Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Better prediction of treatment response to biologics in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) would contribute to optimal individualized treatment. Clinical data suggest that the response of RA patients to treatment with golimumab is much lower among those who switched from adalimumab than among those who switched from etanercept.1 To elucidate the mechanism behind this difference in response to sequential biologic treatment, we examined the effect of TNF inhibitors on ex-vivo cytokine production.Methods:
In a prospective longitudinal cohort study, blood samples were obtained from patients at baseline (before start biologic). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated, washed and pre-incubated for 1 hour with the therapeutic in-vivo concentration of adalimumab, etanercept or golimumab and stimulated for 24 hours with heat killed Candida albicans or Pam3Cys. Cytokine concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα were determined by ELISA. Absolute changes in cytokine levels after inhibition by each TNF inhibitor were calculated and analyzed by means of Spearman rank correlations (rs).Results:
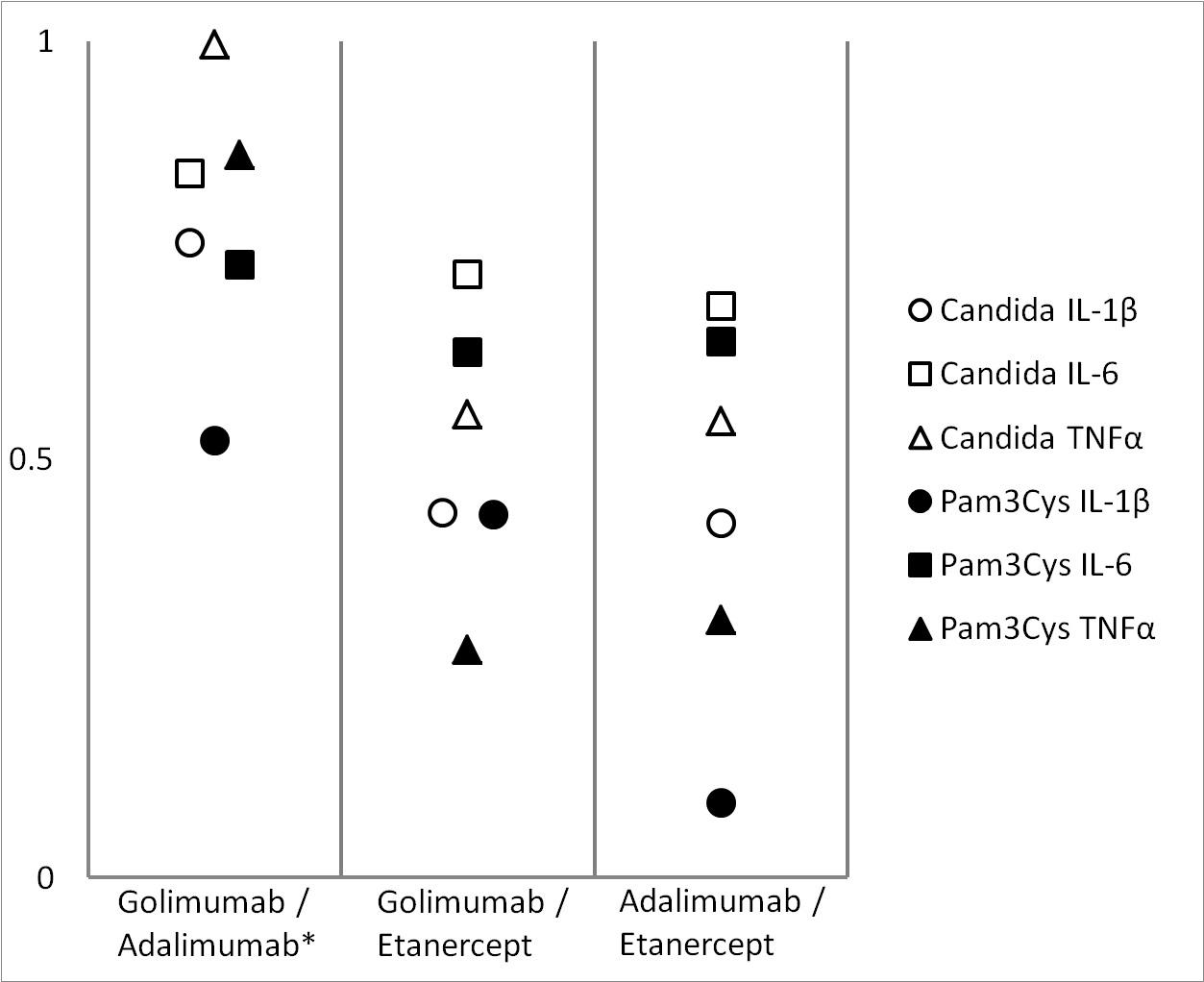
Ex-vivo cytokine profiling was performed in 71 patients: 66% female, age (mean ± SD): 58 ± 11 years, disease duration (mean ± SD): 10 ± 8 years. Golimumab, adalimumab and etanercept significantly (p<0.01) decreased Candida albicans-induced cytokine production of IL-1β and IL-6 and Pam3Cys-induced cytokine production of IL-6. In contrast to etanercept, golimumab and adalimumab decreased the concentration of TNFα below the detection limit (Figure 1). Absolute changes in cytokine levels after inhibition by golimumab or adalimumab were all strongly correlated (rs 0.52 – 0.99, p<0.001). These correlations were much lower or non-significant between etanercept and either golimumab or adalimumab (Figure 2).Conclusion: High similarity between ex-vivo inhibited cytokine profiling by golimumab and adalimumab provides a putative explanation for the previously found inferior treatment response to golimumab after adalimumab failure in RA. This suggests that RA patients who are non-responsive to adalimumab should preferably not switch to golimumab and vice versa. References: 1. Smolen JS, Kay J, Matteson EL, et al. Insights into the efficacy of golimumab plus methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis who discontinued prior anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy: post-hoc analyses from the GO-AFTER study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73(10):1811-8.
Figure 1 Ex-vivo cytokine production. Data are presented as mean+SEM.* p<0.01. Figure 2 Spearman rank correlations of cytokine profiles.* all correlations p<0.001.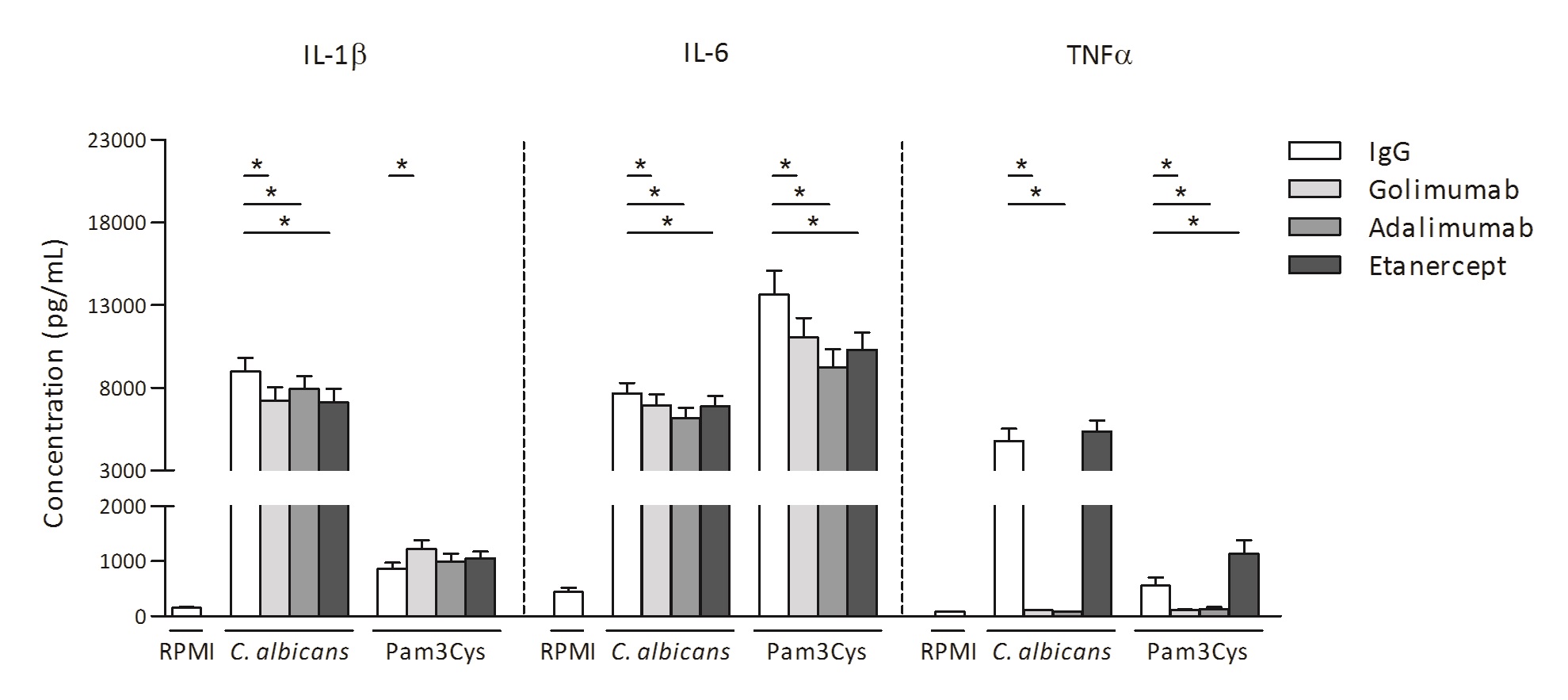
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tweehuysen L, Schraa K, Netea MG, van den Hoogen FHJ, Joosten LAB, den Broeder AA. High Similarity Between Ex-Vivo Inhibited Cytokine Profiling By Golimumab and Adalimumab As a Putative Explanation for Inferior Treatment Response to Golimumab after Adalimumab Failure in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-similarity-between-ex-vivo-inhibited-cytokine-profiling-by-golimumab-and-adalimumab-as-a-putative-explanation-for-inferior-treatment-response-to-golimumab-after-adalimumab-failure-in-rheumatoid-a/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-similarity-between-ex-vivo-inhibited-cytokine-profiling-by-golimumab-and-adalimumab-as-a-putative-explanation-for-inferior-treatment-response-to-golimumab-after-adalimumab-failure-in-rheumatoid-a/

