Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Up to ~60% of SLE patients in North America will develop kidney disease, lupus nephritis (LN), one of the main contributors to disease morbidity and mortality in lupus. Sensitivity to sunlight, which affects >80% of patients, has been reported to provoke LN flares. Despite evidence of neutrophil activation in lupus blood and a pronounced neutrophil proteomic signature in LN urine, the role of neutrophils in lupus nephritis (LN) remains unclear.
Methods: Neutrophils were detected by neutrophil elastase and CD177 IHC. Spatial transcriptomics was performed on class III/IV LN kidneys using Visium 10X. Differential expressed genes (DEGs) between neutrophils (NDN, LDN) and macrophages (MP) were defined using RNAseq data. Spots containing NDNs, LDNs, and MP, their location, and injury pathways associated with their presence, were defined using Variance Adjusted-Mahalanobis to compute scores based on DEGs. Neutrophils and MP were quantified in urine cell pellets collected at DHMC and Johns Hopkins Lupus Centers by deconvolution of DNA methylation data (Illumina).
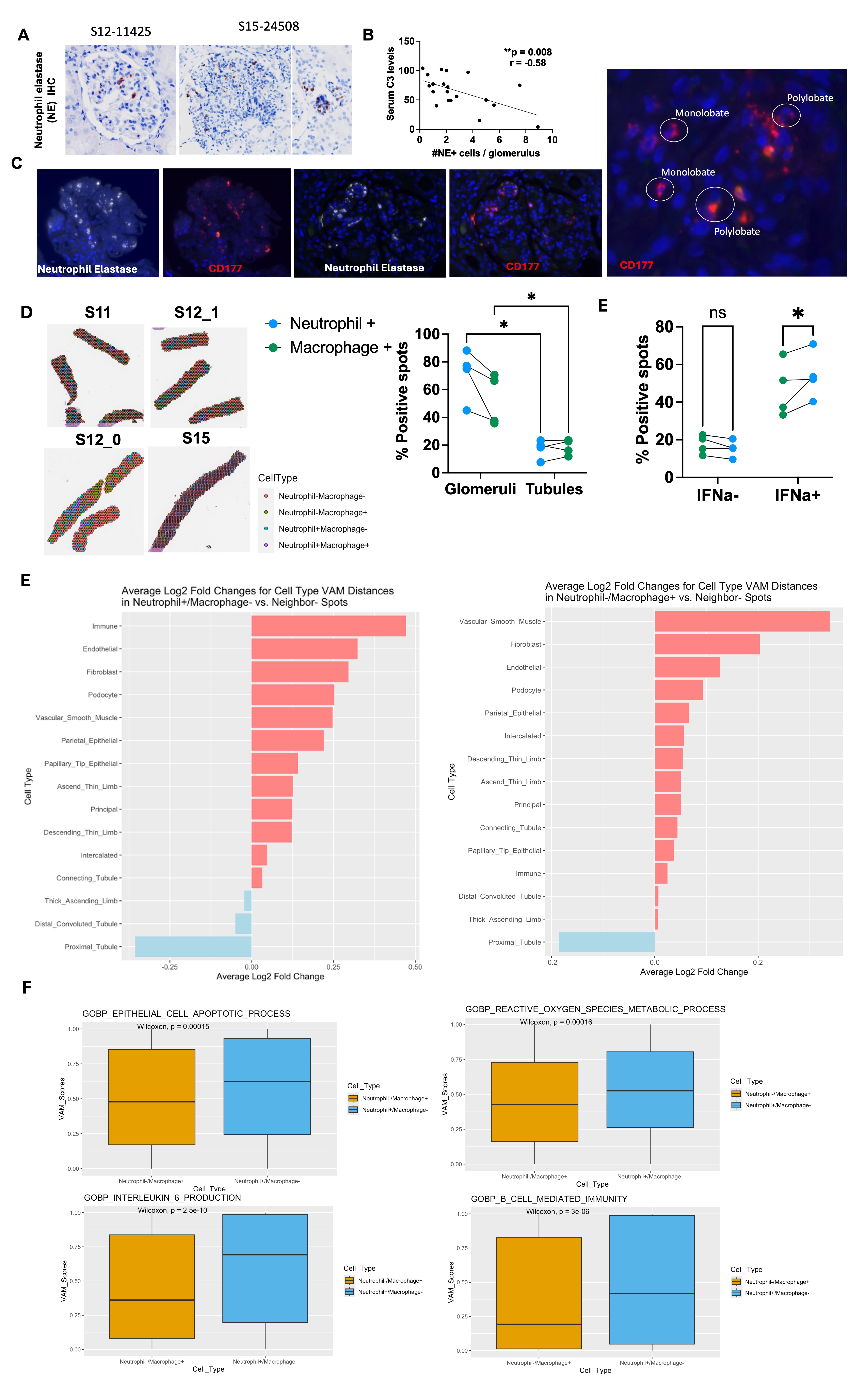
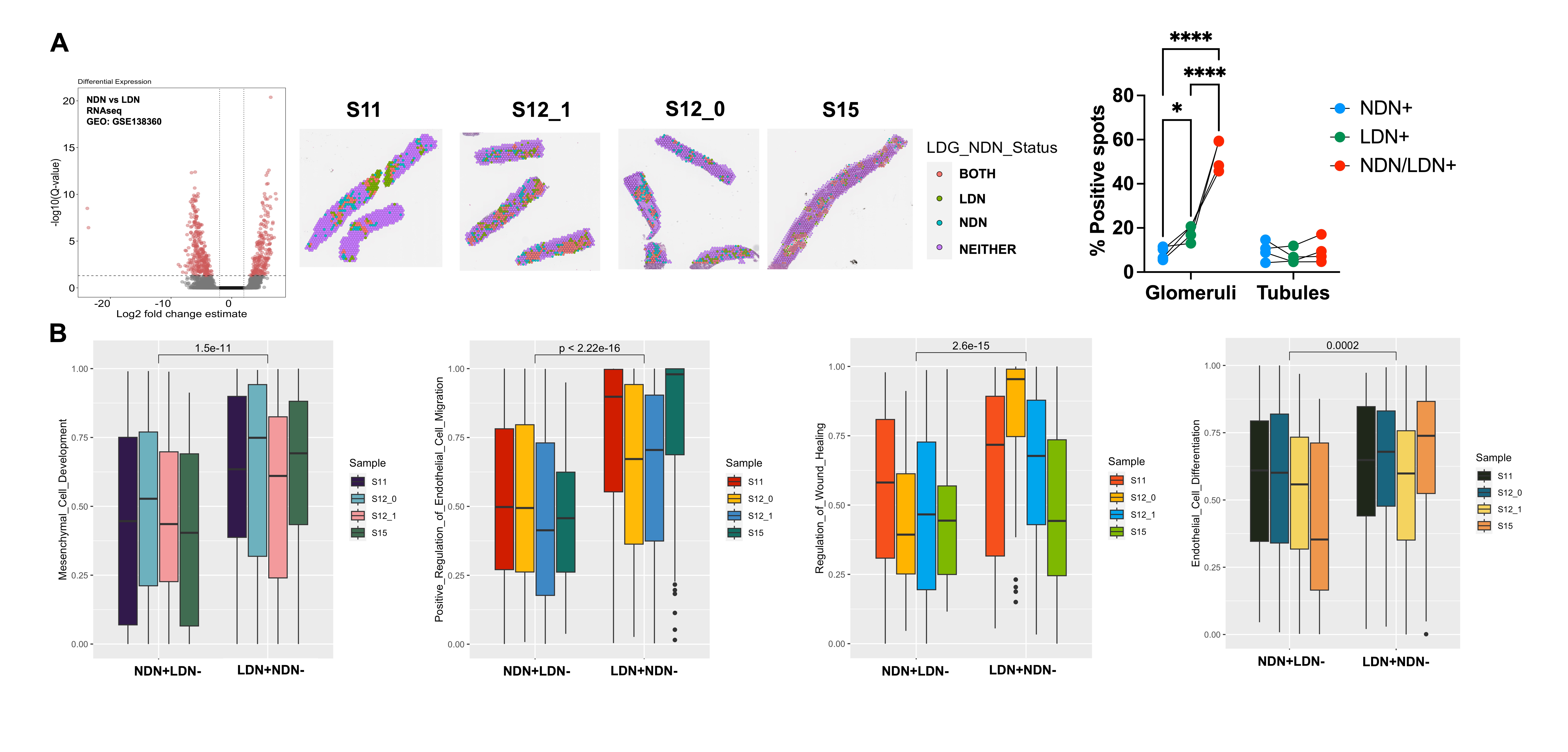
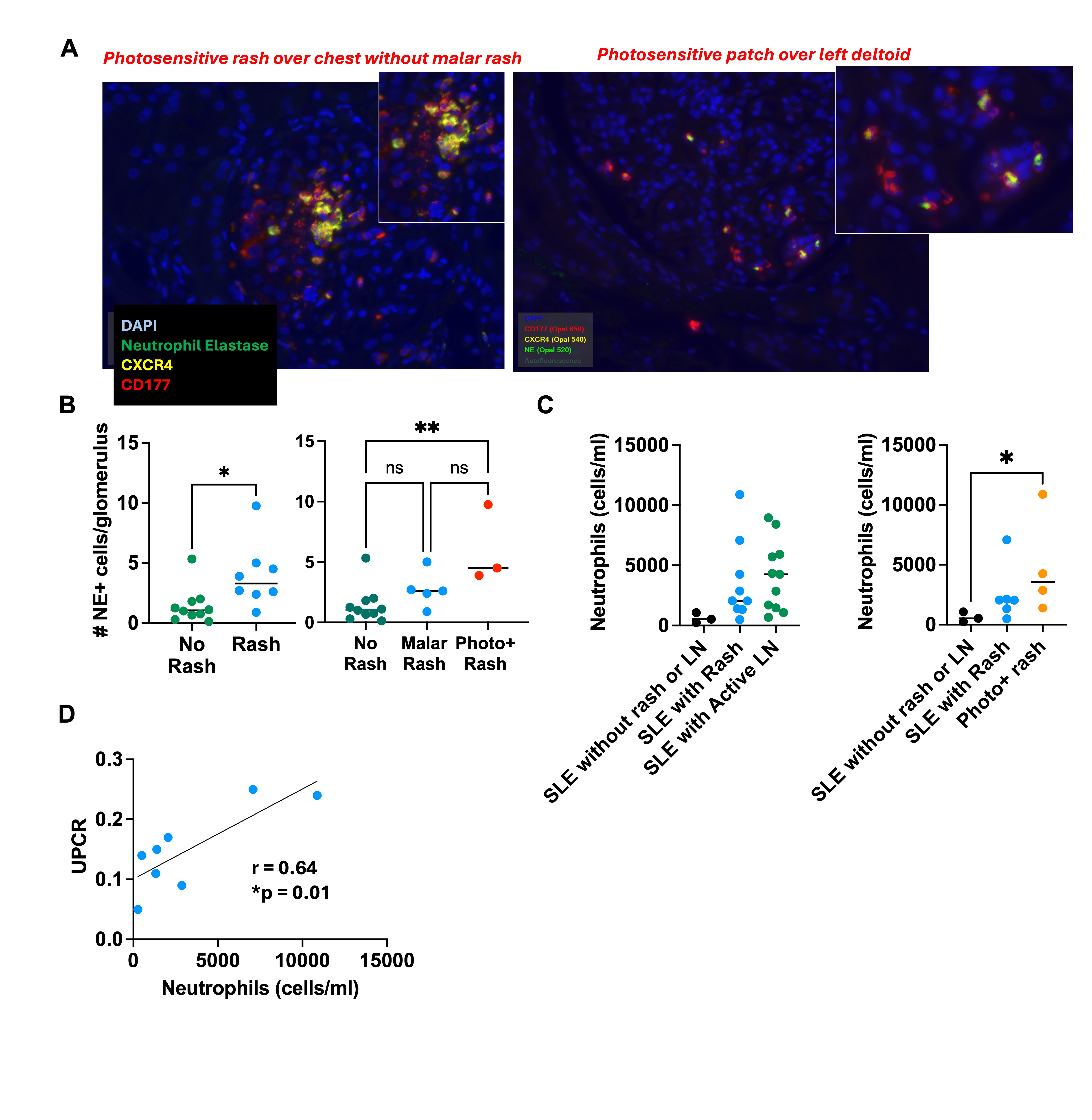
Results: Glomerular neutrophil numbers in LN kidneys inversely correlate with serum C3 (Fig. 1A-B). Neutrophils (NE+CD177+) can be both mono- and poly-lobate (Fig. 1C) and thus likely underestimated by H&E staining. Neutrophils are equally or more represented in LN glomeruli compared to macrophages (Fig. 1D) and are more prevalent in type I interferon positive tissue regions (Fig. 1E). Neutrophils are more concentrated in immune-rich areas of the glomeruli and their presence is associated with increased expression of injury and inflammatory pathways: epithelial cell apoptosis, IL-6 production, ROS metabolism, and B cell Immunity (Fig. 1F). Both normal-density (NDN) and low-density (LDN) neutrophils infiltrated LN glomeruli at comparable levels (Fig. 2A).CXCR4high NDNs are decreased in the blood of LN patients vs. SLE without LN and are enriched among glomerular NDNs. Blood levels of CXCR4high immature (CD10neg) LDN subpopulation are correlated with worse kidney function (lower eGFR). LDN+ spots in LN kidneys have increased expression of renal injury and pro-fibrotic pathways: mesenchymal cell transition, endothelial and epithelial cell migration and differentiation, wound healing (Fig. 2B). Both intra-renal and urinary neutrophils are increased in LN patients with a skin rash at the time of LN flare, particularly in those with a sunlight-triggered rash (photo+,Fig. 3A-C). Urinary neutrophils were increased in SLE patients without LN if they had a malar or photo+ rash at the time of sampling and were associated with increased UPCR.
Conclusion: Neutrophils are abundant in LN glomeruli and urine, demonstrate heterogeneity, and associate with specific pathways of tissue injury, indicative of a pathogenic role. The relationship between high kidney and urine neutrophils and skin rash suggests a neutrophil-mediated communication between the two organs, relevant to sunlight triggered LN flares.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kosarek N, Skydel J, Roy A, Kolling F, Salas L, Burns C, Fava A, Skopelja-Gardner S. Heterogeneous Neutrophil Subsets Infiltrate Glomeruli of Lupus Nephritis Patients and Are Elevated in the Kidneys and Urine of Sunlight-induced Nephritis Flares [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneous-neutrophil-subsets-infiltrate-glomeruli-of-lupus-nephritis-patients-and-are-elevated-in-the-kidneys-and-urine-of-sunlight-induced-nephritis-flares/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneous-neutrophil-subsets-infiltrate-glomeruli-of-lupus-nephritis-patients-and-are-elevated-in-the-kidneys-and-urine-of-sunlight-induced-nephritis-flares/