Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III (1836–1861)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is a multi-system autoimmune disease, characterized by vasculopathy, fibrosis of the skin and internal organs, and autoimmunity with distinct antibodies. SSc associated complications include interstitial lung disease, pulmonary hypertension, and digital ulcers which lead to substantial morbidity and disability for patients. Secondary to medical and functional limitations, patients with SSc may require considerable healthcare resources resulting in significant economic impact. The purpose of this systematic review is to provide a narrative summary of the economic impact and healthcare resource utilization associated with SSc.
Methods: MEDLINE and EMBASE were searched without language restriction from inception to January 20th, 2021. Studies were included if they provided information regarding overall SSc total, direct, and indirect medical costs including medication, diagnostic test, and assistive devices costs. The cost of SSc subtypes and associated complications was additionally collected. Included observational studies had risk of bias assessments through the Joanna Briggs Institute cross-sectional and case series checklists, and the Newcastle-Ottawa Cohort and Case-Control study scales.
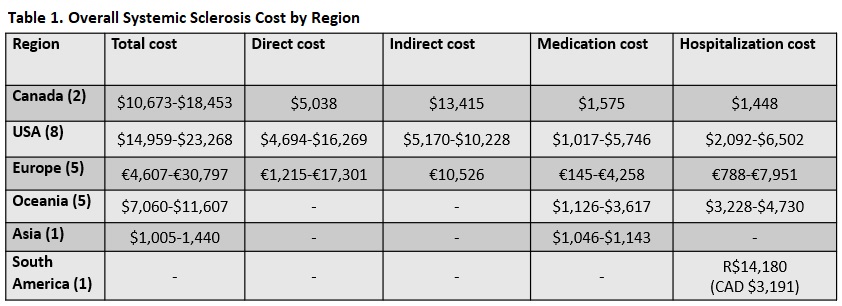
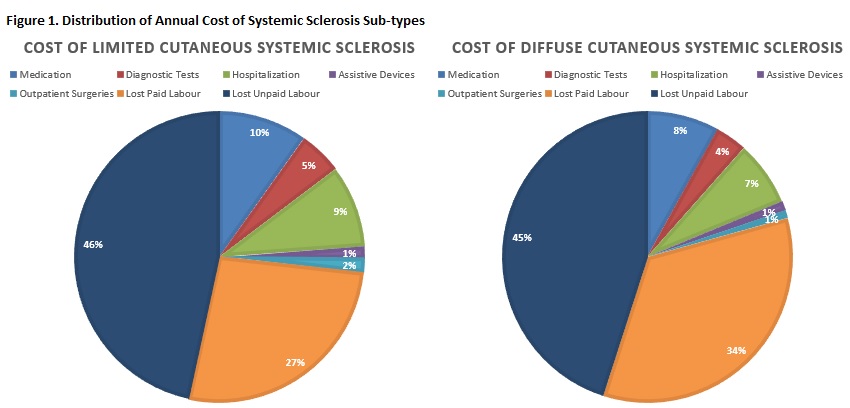
Results: The search retrieved 1777 studies, of which 35 were included representing 20 cross-sectional, 11 cohort, and 4 case-control studies. Studies used various methods of calculating cost including prevalence-based cost-of-illness approach, bottom-up cost analysis, humanistic approach, and health resource units cost analysis. Overall SSc total annual medical cost ranged from USD $14,959-$23,268 in USA, CAD$10,673-$18,453 in Canada, €4,607-€30,797 in Europe, and AUD $7,060 to $11,607 in Oceania. Annual cost for SSc associated with interstitial lung disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension was USD $31,285-$55,446 and $44,454-$63,320, respectively.
Conclusion: Globally, SSc represents significant patient and systemic economic burden. SSc complications are associated with higher economic burden and are highly variable depending on geographical location and medical access. Governmental policies should emphasize prevention of SSc complications as a strategy to mitigate overall cost.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martin Calderon L, Chaudhary M, Pope J. Healthcare Utilization and Economic Burden in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-utilization-and-economic-burden-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-utilization-and-economic-burden-in-systemic-sclerosis/