Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory arthropathy associated with cardiovascular abnormalities. The echocardiography is a non-invasive tool useful in the detection of cardiac abnormalities, which may be the only manifestation of cardiac involvement preceding a global dysfunction. However, echocardiographic differences between PsA patients, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and controls have not yet been well described. Therefore our objective was to analyze the echocardiographic parameters in PsA patients and to compare them with RA patients and controls.
Methods: This case-control study included thirty-six patients (nineteen in each group), aged 40-75 years, with PsA and RA who fulfilled the CASPAR (Classification criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis) and ACR/EULAR 2010 classification criteria, respectively, matched by age, gender and comorbidities with nineteen healthy controls. Exclusion criteria were a poor echocardiographic window, patients with a previous atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular accident or peripheral arterial disease), and pregnancy. A Transthoracic echocardiogram was performed and reviewed by 2 board-certified cardiologists, in all study subjects. Comparisons were done with X2, Kruskall Wallis or ANOVA.
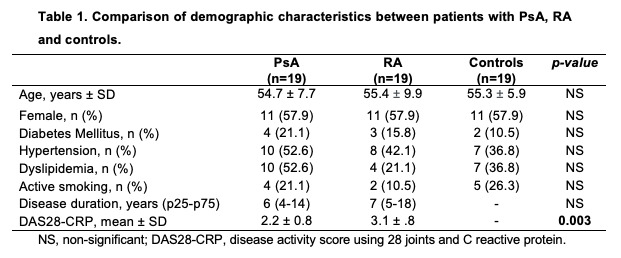
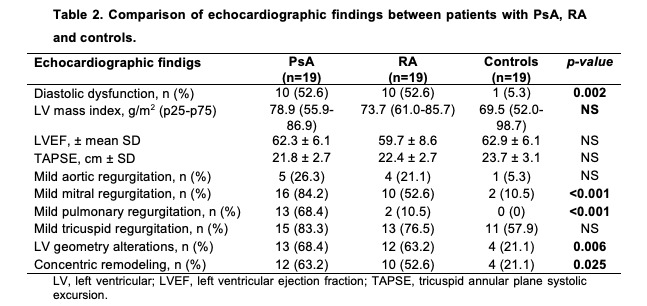
Results: There were not any statistically significant differences found in the demographic characteristics (Table 1). When comparing echocardiographic findings a statistically significant difference was found in the prevalence of diastolic dysfunction, being more prevalent in PsA and RA patients compared with controls (52.6% vs 52.6% vs 5.3%, p=0.002), likewise the presence of mild mitral valve regurgitation was higher (84.2% vs 53.6% vs 10.5%, p=0.001) and mild pulmonary valve regurgitation (68.4% vs 10.5% vs 0%, p=0.001). Prevalence of abnormal left ventricular geometry was higher in PsA and RA patients than controls (68.4% vs 63.2% vs 21.1%, p=0.006). Results are shown in Table 2.
Conclusion: This study shows the high prevalence of echocardiographic alterations in PsA patients compared to the general population, of the same magnitude as patients with RA. We emphasize the value of an echocardiogram for a complete cardiovascular evaluation and early detection of cardiac abnormalities in these patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rodriguez-Romero A, Azpiri-Lopez J, Galarza-Delgado D, Colunga-Pedraza I, Guajardo-Jauregui N, Loya-Acosta J, Meza-Garza A, Cardenas-de La Garza J, Lugo-Perez S, Andrade-Vazquez C, De Leon-Yañez A. Higher Prevalence of Echocardiographic Abnormalities in Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Compared to Controls [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-prevalence-of-echocardiographic-abnormalities-in-psoriatic-arthritis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-compared-to-controls/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-prevalence-of-echocardiographic-abnormalities-in-psoriatic-arthritis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-compared-to-controls/