Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: BEL efficacy in pts with SLE has been previously demonstrated in clinical and real-world studies.1 However, there are limited data on differences in outcomes for pts with SLE with different immunosuppressant (IS) treatment use before BEL initiation. This analysis assessed whether IS-naïve pts with SLE initiating BEL varied in their oral CS (OCS) use and clinical outcomes compared with those initiating BEL after the prior IS treatment.
Methods: This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study (GSK Study 217536) used data from the Komodo Health database of de-identified claims between Jan 2015 and Dec 2022. Eligible adults with SLE in the USA were identified from Jan 2017, allowing for ≥24 months of continuous enrollment before BEL initiation (index date). BEL initiators were categorized into 2 cohorts: BEL-0IS (pts who initiated BEL with no prior IS); BEL-1IS (pts who initiated BEL with 1 prior IS). Baseline (BL) was defined as 24 months pre-index. Pts were followed until the end of enrollment or up to 60 months post index. The incidence of SLE flares, organ damage (OD), OCS use, and healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) were stratified by BL moderate/severe disease severity and evaluated using descriptive statistics.
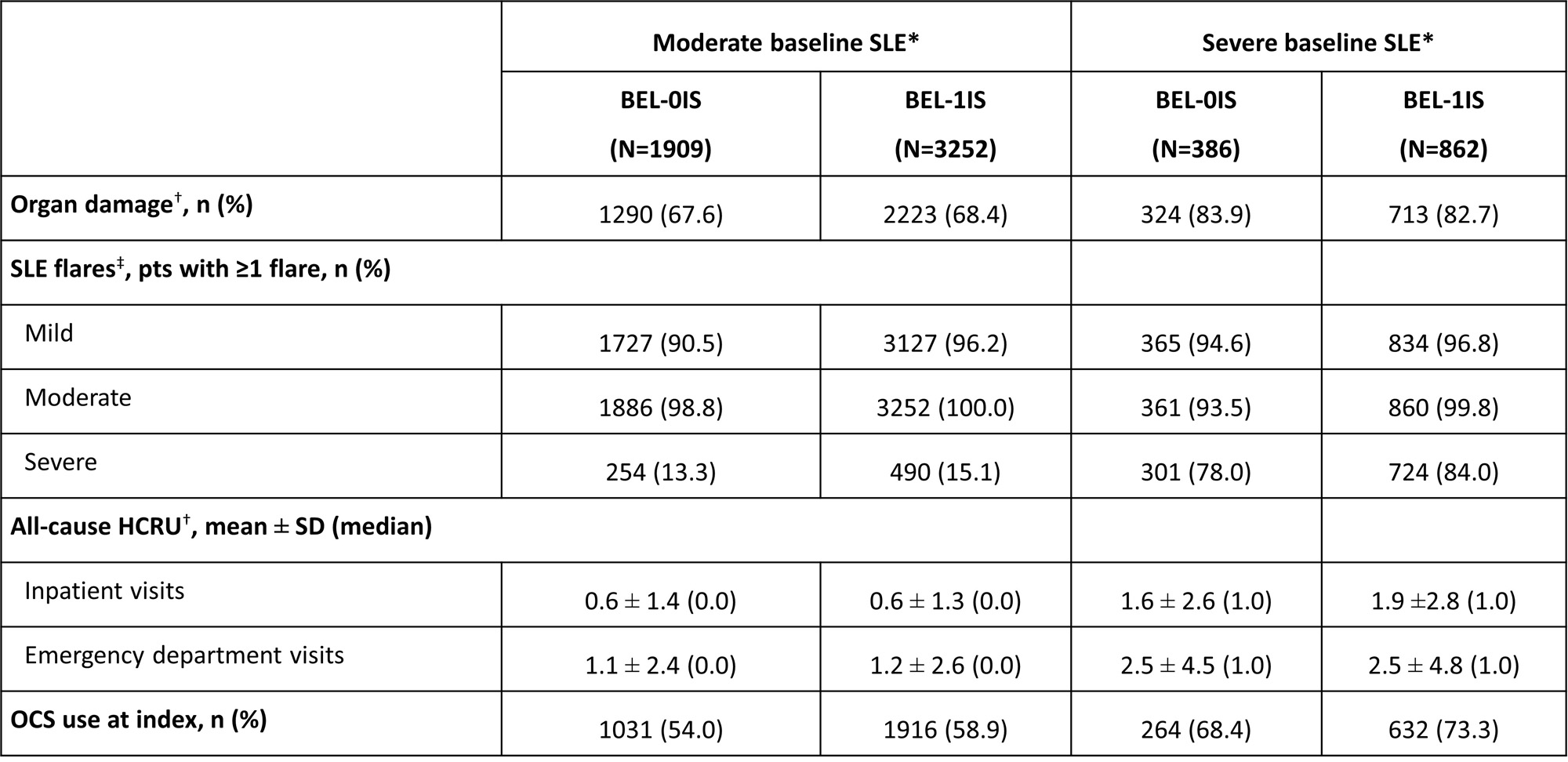
Results: At BL, of the 2719 BEL-0IS pts, 70.2% had moderate and 14.2% had severe SLE; of 4122 BEL-1IS pts, 78.9% had moderate, and 20.9% had severe SLE. BEL-1IS pts had higher BL flare rates (Table), partly due the moderate flare definition necessitating IS use. For both cohorts, BL OD was similar between pts with moderate (BEL-0IS: 67.6%; BEL-1IS: 68.4%) and severe SLE (BEL-0IS: 83.9%; BEL-1IS: 82.7%). All-cause BL HCRU was similar between pts with moderate SLE of both cohorts, but higher in BEL-1IS pts with severe SLE than in BEL-0IS pts. At 6 months post index, mean moderate flare rates (per-patient-year, PPY) were 2.2 for BEL-0IS and 4.7 for BEL-1IS in pts with moderate SLE, and 2.9 for BEL-0IS and 6.1 for BEL-1IS in pts with severe SLE; mean severe flare rates were 0.4 for BEL-0IS and 0.5 for BEL-1IS in pts with moderate SLE, and 1.0 for BEL-0IS and 2.1 for BEL-1IS in pts with severe SLE. Notable difference persisted through 60 months post index. The median time to OD was 32.1 months for BEL-0IS and 26.7 months for BEL-1IS in pts with moderate SLE, and 22.7 months for BEL-0IS and 21.6 months for BEL-1IS in pts with severe SLE. In pts with BL OCS use, the median time to OCS discontinuation was 4.5 months for BEL-0IS and 8.9 months for BEL-1IS in pts with moderate BL SLE, and 6.2 months for BEL-0IS and 11.6 months for BEL-1IS in pts with severe BL SLE. Rates (PPY) of all-cause emergency room visits and inpatient stays were similar between pts with moderate SLE of both cohorts, but BEL-1IS pts with severe BL SLE had higher inpatient stay rates (0.7 vs 0.9).
Conclusion: While most BEL pts were able to discontinue OCS within 12 months post index, BEL-0IS pts were able to discontinue OCS in half the time of BEL-1IS pts. SLE flare rates were also notably lower in BEL-0IS pts, although some differences were observed in the cohorts during the BL. Future studies should further investigate optimal BEL placement in the SLE treatment pathway.
Funding: GSK
Reference: 1 Levy RA et al. Lupus 2021;30:1705–21
*Pts were classified into mutually exclusive groups of mild, moderate, or severe disease using a previously published algorithm, which is based on validated measures of SLE activity and the consensus of expert clinical opinion and considers medications of interest and HCRU associated with an SLE-related condition; †evaluated during the 24-month BL period excluding the index date; ‡SLE flare episodes were identified and classified by severity based on a previously published claims-based algorithm, which considers medications of interest and HCRU associated with an SLE diagnosis or SLE-related condition.
SD, standard deviation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen Y, Worley K, Rabideau B, Rubin B, Wu B, Chang R, DerSarkissian M. Health Outcomes Among Patients (Pts) with SLE Initiating Belimumab (BEL) with and Without the Use of Immunosuppressants in the Previous 2 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/health-outcomes-among-patients-pts-with-sle-initiating-belimumab-bel-with-and-without-the-use-of-immunosuppressants-in-the-previous-2-years/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/health-outcomes-among-patients-pts-with-sle-initiating-belimumab-bel-with-and-without-the-use-of-immunosuppressants-in-the-previous-2-years/