Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster I: COVID-19 & Vaccination (0084–0117)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Persons with immune mediated Inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) are at increased risk of developing herpes zoster (HZ) and postherpetic neuralgia. In 2018, CDC recommended a highly efficacious ( >90% efficacy) adjuvanted recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV, Shingrix) that was licensed as a two-dose series for prevention of HZ for immunocompetent persons age ≥50 years. In a 2018 national survey, ~2.4% of adults age ≥50 years self-reported receipt of RVZ, but RZV coverage in persons with IMIDs is unknown. We estimated the proportion of adults with selected IMIDs who received RZV vaccination between 2018–2019.
Methods: We used medical claims data from the 2017–2019 IBM® MarketScan® (persons age 50–64 years) and 2017–2019 Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Medicare (persons age ≥65 years) databases to examine RZV vaccination in persons with IMIDs (Rheumatoid Arthritis, RA; Ankylosing Spondylitis, AS; Axial Spondyloarthritis, SpA; Psoriatic Arthritis, PsA; Psoriasis, PsO; Inflammatory Bowel Disease, IBD; Crohn’s Disease, CD; Ulcerative Colitis, UD; Systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE). Vaccine coverage was defined as receipt of ≥1 RZV dose. IMIDs were defined using all 3 of the following criteria: (a) ≥2 outpatient visits for their respective conditions, and (b) ≥1 claim for disease-specific medications, and (c) ≥1 visit to a relevant specialist (rheumatologist for RA, AS, SpA, PsA, SLE; gastroenterologist for IBD, CD, UC; dermatologist for PsO). RZV vaccination was defined using NDC and CPT codes.
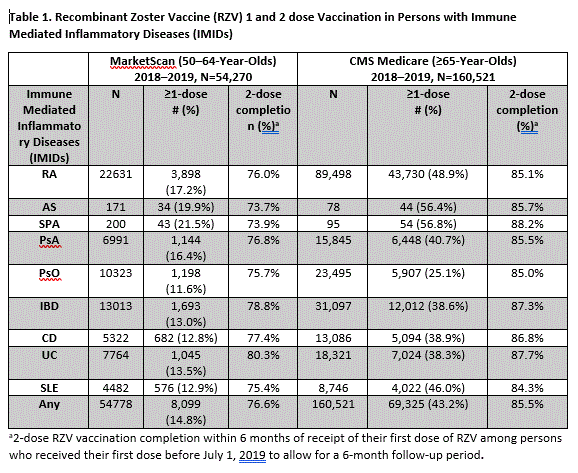
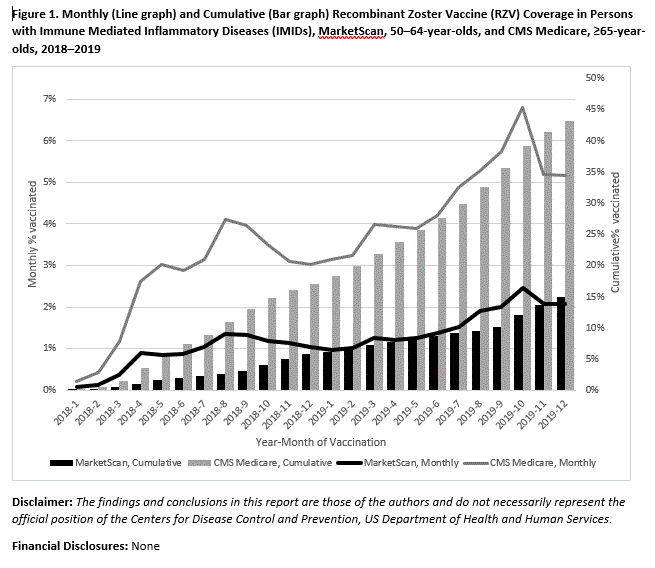
Results: Among the 54,270 MarketScan enrollees with IMIDs, 14.8% received ≥1 dose of RZV, ranging from 11.6–21.5% depending on condition [Table 1]. There were 160,521 Medicare enrollees with IMIDs, among whom 43.2% had received ≥1 dose of RZV, ranging from 25.1–56.8% depending on the condition. Persons with RA, AS, and SPA had the highest proportion vaccinated and persons with PsO had the lowest proportion. Among persons who initiated RZV vaccination, two-dose series completion within 6 months was 76.6% in MarketScan enrollees as compared to 85.5% in Medicare enrollees. Cumulative RZV vaccination and frequency of persons vaccinated monthly steadily increased during 2018–2019 [Figure 1]. When provider specialty prescribing vaccination was known among ≥65 year-olds (90% of vaccine doses), it was most frequently prescribed by physicians in family practice or internal medicine (52.9%) and pharmacists, (14.3%), and uncommonly by rheumatologists, dermatologists, or gastroenterologists (< 1% each).
Conclusion: A substantial proportion of adults age ≥50 years with IMIDs have received RZV vaccination; approximately 15–25% who received the first dose of RZV did not complete the 2-dose series within 6 months. RZV vaccination with at least one dose and 2-dose series completion was higher in ≥65 year-olds than 50–64 year-olds. Coverage in persons with IMIDs and in older ages may be higher than the general or younger populations because of physician recommendation for RZV or patient perception of increased risk for HZ. Additional data on efficacy and safety of RZV vaccination in this population, and vaccine policy recommendations may help to further increase RZV coverage.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leung J, Anderson T, Dooling K, Xie F, Curtis J. Herpes Zoster Recombinant Zoster Vaccination Among Adults Age ≥50 Years with Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases in the United States [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/herpes-zoster-recombinant-zoster-vaccination-among-adults-age-%e2%89%a550-years-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-in-the-united-states/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/herpes-zoster-recombinant-zoster-vaccination-among-adults-age-%e2%89%a550-years-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-in-the-united-states/