Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Inflammatory and auto-immune disease are associated to comordities. Indeed, patients suffering from arthritis rheumatoid disease (ARD) such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) and spondylarthritis (SA) have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, neoplasia, and infectious. We aimed to assess the efficacity of a multidisciplinary program (rheumatologist, cardiovascular, physiotherapist and dietetionnary) in the management of the comorbidities in chronic rheumatism.
Methods: Patients aged over 18, with ARD who were assessed in hospitalization day since 1st January 2023, to 31st December 2023 were included. We excluded patient with gouth and chondrocalcinosis. Assessement was carried out by means of the following criterias: cardiovascular risk factors, vaccinations status (anti-influenza, diphteria-tetanus-polyomyelitis (DTP), anti-pneumoccocal), physical activity, ditetic and osteoporosis. These items were evaluated at the inclusion (M0), at 3 months (M3) and at 6 months (M6).
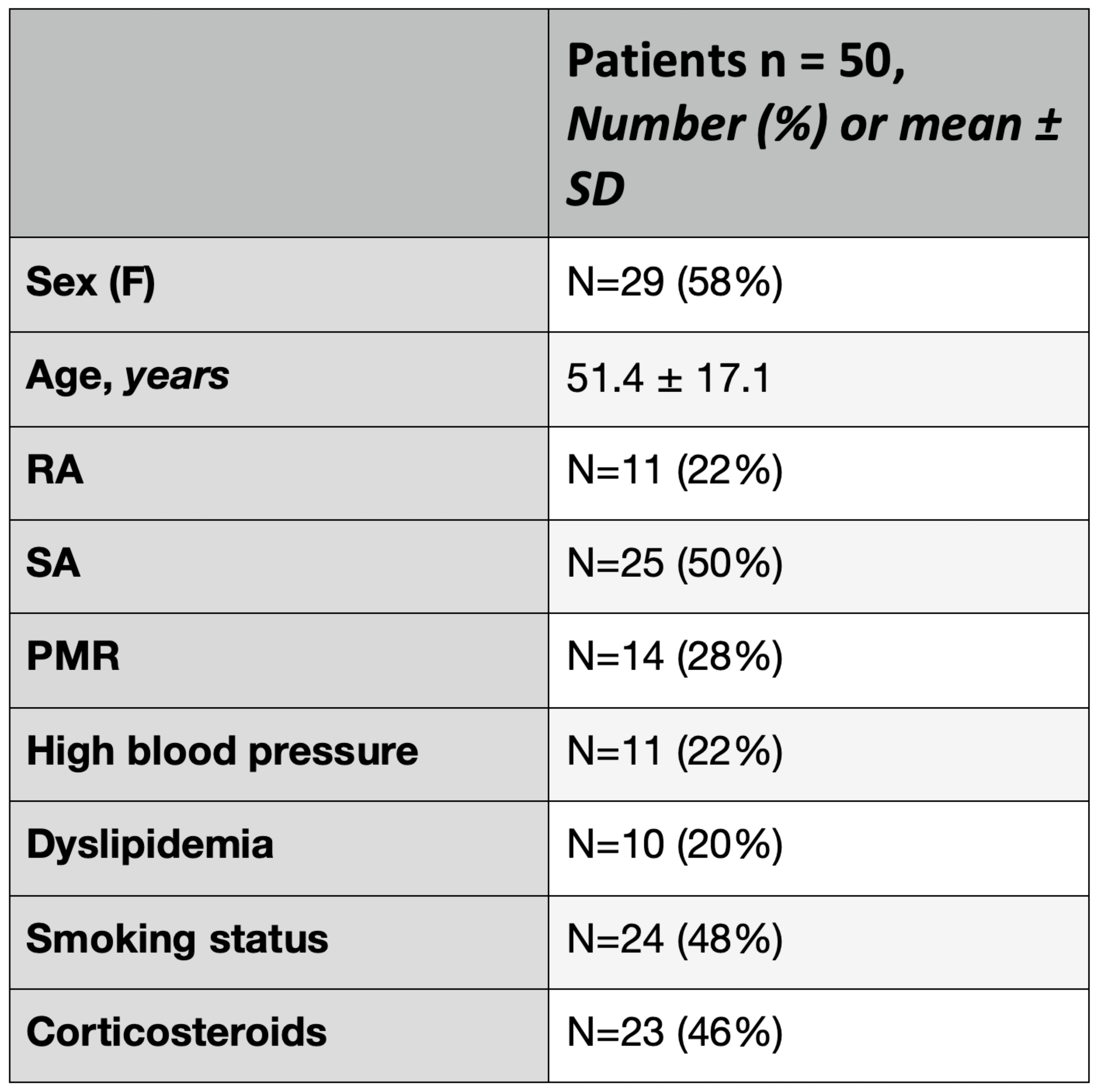
Results: Of the 54 patients analyzed, 50 patients were inclued. Demographic and clinical characteristics are summarized in table 1. Mean age was 51.4 years old ± 17.1 SD. 6 patients already had a biologic treatment, 46% (n=23) corticosteroids, 50% (n=25) non-streroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The mean SCORE2 was 2.4. 64% (n=32) patients were not up to date to their vaccination. Only one patient followed the national campagne for the screening of neoplasia (breast, cervitis, colon).
At M3, we observed that 20% (n=10) were engaging physical activity following our recommendations. In addition, 60% (n=30) of patients had adapted their diet in line with the recommendations of the French Society of Rheumatology. 54% (n=27) of patients had undergone an oncological screening. 98% (n=49) of patients were up to date to their vaccines.
At M6, all smokers had reduced their consumption. 41.6% of the smokers had quit smoking. Furthermore, 52% (n=26) of patients were physically active. 74% (n=37) adhered to an adequate diet. 74% (n=37) of patients underwent oncology screening.
Patients suffering from spondylarthritis showed better adherence to the I-CARE program (better control of cardiovascular risk factors, better dietary compliance, higher rate of oncology screening) p< 0.001.
Conclusion: Our study reveals that a systematic screening prevention program leads to a better control of the comorbidities for the patients suffering from ARD and thus even on a short follow-up of 6 months period. This program should be integrated in the management of ARD. Indeed, when patients are awarded of the risk factors, they are quickly modifying their way of life. This program could lead to a decrease of the morbi-mortality in ARD, but to reach this objective, patients should be placed at the heart of the treatment process.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mouamnia A. I-CARE Program: Interest of Multidisciplinary Systematic Screening Program for Comorbidities for Patients Suffering from Arthritis Rheumatoid DiseasE: A Real Life Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/i-care-program-interest-of-multidisciplinary-systematic-screening-program-for-comorbidities-for-patients-suffering-from-arthritis-rheumatoid-disease-a-real-life-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/i-care-program-interest-of-multidisciplinary-systematic-screening-program-for-comorbidities-for-patients-suffering-from-arthritis-rheumatoid-disease-a-real-life-study/