Session Information
Session Type: ACR Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Over the last decade, the disease modifying effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Tumor Necrosis Factor inhibitors (TNFi) have resulted in conflicting studies. No study has examined their relationship longitudinally addressing both NSAID and TNFi use. The objective of this study was to explore the direct and interactive effects of NSAIDs and TNFi on radiographic progression in Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS).
Methods: We included 527 patients meeting the modified New York criteria in a prospective cohort with at least 2 years of clinical and radiologic follow up. Progression was defined longitudinally, with >=2 modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) unit increase in 24 months. To avoid ceiling effects, patients with high mSASSS scores were censored when they could not meet the definition of progression over the next follow up period. We used a longitudinal mixed-effects multivariable logistic regression model to determine the associations of TNFi use and NSAID use with radiographic progression.
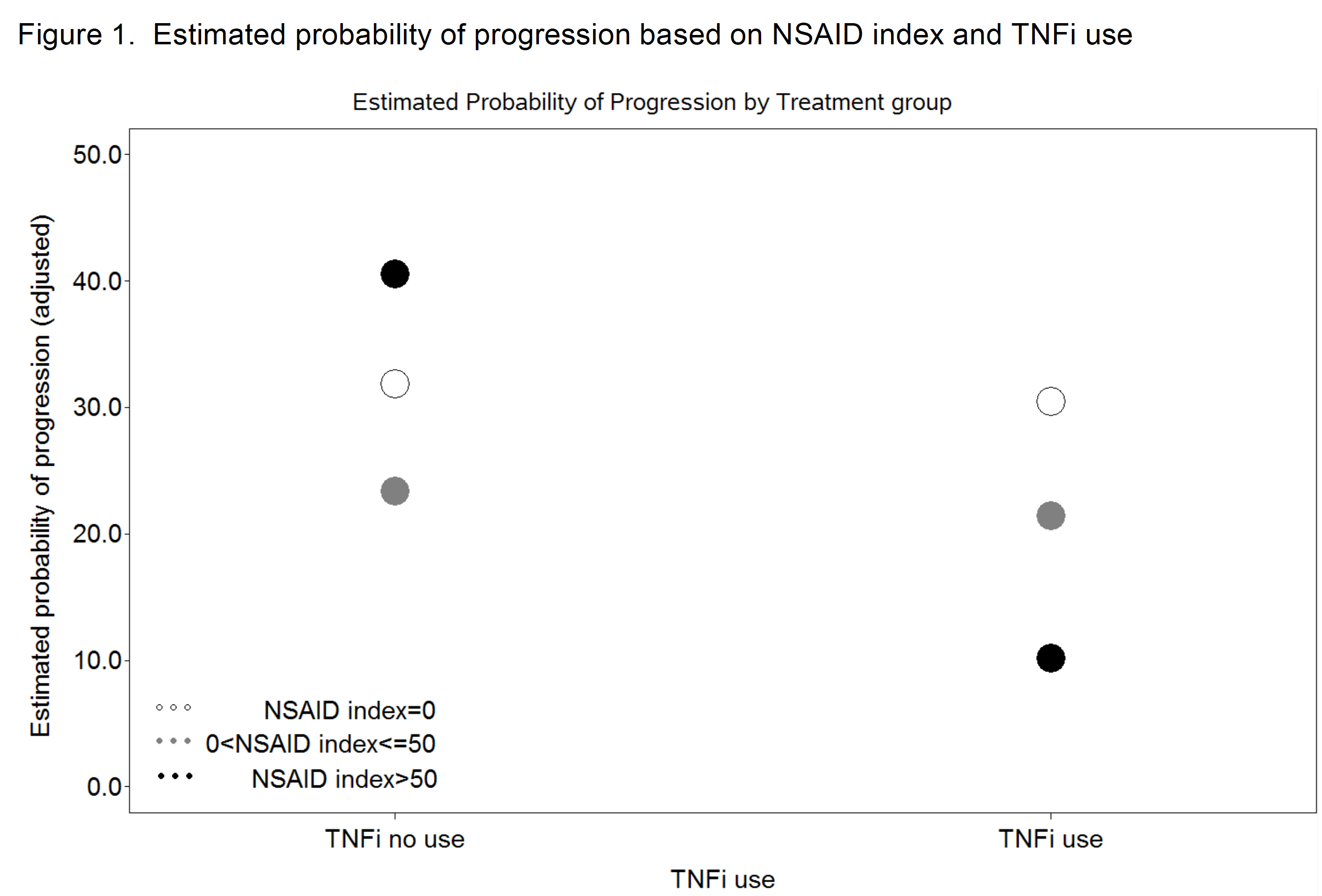
Results: Of the 527 patients, 75.7% were male with a baseline mean (SD) age and disease duration of 42.5(13.28) and 18.45(13.13) years respectively. The baseline median mSASSS was 5.36 [IQR 0.00, 28.00] and patients were followed for a mean of 4.29(2.5) years. NSAIDs and TNFi were used in 78.0% and 58.4% of patients respectively. Of 1413 visits included in this analysis, 38%, 29% and 23% had an NSAID index of 0, >0 & =<50, and >50 respectively. Multivariable results showed significant interaction between TNFi and NSAIDs (p=0.034) indicating lower progression for only those using TNFi and high dose NSAIDs [index >50]; (OR=0.17, 95%CI 0.05, 0.55, p=0.003).
Conclusion: Use of NSAIDs and TNFi in AS patients has a synergic effect in slowing radiographic progression with the greatest effect in those using both high-dose NSAIDs and TNFi. 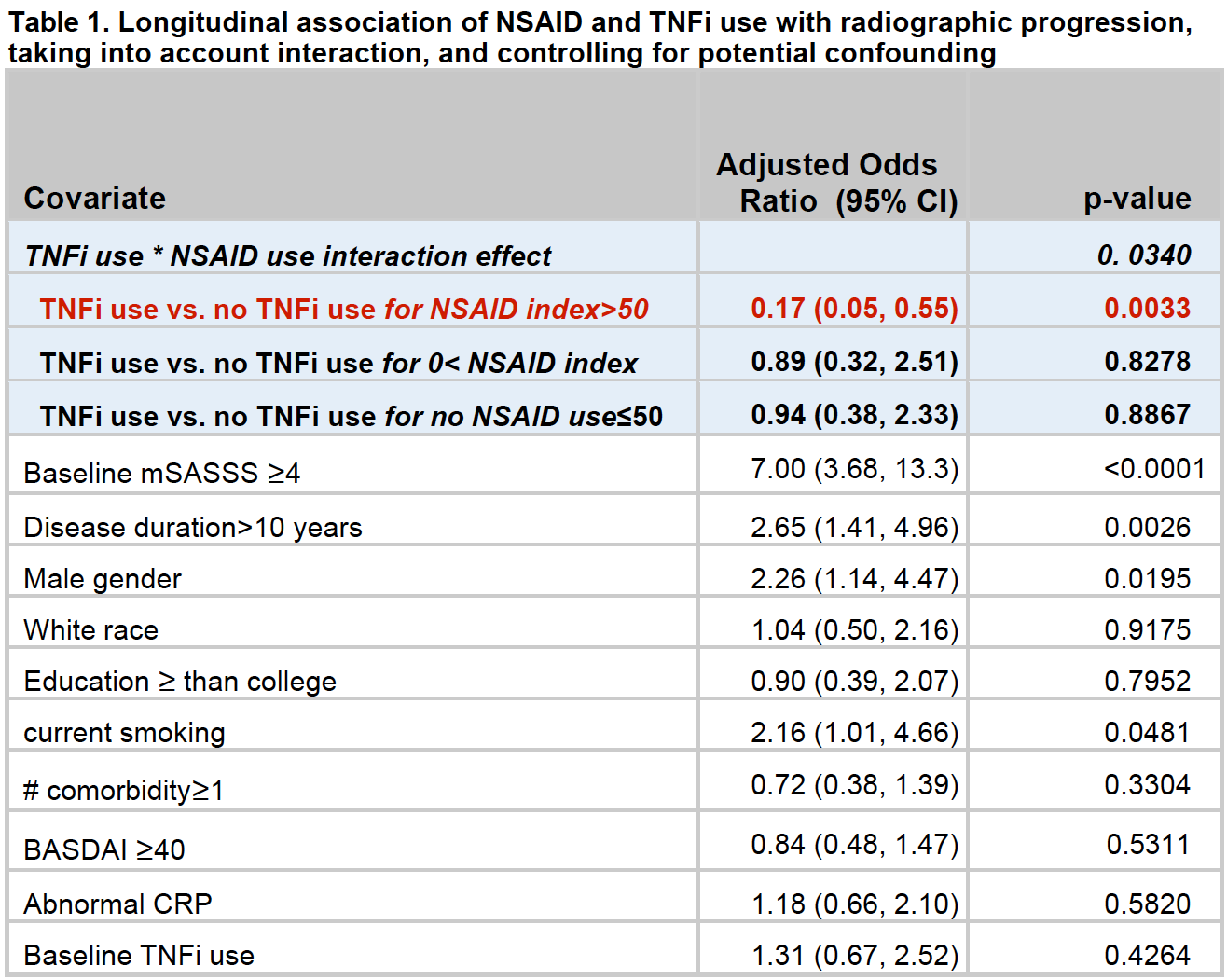
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gensler LS, Reveille JD, Lee M, Learch T, Brown M, Rahbar MH, Weisman M, Ward M. High Dose Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Use Results in Less Radiographic Progression in Ankylosing Spondylitis – a Longitudinal Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-dose-nonsteroidal-anti-inflammatory-drugs-nsaids-and-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-use-results-in-less-radiographic-progression-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-longitudinal-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-dose-nonsteroidal-anti-inflammatory-drugs-nsaids-and-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-use-results-in-less-radiographic-progression-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-longitudinal-analysis/