Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2377–2436) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab, a BAFF inhibitor, is an effective treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but biomarkers predicting treatment response remain elusive. We aimed to identify protein signatures associated with clinical response to belimumab.
Methods: We conducted a prospective observational study of patients with SLE initiating belimumab treatment. Samples were available at baseline (prior to treatment initiation; T0; Nf69), month 3 (T1; Nf63), and month 6 (Nf69). Complete clinical data were available for 64 patients, who were finally included for analysis. Using NUcleic acid Linked Immuno-Sandwich Assay (NULISA) technology (1), we simultaneously measured 250 protein markers at each timepoint in normalised protein quantification units (NPQ). Clinical response was defined as a ≥4-point reduction in SLEDAI-2K score at T2. Mixed-effects models were employed to identify proteins associated with response and temporal changes, with false discovery rate (FDR) correction.
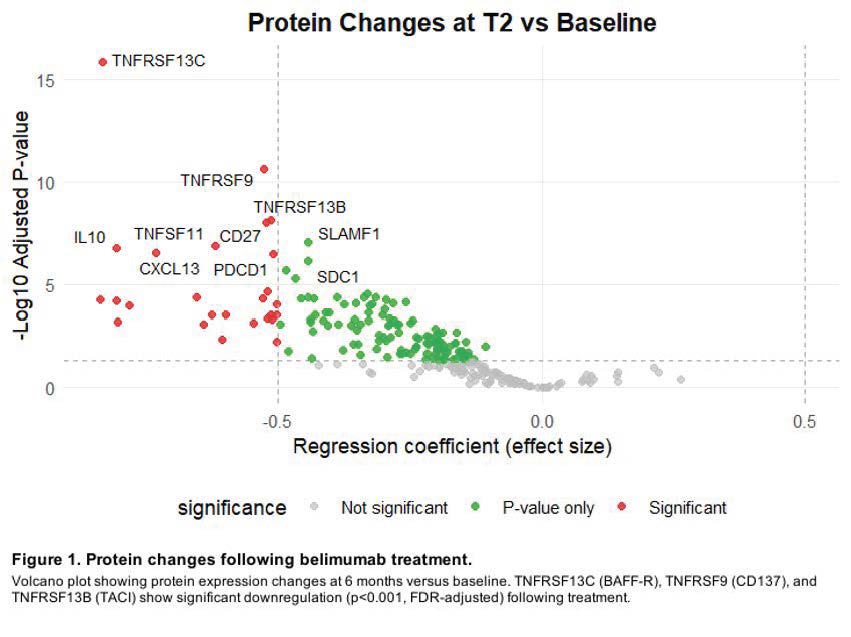
Results: The main effects analysis demonstrated a strong modulation of BAFF pathway proteins at T2, with TNFRSF13C (BAFF-R) showing significant reduction from baseline to month 6 (NPQ: T0 13.059, T2 12.220; p < 0.001). Similar decreases were observed in TNFRSF9 (CD137; NPQ: T0 11.269, T2 10.704; p < 0.001) and TNFRSF13B (TACI; NPQ: T0 12.713, T2 12.183; p < 0.001) with FDR-adjusted values (figure 1). Additionally, interaction analysis revealed distinct temporal patterns between responders and non-responders, with MMP9 and VEGFD showing significant treatment-response interactions at T2 (FDR-adjusted p=0.040 for both) (figure 2).
Conclusion: This high-resolution proteomic analysis provides molecular validation of belimumab mechanism of action through BAFF pathway modulation and identifies novel protein signatures associated with treatment response. The technical capabilities of NULISA enabled detection of both on-target drug effects as well as less well-described effects on other molecular targets, demonstrating its utility for biomarker discovery in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tsoi A, Nikolopoulos D, Sherina N, Parodis I. High-Resolution Proteomic Profiling Validates BAFF Pathway Modulation and Reveals Novel Biomarker Signatures in Belimumab Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-resolution-proteomic-profiling-validates-baff-pathway-modulation-and-reveals-novel-biomarker-signatures-in-belimumab-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-resolution-proteomic-profiling-validates-baff-pathway-modulation-and-reveals-novel-biomarker-signatures-in-belimumab-treatment/

.jpg)