Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC), a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits interleukin 17A, is approved for treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). However, there is lack of real-world evidence on SEC treatment outcomes, disease activity, physical functioning and on its retention, especially in anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) naïve patients and patients pretreated with different anti-TNFs in medical history.1
The aim of this interim analysis is to evaluate SEC treatment outcomes on disease activity, physical functioning and retention rates in AS patients stratified by number of anti-TNFs (naive, 1 or ≥2) in medical history.
Methods: AQUILA is an ongoing, multi-center, non-interventional study. AS and psoriatic arthritis patients treated with SEC in daily practice are enrolled and observed from baseline (BL, d0 or d1 of study start) up to week 52 according to clinical routine. Real-world effectiveness of SEC was assessed prospectively and analyzed as observed. Here, we report interim results of SEC effectiveness on different treatment outcomes in AS patients by means of validated questionnaires such as patient´s global assessment (PGA), Bath Ankylosing Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), and Assessment of Spondyloarthritis Health Index (ASAS-HI). In addition, retention rates (time from study inclusion until premature SEC treatment discontinuation) were assessed through Kaplan-Meier plots. This interim analysis focuses on anti-TNF naïve and AS patients treated with 1 anti-TNF or ≥2 anti-TNFs in medical history. Wilcoxon tests were conducted to show significant differences between the subgroups.
Results: At BL, 311 AS patients were included; 72 (23.2%) of them received SEC already for more than 1 day up to more than 6 months before BL. Most AS patients were anti-TNF-experienced (71.1%): 82 (26.4%) and 139 (44.7%) AS patients had 1 or ≥2 prior anti-TNF treatments, respectively. BL scores for PGA, BASDAI and ASAS-HI were similar between the different anti-TNF subgroups. Constant improvement was shown in all parameters from BL up to week 52, irrespective of prior anti-TNF treatment (PGA-anti-TNF naïve: 5.9 to 3.5, PGA-1 anti-TNF: 6.1 to 4.2 and PGA-≥2 anti-TNFs: 6.7 to 5.1; BASDAI-anti-TNF naïve: 5.3 to 3.4, BASDAI-1 anti-TNF: 5.5 to 3.7 and BASDAI-≥2 anti-TNFs: 5.7 to 4.7). However, overall better improvement was observed in anti-TNF naïve patients, as seen by the example of ASAS-HI (Fig. 1). Between 30% and 40% of patients prematurely discontinued SEC treatment in the subgroups 1 anti-TNF and ≥2 anti-TNFs, respectively, while only about 20% did so in the anti-TNF naïve AS patients (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: SEC has shown to improve disease activity, physical functioning and QoL in anti-TNF-naïve and pretreated AS patients in a real-world setting. The benefits of SEC were numerically more distinct in anti-TNF-naïve patients. Moreover, SEC demonstrated high retention rate, particularly in anti-TNF-naïve patients, thereby confirming previously reported real-world data on SEC from EuroSpA research collaboration network.2
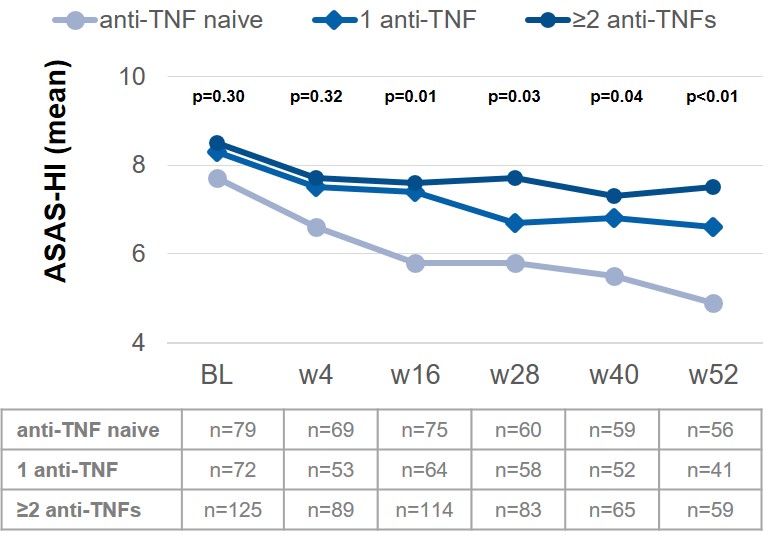 Figure 1: Change of health in AS patients treated with SEC stratified by anti-TNF pretreatment
Figure 1: Change of health in AS patients treated with SEC stratified by anti-TNF pretreatment
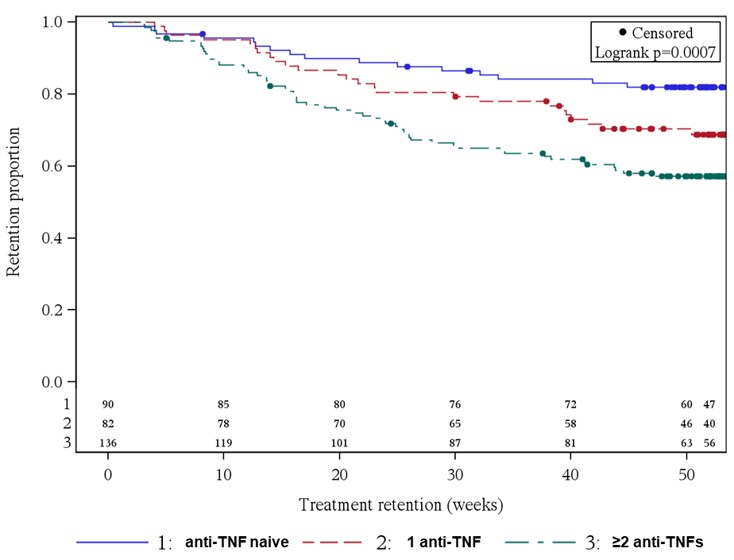 Figure 2: SEC treatment retention depending on anti-TNF pretreatment (Kaplan-Meier plot)
Figure 2: SEC treatment retention depending on anti-TNF pretreatment (Kaplan-Meier plot)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiltz U, Brandt-Jürgens J, Kästner P, Riechers E, Peterlik D, Tony H. How Do TNF-alpha-Inhibitors in Medical History Affect Patient Reported Outcomes and Retention in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Treated with Secukinumab in Real World? – German Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-do-tnf-alpha-inhibitors-in-medical-history-affect-patient-reported-outcomes-and-retention-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-treated-with-secukinumab-in-real-world-german-observational/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-do-tnf-alpha-inhibitors-in-medical-history-affect-patient-reported-outcomes-and-retention-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-treated-with-secukinumab-in-real-world-german-observational/
