Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Recent studies have shown that monocytes, macrophages, and conventional DCs, but not plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC), are major sources of IFNα in cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE). However, novel medications targeting pDCs reduce IFNα levels and improve CLE. Granzyme B is a proteolytic enzyme that induces apoptosis, and large concentrations are produced by pDCs in CLE, yet its role in modulating signaling pathways, including IFNα release, has not been elucidated.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were obtained from 25 CLE patients. PBMCs were co-incubated for 20 hours with 500U of recombinant human granzyme B alone or with either 100ug/mL C307 (TLR7 agonist), 10ug/mL TL8-506 (TLR8 agonist), 1.5uM CpG (TLR9 agonist) or 60ug/mL cGAMP (STING agonist). Positive controls were PBMCs stimulated separately with only C307, TL8-506, CpG or cGAMP. Supernatants were then analyzed for IFNα production via ELISA.
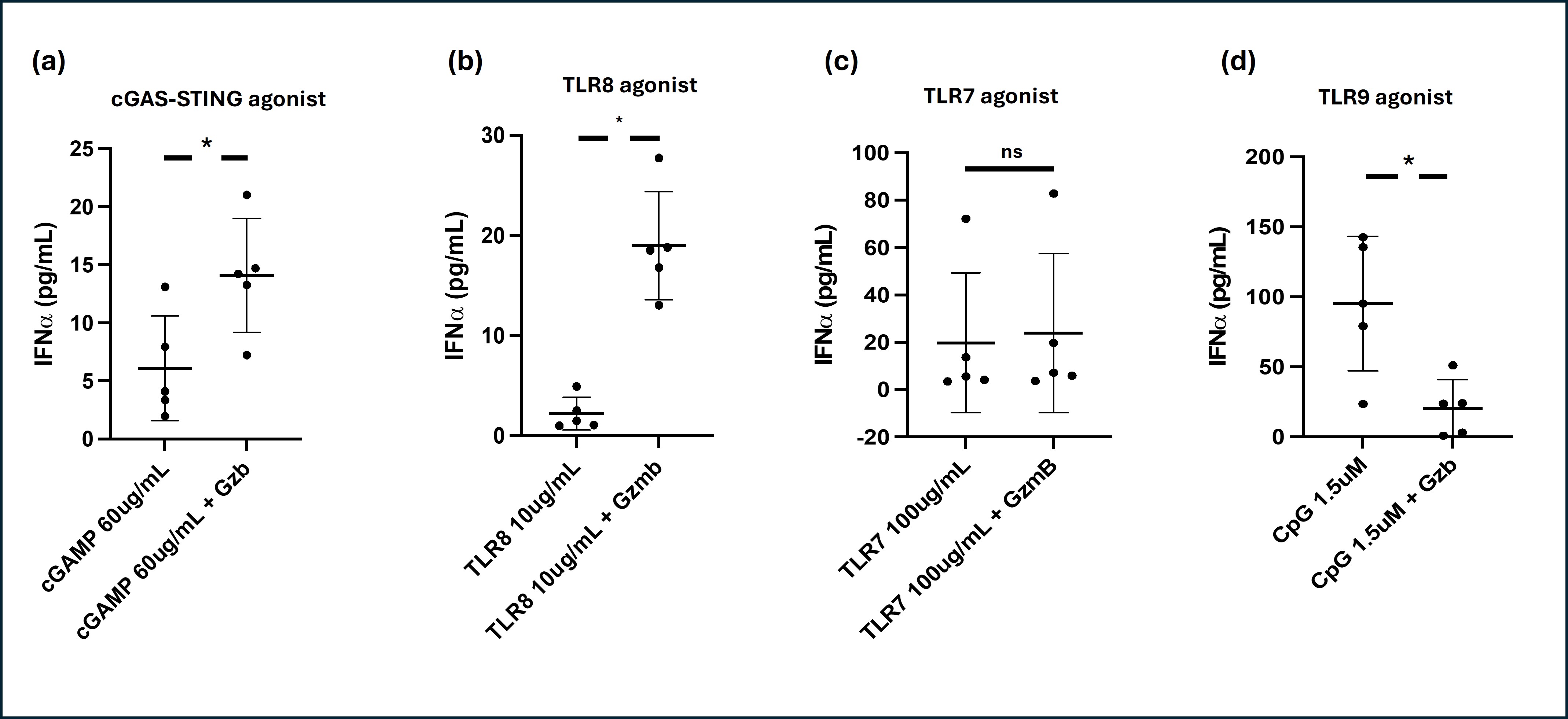
Results: PBMCs incubated with granzyme B alone did not produce any IFNα (n=5). PBMCs co-incubated with granzyme B and C307 (n=5) did not result in any significant change in IFNα production compared to PBMCs incubated with C307 alone (mean IFNα 20.0±13.3 vs. 22.7±15.3 pg/mL respectively, p=0.11). PBMCs co-incubated with granzyme B and CpG (n=5) significantly reduced IFNα production compared to PBMCs incubated with CpG alone (mean IFNα 20.6±9.1 vs. 95.2±21.5 pg/mL respectively, p< 0.01). However, PBMCs co-incubated with granzyme B with either TL8-506 (n=5) or cGAMP (n=5) produced significantly increased IFNα compared to PBMCs incubated with either TL8-506 or cGAMP alone (for TL8-506, mean IFNα 18.9±2.4 vs. 2.2±0.7 pg/mL respectively, p< 0.01; for cGAMP, mean IFNα 14.1±2.2 vs 6.1±2.0 pg/mL respectively, p< 0.01).
Conclusion: CpG stimulates the TLR9 pathway primarily on pDCs and granzyme B may have a negative feedback effect in suppressing TLR9-induced IFNα release from pDCs, as suggested by recent studies. Granzyme B may not affect the TLR7 pathway which is also highly expressed on pDCs. However, monocytes and macrophages primarily use the TLR8 and STING pathways for IFNα production. Granzyme B which is produced in large numbers by pDCs may potentiate IFNα release by enhancing the TLR8 or STING pathways on macrophages and monocytes in CLE. Outside of its role in inducing apoptosis, granzyme B may be a bridge between pDCs and other immune cells by modulating signaling pathways, in particular that of type-1 IFN in CLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khosravi T, Eldaboush A, Kang D, Werth V. Granzyme B as a regulator of interferon alpha production in cutaneous lupus erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/granzyme-b-as-a-regulator-of-interferon-alpha-production-in-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/granzyme-b-as-a-regulator-of-interferon-alpha-production-in-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus/