Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster III: Other Rheumatic & Musculoskeletal Diseases (1022–1060)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) and polymyositis (PM) are rare heterogenous systemic autoimmune disorders with primary target of muscle, skin, but can also impact multiple other organs. The objective of this study was to systematically review and synthetize evidence on healthcare resource utilization (HCU) and cost of treating DM/PM in the United States (US).
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted using MEDLINE and Embase databases. Primary studies of any design enrolling 10 or more patients with DM/PM, published in the English language between 2011–2021 were included irrespective of country or region. Each eligible article was independently reviewed by two reviewers. The title and study abstracts were reviewed to assess eligibility for full-text review. Data on the clinical, humanistic, and economic burden in DM/PM patients in the US were extracted. The economic burden data is presented below.
Results: A total of 3624 records were retrieved from medical databases, 393 records underwent full-text review, and 210 were included in data abstraction. Additional 8 papers were included from searching reference lists of identified studies. HCU and/or costs related to DM/PM in the US were reported in 13 studies. Patients with DM/PM had a significantly higher number of medical visits ( >50% directly related to DM/PM care), inpatient admissions, emergency room visits, as well as visits to rheumatologists, neurologists and physical therapy care, compared to matched controls (Table 1). When hospitalized, patients with DM/PM required more specialized tests and procedures, typically with 1.11 to 1.88-day longer length of stay, compared to controls. The total annual cost of hospitalization due to DM in the US was estimated at $49 million and $168 million for juvenile and adult patients, respectively, with a substantial cost increase to $644 million for hospitalizations due to various morbidities or comorbidities in adult patients (DM as secondary inpatient diagnosis). These costs were increased by 27–64% when compared with inpatients without DM. On average, mean hospital costs to payers were $55,000, which was $13,000 higher relative to inpatients without DM/PM (Table 2). Two studies evaluated indirect costs related to DM/PM and showed an increased, disease-related productivity loss (on average, 2 workdays loss vs matched controls, or 27.65% missed workdays/week) that was also associated with disease flare frequency.
Conclusion: Most of the published evidence focuses on direct hospital care suggesting DM/PM generate significant costs to the healthcare system. Moreover, there is significant direct and indirect economic burden related to the treatment of DM/PM, suggesting unmet need for exploring novel therapeutics in clinical trials to safe and efficacious therapies. Given the limited evidence on the HCU and associated costs of DM/PM in the US, additional research on this topic is warranted.
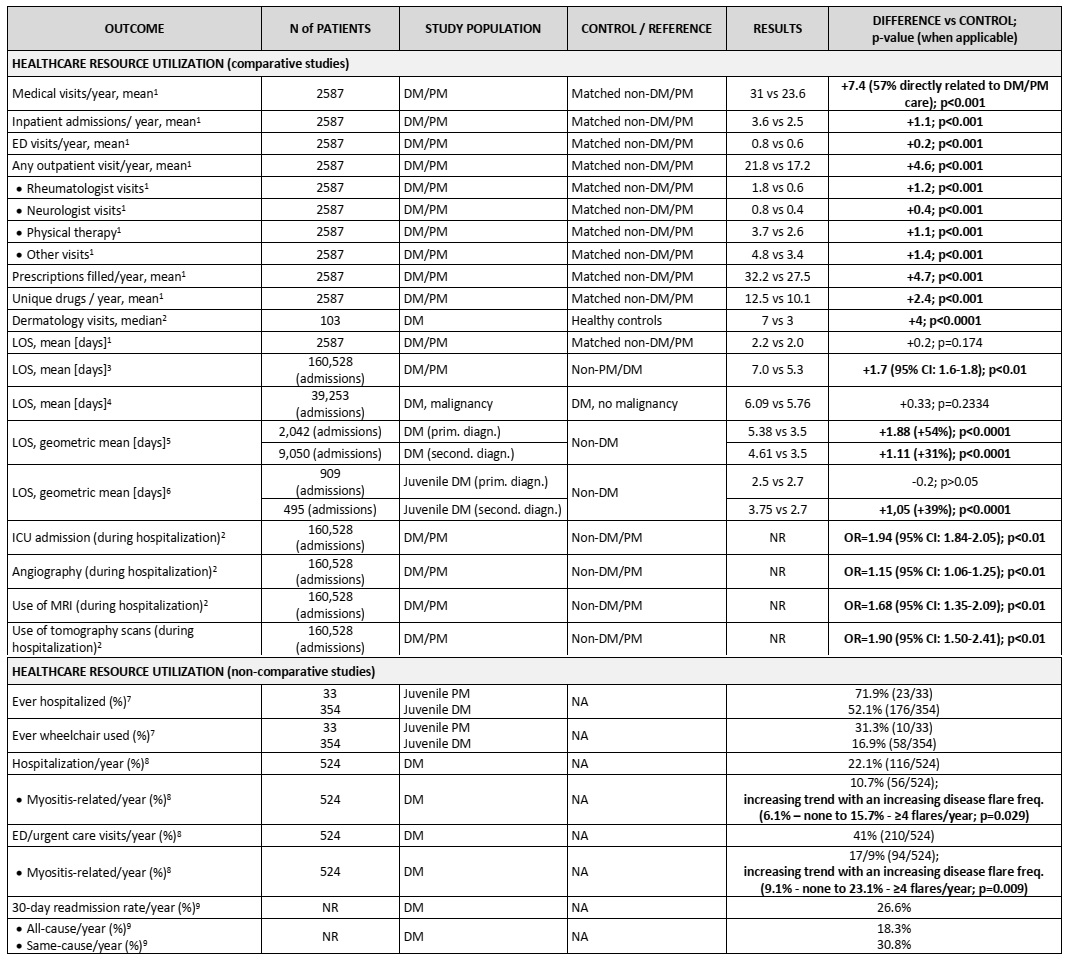 Table 1.Healthcare resource utilization in DM/PM (References: 1 Bradford Rice 2016; 2 Robinson 2016; 3 Ungprasert 2020; 4 Tripathi 2020; 5 Kwa 2017; 6 Kwa 2018; 7 Shah 2013; 8 Christopher-Stine 2020; 9 Zhang 2019).
Table 1.Healthcare resource utilization in DM/PM (References: 1 Bradford Rice 2016; 2 Robinson 2016; 3 Ungprasert 2020; 4 Tripathi 2020; 5 Kwa 2017; 6 Kwa 2018; 7 Shah 2013; 8 Christopher-Stine 2020; 9 Zhang 2019).
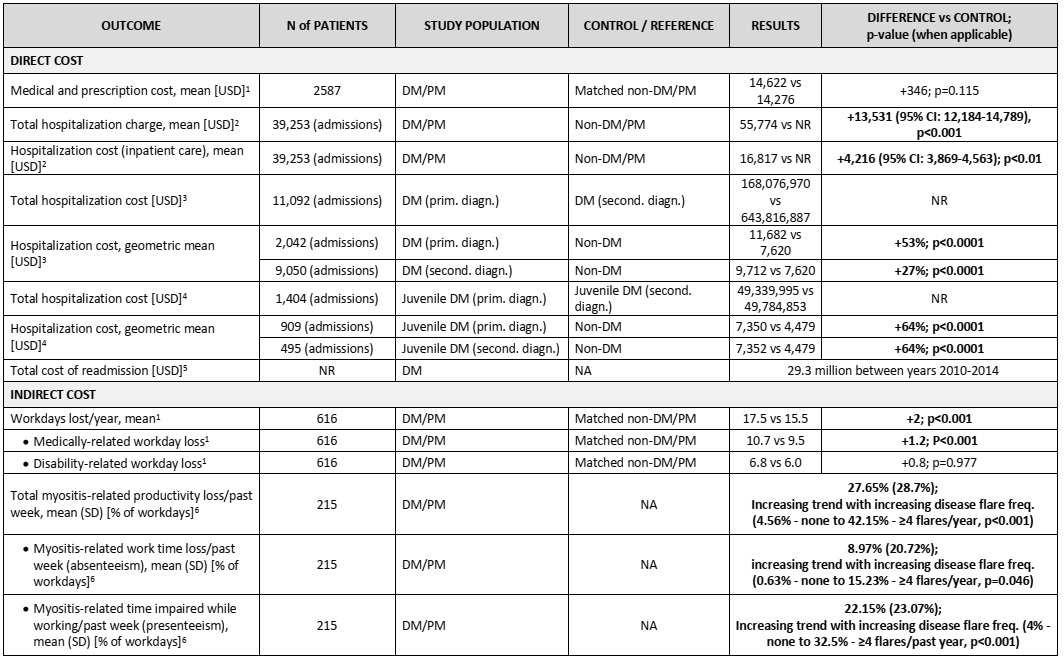 Table 2. Direct and indirect cost of DM/PM (References: 1 Bradford Rice 2016, 2 Ungprasert 2020; 3 Kwa 2017; 4 Kwa 2018; 5 Zhang 2019; 6 Christopher-Stine 2020).
Table 2. Direct and indirect cost of DM/PM (References: 1 Bradford Rice 2016, 2 Ungprasert 2020; 3 Kwa 2017; 4 Kwa 2018; 5 Zhang 2019; 6 Christopher-Stine 2020).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aggarwal R, Gwathmey K, Leff R, Pisarczyk K, Aleksanderek I, Palaniswamy K, Henig N. Healthcare Resource Utilization and Costs of Dermatomyositis and Polymyositis in the United States: A Systematic Literature Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-resource-utilization-and-costs-of-dermatomyositis-and-polymyositis-in-the-united-states-a-systematic-literature-review/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-resource-utilization-and-costs-of-dermatomyositis-and-polymyositis-in-the-united-states-a-systematic-literature-review/
