Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: In order to understand the genetic factors that lead to early remission in RA, we performed a GWAS to uncover important biological pathways.
Methods: We collected 5,635 untreated patients with RA from 10 centers throughout Europe. We defined remission as DAS28CRP < 2.6 at 6 months. We estimated the genetic component of remission using LDAK-PCGC. Next, we ran a GWAS in each cohort, correcting for age, sex and population stratification, and combined the results with an inverse-variance weighted meta-analysis with fixed-effects. Positional and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) mapping was performed using FUMA. For transcriptional analyses, we used AMP-I [1] single cell RNAseq synovial biopsies (n=55 RA patients), Zurich cohort of 26 synovial tissues across 5 arthritides, PEAC synovial biopsies RNAseq (n=355 RA patients [2]) from unstimulated and stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and circulating CD4+ T-cell eQTL data from untreated RA patients (NEAC) [3].
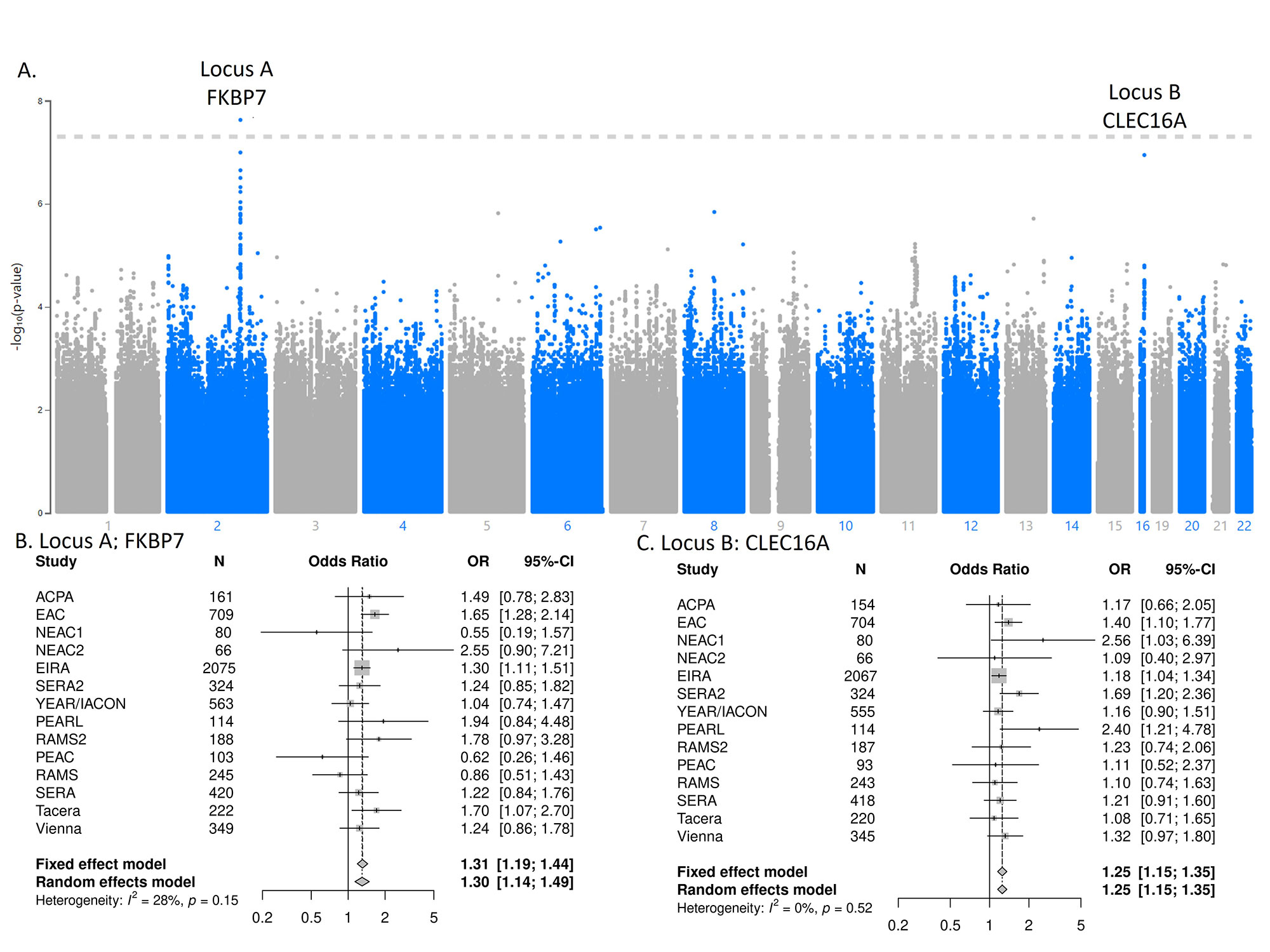
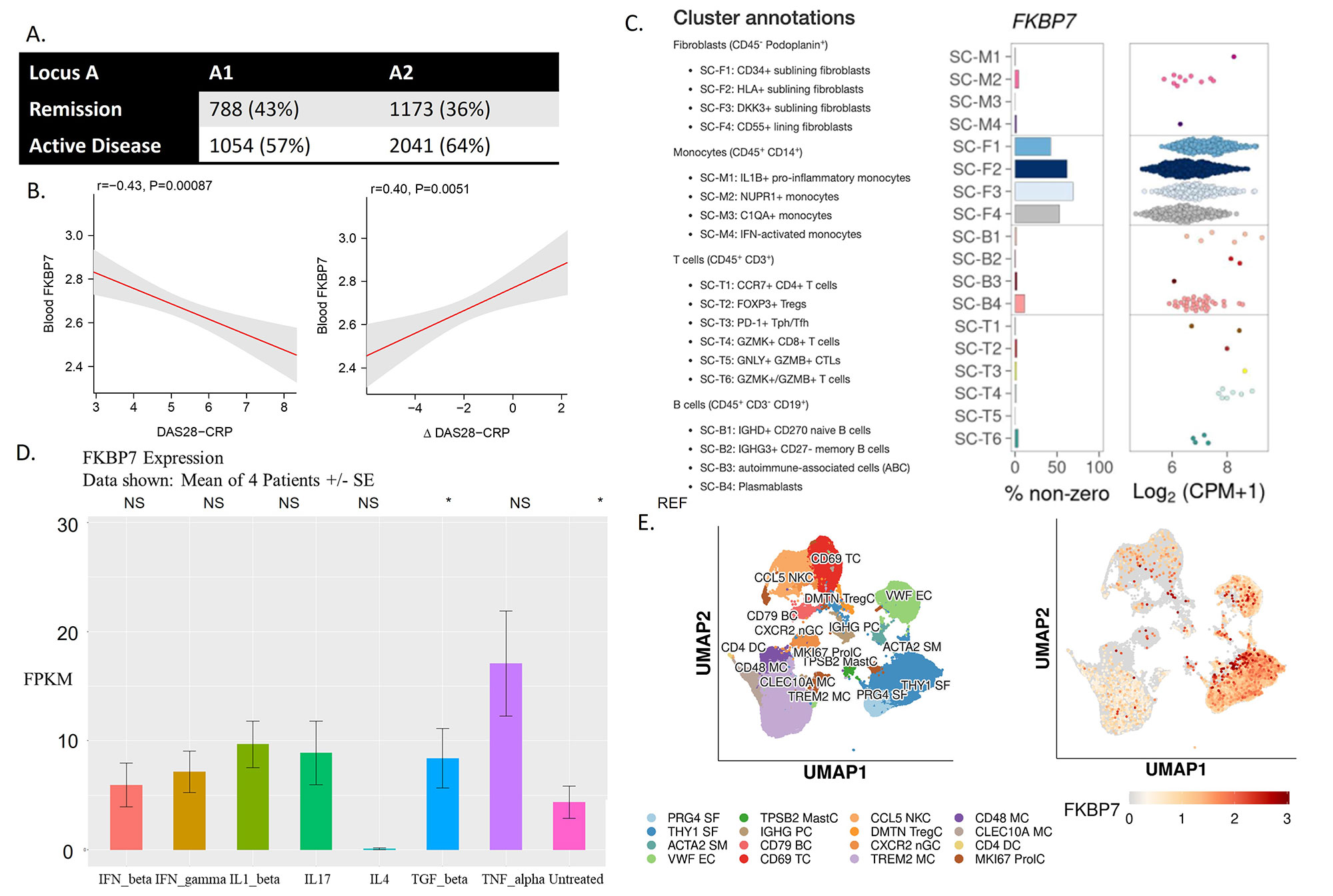
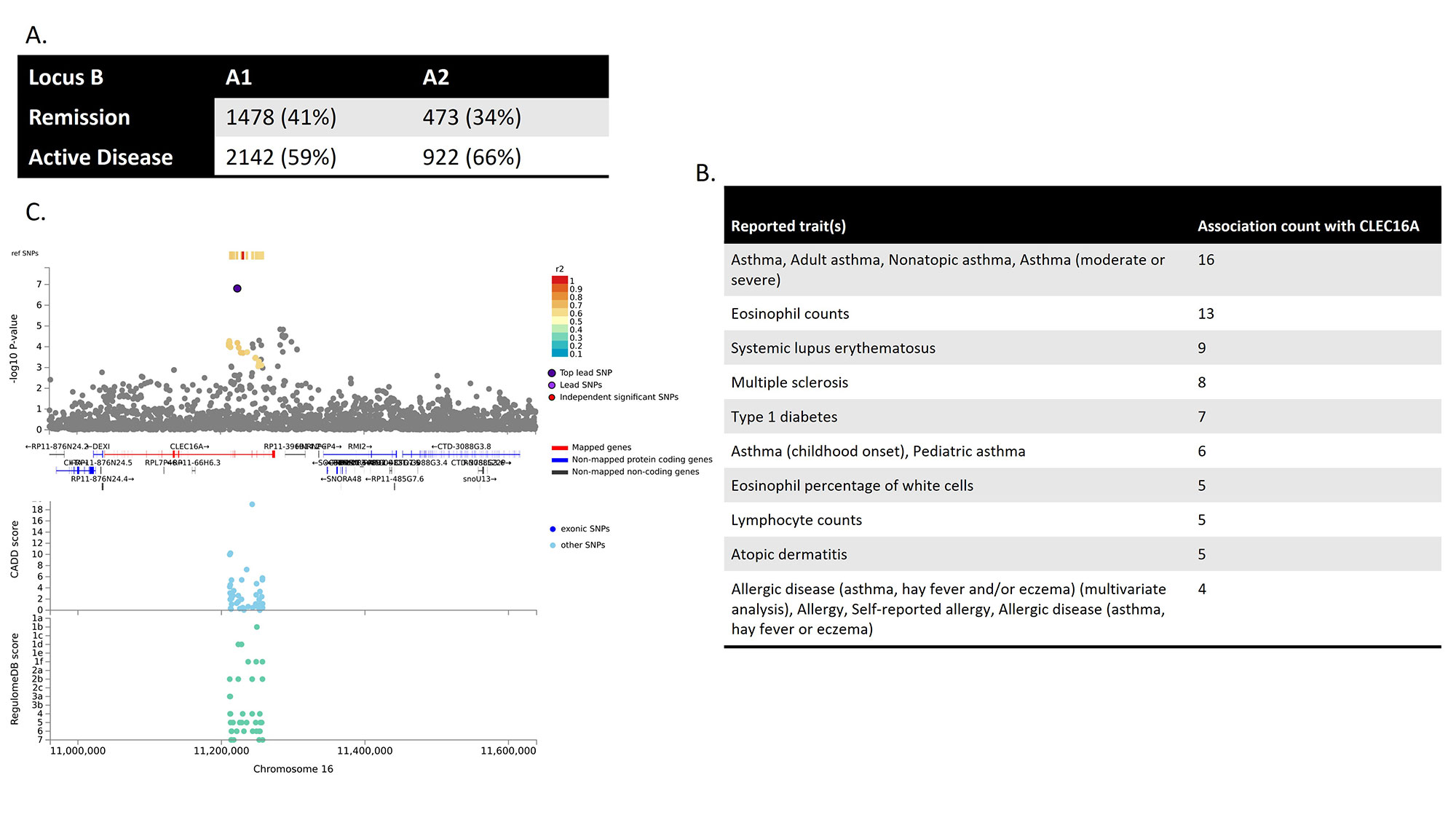
Results: In our data, 16% of phenotypic variance was explained by genetics (h2). Polygenic risk score analysis showed this was not attributable to established RA susceptibility variants. Our GWAS uncovered 2 loci of interest; a genome-wide significant hit (locus A, rs16866400, Chr2:179448911, P = 2.36 x 10-8) and a suggestive hit (locus B, rs11645657, Chr16:11223454, P = 1.13 x 10-7) (Figure 1). Locus A was positionally mapped to TTN(-AS1), a gene, expressed in muscle, with an eQTL for fk506 (tacrolimus) binding protein (FKBP7) in fibroblasts. Our data show that this variant affects transcription in FLS and that FKBP7 is differentially expressed in FLS. In the PEAC biopsies we demonstrate that the remission-associated allele increases transcription of FKBP7 in synovia, which correlates with lower baseline disease activity and better treatment response. We also observed a decrease in FKBP7 expression in FLS when treated with IL4 and an increase when treated with TNF (Figure 2). The leading SNP in locus B is likely itself regulatory, given its high regulatory scores (regulomeDB rank = 2B, CAD score = 1.5) and the lack of strong LD to alternative SNPs, suggesting a self-regulatory nature. Based on the ChromHMM and eQTL data, this SNP affects enhancement in FLS and is an eQTL in early RA CD4+ T-cells for CLEC16A, a gene with variants associated with multiple autoimmune disorders, ranging from MS to seronegative RA [4]. Additionally, CLEC16A KO mice exhibit an autoimmune phenotype reversed by JAK/STAT inhibition [5] (Figure 3).
Conclusion: We have identified two genes whose expression is associated with remission in patients with early RA: FKBP7 and CLEC16A. The FKBP7 pathway seems to be FLS mediated. We are performing further experimental studies to investigate both genes. Based on our current work we postulate a broadening of the conventional B- and T-cell focus in RA treatment to also include FLS.
References:
1. Zhang et al, 2019, Nat Imm.
2. Lewis et al, 2019, Cell Rep.
3. Thalayasingam et al, 2018, A&R.
4. Skinningsrud et al, 2010, ARD.
5. Pandey et al, 2021, Sci. Rep.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge support by RTCure, the IMI2 JU (grant 777357), RTCure, ZonMW (grant 90719069), MRC/Versus Arthritis MATURA Consortium, Versus Arthritis and NIHR.
FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads; CPM, counts per million
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maurits M, Abasolo Alcazar l, van den Akker E, Askling J, Barton A, Blüml S, Böhringer S, Cope A, Emery P, Eyre S, Gaddi P, Gonzalez I, Goodyear C, van der Helm-van Mil A, Hu X, Huizinga T, Isaacs J, Jelinsky S, Johannesson M, Jurado Zapata S, Ke C, Klareskog L, Lendrem D, Lewis M, Liu M, Martin P, McInnes I, Micheroli R, Morgan A, Morton F, Naamane N, Orozco G, Ospelt C, Padyukov L, Paterson C, Plant D, Porter D, Pratt A, Raychaudhuri S, Reynard L, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Sieghart D, Studenic P, Taylor J, Toes R, Verstappen M, Verstappen S, Westerlind H, Winkler A, Knevel R. GWAS Identified New Genes in Synovial Fibroblasts Linked to Early Remission in RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gwas-identified-new-genes-in-synovial-fibroblasts-linked-to-early-remission-in-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gwas-identified-new-genes-in-synovial-fibroblasts-linked-to-early-remission-in-ra/