Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Gouty arthritis (gout) is primarily cared for in ambulatory care settings. Yet, there are few nationally representative data on ambulatory health care utilization of this condition. The goal of this study is to analyze the quantity of visits for gout and its trends in the US between 1993 and 2009.
Methods: We combined the data from National Ambulatory Medical Care Surveys (NAMCS) and National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Surveys (NHAMCS) from 1993 to 2009 where the unit of analysis was the outpatient visit. Gout visit was defined as a visit with physician-prescribed gout diagnosis, or a visit associated with a prescription of allopurinol or colchicine. Patients younger than 20 or older than 90 were excluded. Data were analyzed using SVY suite of commands in STATA. Time trends were tested using Poisson regressions.
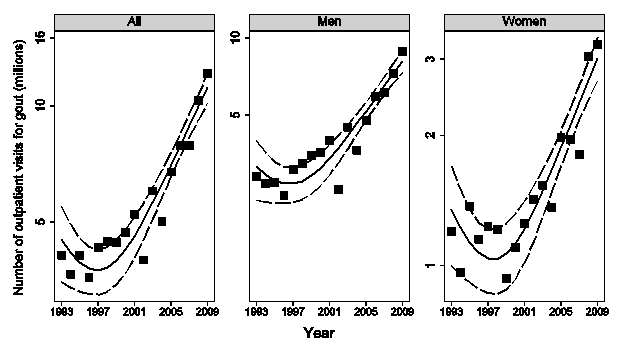
Results: For men, the annual number of visits for gout increased from 2.9 million at 1993 to 8.9 million at 2009; for women, it increased from 1.2 million to 3.2 million. The total number of visits for gout increased from 4.1 million at 1993 to 12.1 million at 2009. The increase of gout visits was highly significant (p<0.001) (Figure 1). When examined as a proportion of all ambulatory care visits, the proportion of gout visits increased from 13.0 per 1000 (10.0‰, 17.2‰) to 25.5 per 1000 (21.0‰, 31.1‰) among men and 3.2 per 1000 (2.0‰, 5.1‰) to 5.8 per 1000 (4.4‰, 7.7‰) among women (Figure 2). The increase was evident in all age groups but was large only among the 60+ age group. Overall, in age-gender adjusted Poisson regressions the 2006-2009 time period was associated with a relative risk for 1.6 (1.4, 1.9) compared to the 1993-2005 time period.
Conclusion: The frequency of gout increased over three fold between 1993 and 2009, and most of the increase occurred after 2005. The gout awareness campaign funded by the industry could be the explanatory factor.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Disclosure:
E. Krishnan,
Takeda,
2,
Takeda,
5;
L. Chen,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gout-in-ambulatory-care-settings-in-the-us-1993-2009/