Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Antibodies to citrullinated and other modified proteins play a critical role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The prevalence and degree of multi-site peptide reactivity of these antibodies in patients classified as “seronegative” is unclear.
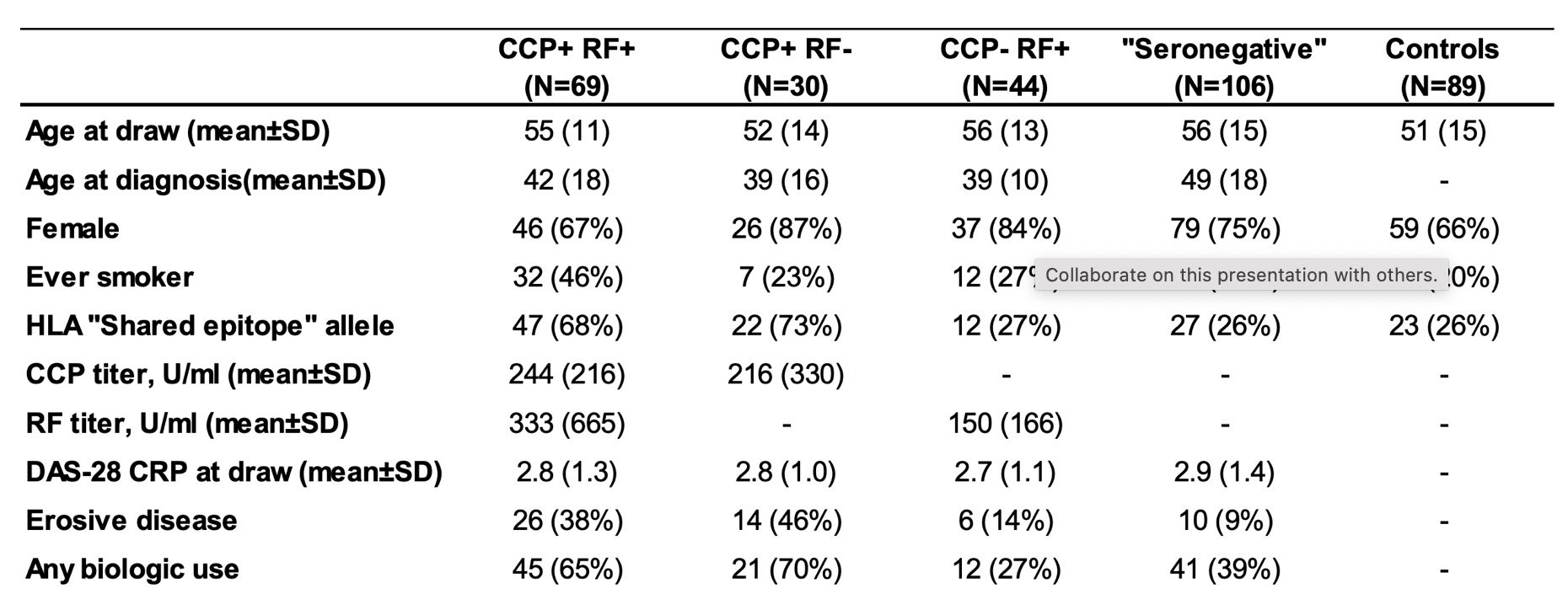
Methods: An ultra-dense peptide array consisting of two million sequences was manufactured using photolithography. The peptide library was random but biased to include the sequences of filaggrin, fibrinogen, vimentin, collagen II, enolase, histones, and 14-3-3 eta with native, citrullinated, and carbamylated epitopes. A machine-learning algorithm identified 314 RA-specific peptides from a testing cohort of 140 RA patients, 480 healthy controls, and 136 disease controls based on signal-to-noise ratio. A validation cohort of 249 patients with RA (Table 1) was then analyzed on the basis of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) and rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity.
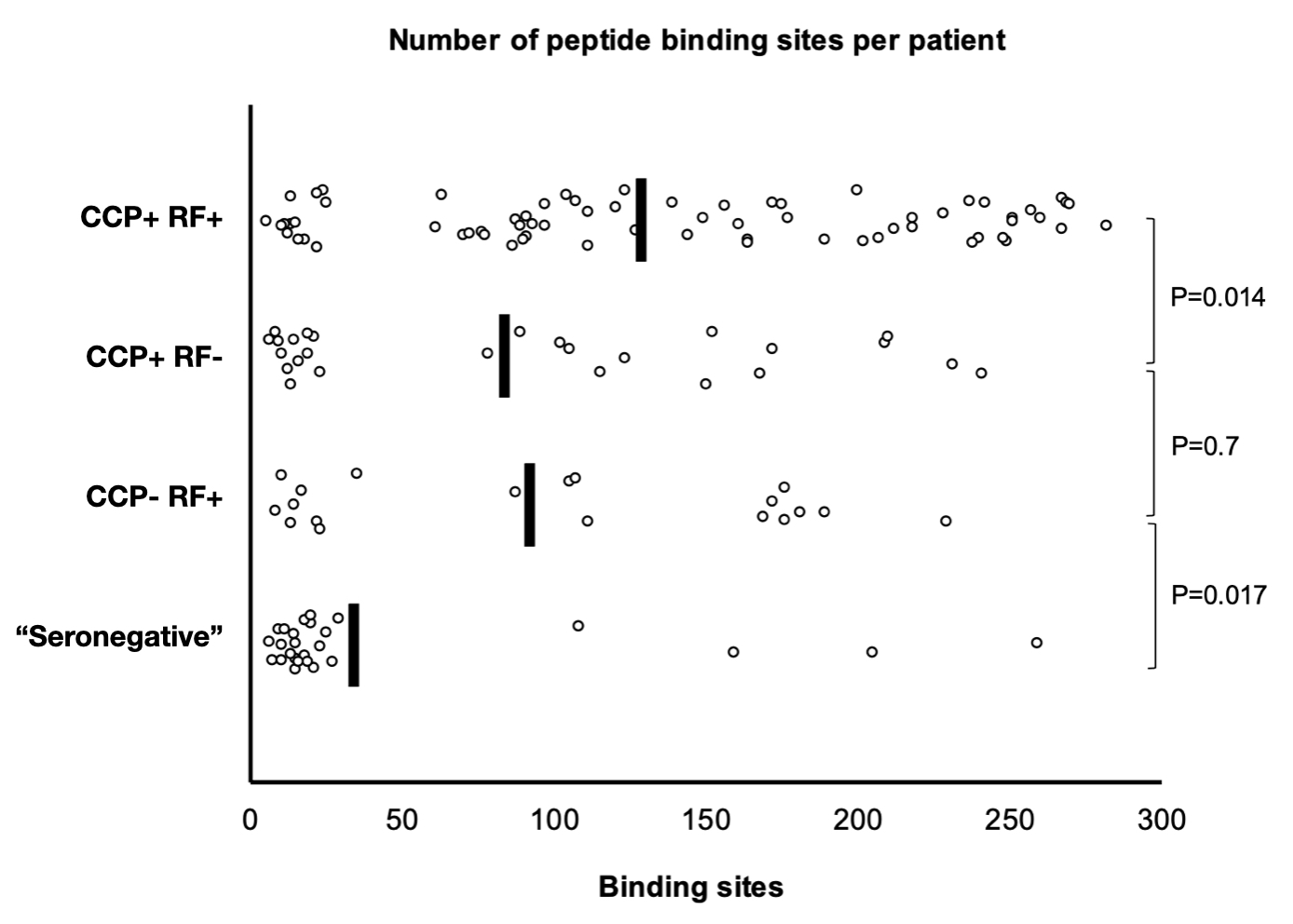
Results: The validation cohort included 106 patients (43%) who were negative for both CCP and RF (“seronegative”). Within this group, 25% had antibody binding to at least one site in the library of 314 peptides, compared with 98% of patients in the CCP and RF positive group (p< 0.0001). Only one control patient (1%) had any positive result. A heat-map of peptide reactivity is shown in Figure 1. Multi-site reactivity was more limited among the “seronegative” patients, with only 4% having antibody binding to at least 50 sites, compared to 80% in the CCP and RF positive group (p< 0.0001) (Figure 2). There was no significant difference in the ratio of antibodies to carbamylated vs. citrullinated proteins between “seronegative” and CCP positive patients. The presence of any HLA shared epitope allele was associated with positivity in this assay, with odds ratios of 3.56 (95%CI 1.99-6.37) for any binding and 4.22 (95%CI 2.22-6.37) for binding to greater than 50 sites.
Conclusion: This high-throughput assay demonstrated the presence of modified protein antibodies in a subset of “seronegative” patients, though multi-site reactivity was rare relative to CCP positive patients. This suggests that the mechanisms driving polyreactivity are features of seropositive RA and “seronegative” disease may have unique pathogenic features even when autoantibodies are present.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Richter M, Krishnamurthy H, Posso S, Carlin J, Buckner J. High-throughput Testing for Modified-protein Antibodies in Patients Diagnosed with “Seronegative” Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-testing-for-modified-protein-antibodies-in-patients-diagnosed-with-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-testing-for-modified-protein-antibodies-in-patients-diagnosed-with-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis/