Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The association between systemic sclerosis (SSc) skin histology and clinical findings is not fully characterized. In two SSc trials, we developed a scoring system to evaluate histologic change. The purpose of this study is to determine (1) the reliability of our histology scores and (2) if histologic features correlate with clinical findings.
Methods: Skin biopsies were assessed from patients enrolled in Nilotinib (n=7) and Belimumab (n=18) trials. Our skin histology scoring approach, developed with dermatopatholgist (CM) consultation, includes skin thickness (epidermis to subcutis), follicle count, and semi-quantitative (0-3) assessment of infiltrate, collagen density, alpha-smooth muscle actin (aSMA) and CD34 staining intensity, and global histologic severity. Blinded to prior scores, a dermatopathogist (CM) and second pathologist (YZ), oriented to our approach, analyzed a sub-sample of biopsies. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated for inter- and intra-rater reliability. Spearman correlations were used to correlate histology scores (baseline, 52-weeks post-treatment, and overall) and clinical variables (local and total modified Rodnan skin score (MRSS), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), c-reactive protein (CRP), 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36), and physician global assessment (PGA)).
Results: 56 biopsies were analyzed from 26 diffuse SSc patients (median (IQR) disease duration 0.8 (0.54) years). Most were female (77%), Caucasian (73%), and RNA polymerase III positive (58%). Median (IQR) baseline MRSS was 25 (9). Reliability was excellent (ICC≥0.90) for follicle count and intra-rater CD34; good (0.75< ICC >0.90) for thickness, inter-rater CD34, intra-rater collagen density, and intra-rater global score; and moderate (0.5< ICC >0.75) for infiltrate, intra-rater collagen density, aSMA, and inter-rater global score.
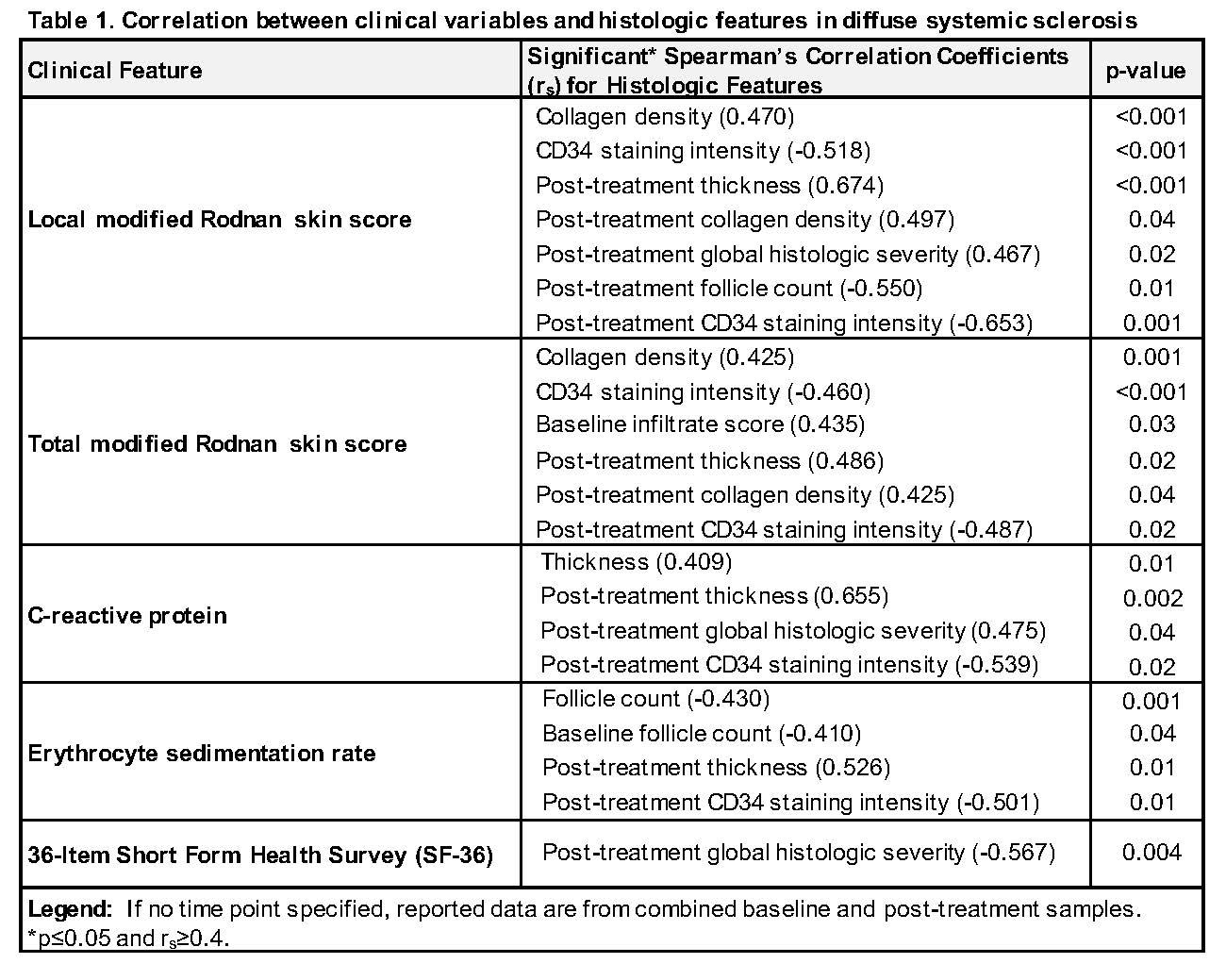
Histologic scores correlated moderately with MRSS, ESR, CRP, and SF-36 (Table 1). Post-treatment local MRSS correlated with thickness (r=0.674, p< 0.001), collagen density (r=0.497, p=0.04), global histologic severity (r=0.467, p=0.02), follicle count (r=-0.550, p=0.01), and CD34 stain intensity (r=-0.653, p=0.001). However, local MRSS did not correlate with infiltrate score or PGA and weakly correlated with aSMA stain intensity (r=0.337, p=0.01). In stratified analysis, collagen density correlated with local MRSS in patients with low (< 1) but not high (≥1) infiltrate score (r=0.578, p< 0.001 vs. r=0.253, p=0.256). Total MRSS correlated with collagen density (r=0.425, p=0.001) and CD34 stain intensity (r=-0.460, p< 0.001). Total MRSS and thickness correlated positively in patients with low infiltrate (r=0.326, p=0.05) but negatively in patients with high infiltrate (r=-0.456, p=0.03).
Conclusion: Our scores demonstrate moderate to excellent reliability, thus have potential to be used across centers. Histologic features correlate with MRSS, inflammatory markers, and patient reported outcomes. However, infiltrate does not correlate with MRSS and confounds the correlation of MRSS with collagen density and thickness. This supports further study of skin histology as an SSc outcome measure.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Showalter K, Magro C, Orange D, Zhang Y, Agius P, Finik J, Spiera R, Gordon J. Histologic Features Correlate with the Modified Rodnan Skin Score, Serum Inflammatory Markers, and Patient Reported Outcomes in Patients with Early, Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/histologic-features-correlate-with-the-modified-rodnan-skin-score-serum-inflammatory-markers-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/histologic-features-correlate-with-the-modified-rodnan-skin-score-serum-inflammatory-markers-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/