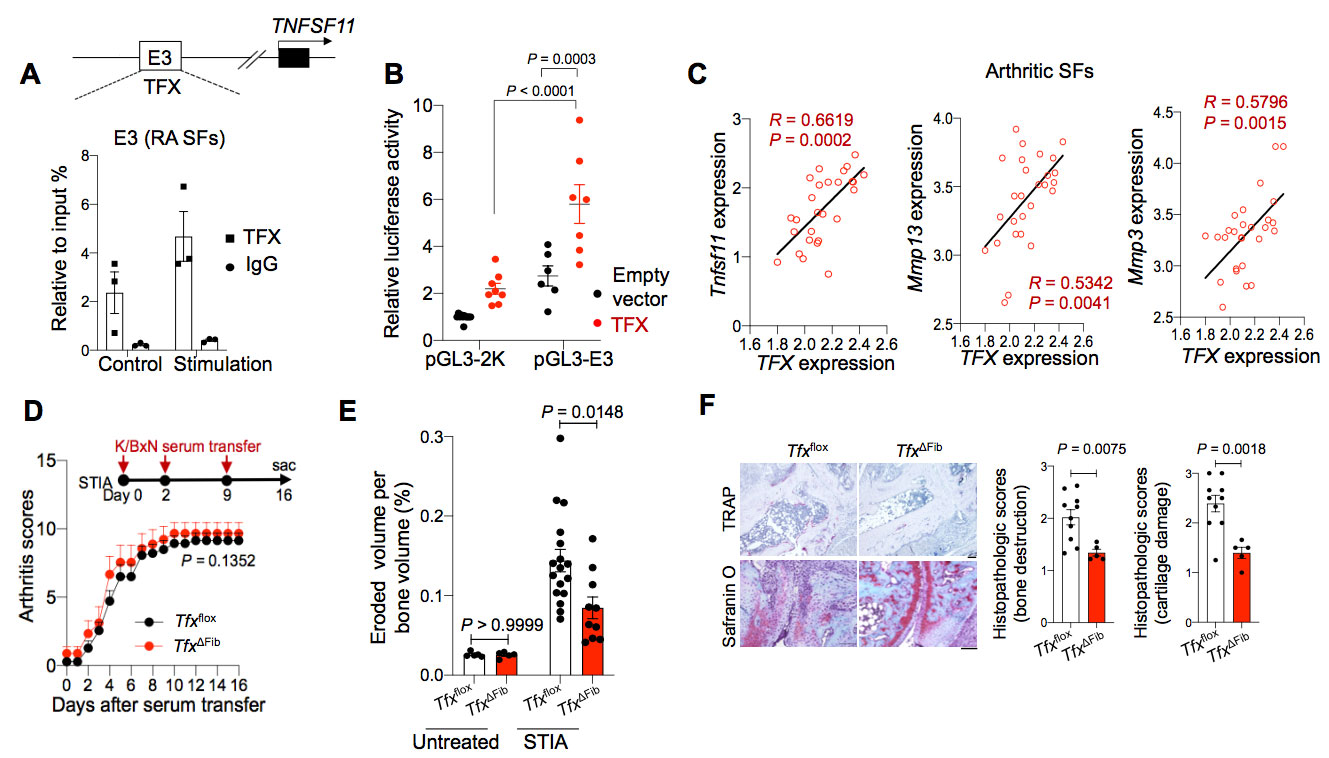
Methods: We performed single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) and epigenomic analyses of arthritic SFs to study the transcriptional mechanism underlying the tissue-destructive gene expression in SFs. Luciferase assay was performed to examine the functions of candidate enhancer elements and transcription factor (TFX) in vitro. We further generated the enhancer knockout (KO) mice and fibroblast-specificTFXconditional knockout mice and analyzed their phenotypes under steady state and arthritic conditions.
Results: Epigenomic analysis of arthritic SFs identified five distal enhancer elements (E1 to E5) upstream of the RANKL gene locus. Among the homologous regions of the five elements in mice, E3 was found to be capable of efficiently inducing RANKL transcriptional activity in an in vitro reporter assay. We further identified transcription factor TFX binds to E3 region and further enhanced RANKL gene transcription. Mice lacking E3 region displayed a reduced joint damage with a decreased RANKL expression in SFs under arthritic conditions, while retaining normal bone metabolism at steady state. Fibroblast-specific TFX deletion resulted in ameliorated bone and cartilage damage under arthritic conditions without affecting the inflammation.
Conclusion: Therefore, TFX drives the polarization toward tissue-destructive fibroblasts in arthritis. These findings provide a mechanistic basis for pathogenic fibroblast polarization in arthritis and have important clinical implications.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
YAN M, Komatsu N, Muro R, Takaba H, Nitta T, Okamoto K, Tsukasaki M, Takayanagi H. Identification of a Transcription Factor That Drives Polarization Toward Tissue-destructive Fibroblasts in Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-a-transcription-factor-that-drives-polarization-toward-tissue-destructive-fibroblasts-in-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-a-transcription-factor-that-drives-polarization-toward-tissue-destructive-fibroblasts-in-arthritis/