Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster I: Inflammatory Arthritis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: MRI of the sacroiliac joints (SIJs) is widely used for diagnosing and monitoring patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA). However, local radiologists might be less familiar with assessing MRIs in SpA potentially leading to misinterpretations affecting the final diagnosis. Our aim was to compare assessments of SIJ MRIs in local MRI reports from routine care in 5 European countries with re-reads by central experts in patients with a diagnosis of axial SpA (axSpA) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) to estimate the extent of over- or underreporting of features and misclassification.
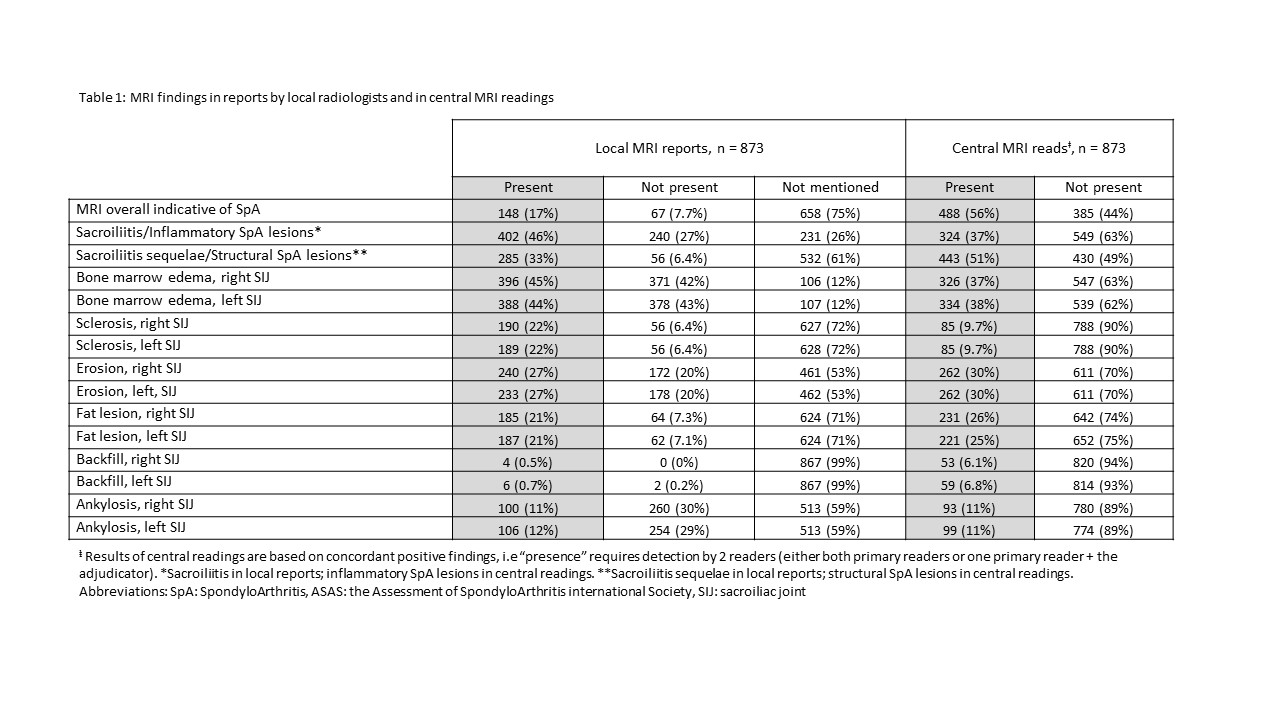
Methods: We included patients with a diagnosis of axSpA or PsA in a clinical patient registry from one of 5 European countries (DANBIO, Denmark; SCQM, Switzerland; ATTRA, Czech Republic; biorx.si, Slovenia; ICEBIO, Iceland; all participating in the EuroSpA Research Collaboration Network) with an available MRI of the SIJs and a corresponding local MRI report. MRIs were collected and read centrally by 2 experienced readers, blinded to clinical (except sex and age) and other imaging information. Readers registered whether the MRI was overall indicative of axSpA. In case of disagreement, MRIs were adjudicated by an experienced musculoskeletal radiologist (member of the ASAS/EULAR MRI group). Furthermore, presence/absence of inflammatory and structural lesions (details in Table 1) were registered. Similar information was extracted from the local reports. Findings in local reports and central assessments were compared using central reads as reference standard.
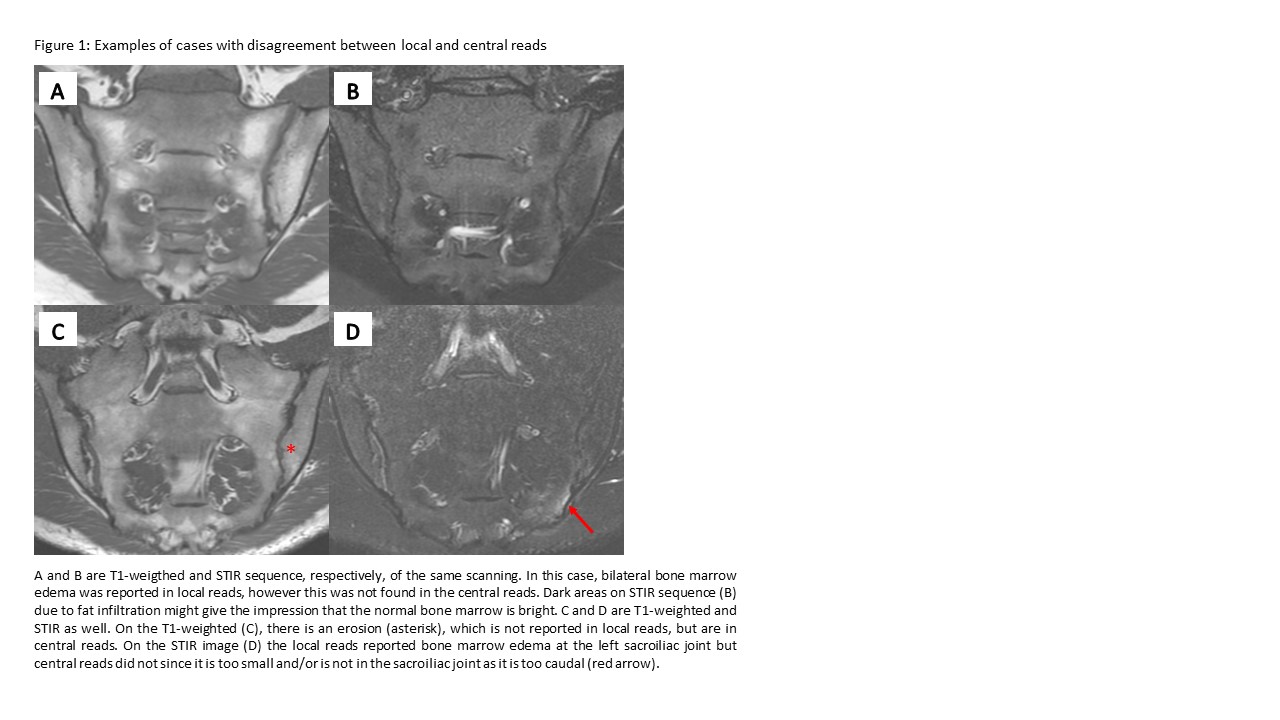
Results: Overall, 873 patients with an MRI of the SIJs and a corresponding local MRI report were included; mean age 37.9 years, 475 (54%) male and 704/169 diagnosed with axSpA/PsA (Table 1). Sacroiliitis/inflammatory SpA lesions were reported more often in local vs central reads (46% vs 37%). Sacroiliitis sequelae/structural SpA lesions were reported less often in local vs central reads (33% vs 51%). In 17% of cases, local reads explicitly reported if the MRI was overall indicative of axSpA or not. On lesion level, bone marrow edema (BME) was the most frequent lesion judged present, both in local and central reads (right/left joint 45%/44% vs 38%/37%, respectively), followed by erosion (27%/27% vs 30%/30%). Compared with central reads, local reads tended to overestimate presence of BME and sclerosis, underestimate/not assess backfill, while the frequency of erosions, fat and ankylosis was similar. Figure 1 shows examples with disagreement.
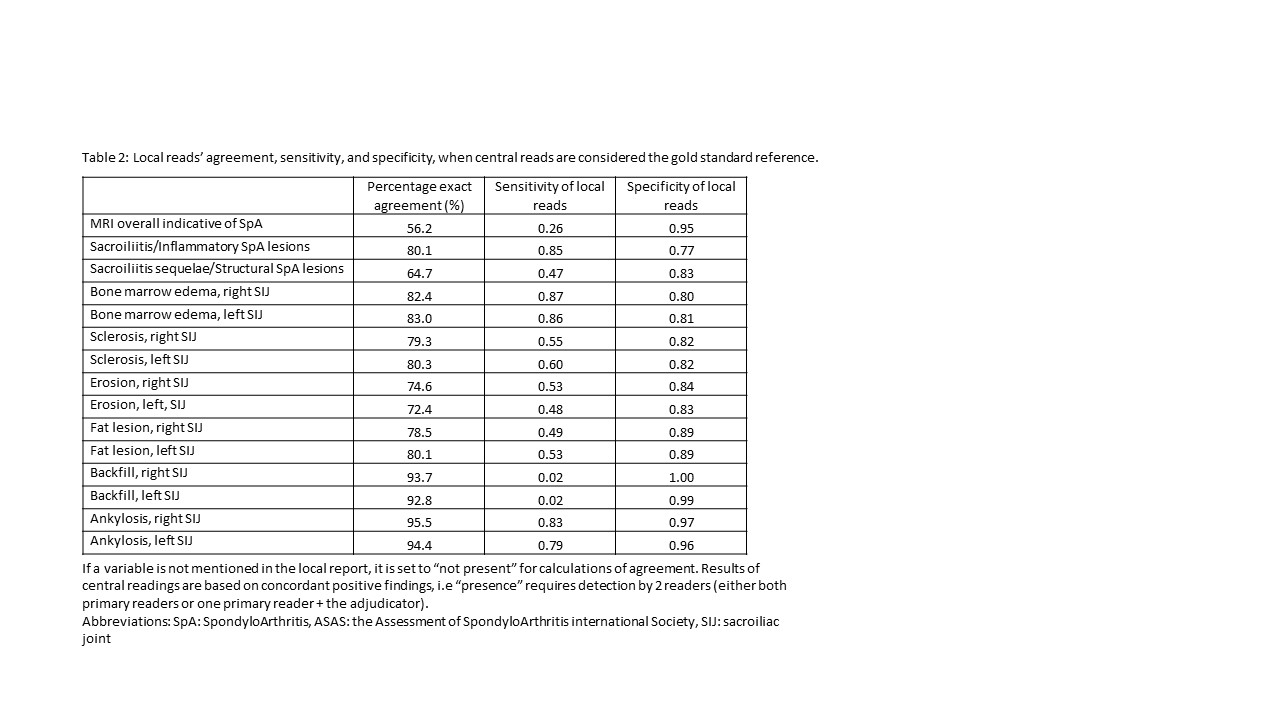
The sensitivity and specificity of local reads were 0.85 and 0.78 for sacroiliitis/inflammatory SpA lesions, and 0.48 and 0.83 for sacroiliitis sequelae/structural SpA lesions, respectively (Table 2). For individual lesions, the sensitivity of local reads was highest for BME and ankylosis, followed by sclerosis. The specificity of local reads was ≥0.80 for all lesions.
Conclusion: This large European real-world study overall showed moderate agreement between local and central reads, but also demonstrated that local radiologists tend to overestimate inflammatory lesions and underestimate structural lesions in routine care SIJ MRIs. This advocates for further training of local radiologists to optimize the diagnostic accuracy of MRI in SpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hadsbjerg A, Krabbe S, Vladimirova N, Ciurea A, Bubova K, Gregová M, Nissen M, Moeller B, Micheroli R, Pedersen S, Zavada J, Snoj Z, Pintaric K, Gudbjornsson B, Rotar Z, Eshed i, Sudol-Szopinska I, Gosvig K, Diekhoff T, Lambert R, de hOoge M, Elmo H, Hetland M, Oernbjerg L, Ostergaard M. How Accurate Are Assessments by Local Radiologists of Sacroiliac Joint MRIs in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis in Routine Clinical Practice?- Evidence from 873 Patients in Five European Countries [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-accurate-are-assessments-by-local-radiologists-of-sacroiliac-joint-mris-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-in-routine-clinical-practice-evidence-from-873-patients-in-five-europea/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-accurate-are-assessments-by-local-radiologists-of-sacroiliac-joint-mris-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-in-routine-clinical-practice-evidence-from-873-patients-in-five-europea/