Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Biomarkers
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Small RNAs (sRNAs), including microRNAs (miRNAs) and yRNA-derived sRNAs (yDRs), are important gene regulators and markers of disease. HDL, while known for its anti-atherogenic function, can traffic sRNAs between cells to alter gene expression and thus cellular function. Additionally, HDL interacts with cells of the immune system and synovial fibroblasts, making it an important sRNA carrier to examine in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). HDL carries yDRs, some of which are known to promote apoptosis. Apoptosis is impaired in RA, particularly in the synovial fibroblasts of RA patients. The purpose of this study was to determine if HDL-bound yDRs are altered in RA and if they are associated with disease measures.
Methods: HDL was purified from 30 patients with RA and 30 control subjects matched for age, race and sex subject plasma by density gradient centrifugation and fast protein liquid chromatography. Total RNA was extracted from the purified HDL. Next generation sequencing (NGS) was performed on sRNA libraries by Illumina NextSeq500. The TIGER pipeline was used to quantify yDRs. The yDRs were compared between RA and control subjects by DESeq2 with 5% false discovery rate multiple comparison adjustment by Benjamini-Hochberg method. Spearman correlation was used to determine relationship between sRNAs and disease measures.
Results: HDL-bound yDRs as a class were significantly reduced 36% among patients with RA compared to control subjects (p=0.03) (Figure 1). Eighteen yDR sequences were significantly reduced up to 5-fold among RA versus control subjects (Padj < 0.05) (Figure 2). Among these altered yDRs, 17 map to the 5’ and 3’ ends of RNY4 (Ro60-associated yRNA 4), with only minor sequence variation. Based on NGS the two most abundant sequences aligning to each end of RNY4 were significantly associated with swollen joint count (ydr-ccccccactgctaaatttgactggctt, Rho=0.39, p=0.04; and ydr-ggctggtccgatggtagtgggttatcagaact, Rho=0.40, p=0.03), but were not altered based on disease modifying antirheumatic drug use, seropositivity or erosive disease (all P >0.05).
Conclusion: HDL-bound yDRs are reduced in patients with RA and several yDRs are associated with swollen joint count. Further work will be necessary to validate these findings and to determine the functional role of these HDL-bound yDRs in RA.
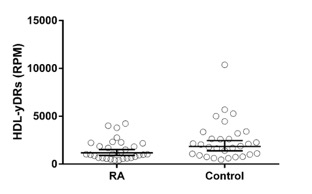 Figure 1. HDL-bound yRNA-derived sRNAs as a class are significantly reduced 36% among patients with RA compared to control subjects(P=0.03). Each dot represents an individual subject’s total HDL-yDR reads per million. Bars indicate geometric mean and 95% confidence intervals.
Figure 1. HDL-bound yRNA-derived sRNAs as a class are significantly reduced 36% among patients with RA compared to control subjects(P=0.03). Each dot represents an individual subject’s total HDL-yDR reads per million. Bars indicate geometric mean and 95% confidence intervals.
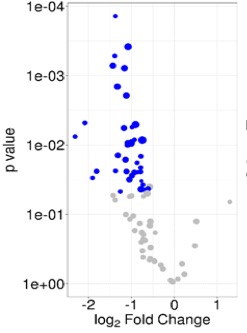 Figure 2. Volcano plot displaying difference in HDL-bound yDR sequences in RA versus control subjects. Blue dots indicate sequences which are reduced among RA patients.
Figure 2. Volcano plot displaying difference in HDL-bound yDR sequences in RA versus control subjects. Blue dots indicate sequences which are reduced among RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu Q, Sheng Q, Solus J, Michell D, Vickers K, Allen R, Stein C, Ormseth M. HDL-bound yRNA-derived Small RNAs Are Altered in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hdl-bound-yrna-derived-small-rnas-are-altered-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hdl-bound-yrna-derived-small-rnas-are-altered-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/
