Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0691–0721) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) often require long-term glucocorticoid therapy. The prevalence, types, and underlying factors of glucocorticoid toxicity in IgG4-RD patients remain unknown. We aimed to describe the prevalence, types, and associated factors of glucocorticoid toxicity in our IgG4-RD cohort.
Methods: We retrospectively included patients diagnosed with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) based on the Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria and/or the 2019 ACR/EULAR classification criteria who had received glucocorticoid treatment for a minimum of one month and were followed up for at least one year. We categorized them into clinical phenotypes: pancreatobiliary (group 1), retroperitoneal/aortic (group 2), head and neck limited (group 3), Mikulicz/systemic (group 4), and undefined (group 5). From the medical records, we collected demographic, clinical, and treatment variables. We focused on prednisone usa during the first year of treatment, including the mean daily dose of prednisone, accumulated prednisone dose, maximum prednisone dose, and duration of prednisone treatment. To assess glucocorticoid toxicity, we employed the definitions proposed in the Glucocorticoid Toxicity Index, along with its domains and appendixes.
Results: Fifty-seven patients were included with a mean age of 53±15.8 years, of whom 34 (59.6%) were male. Fifteen (26.3%) belong to group 1, six (10.5%) to group 2, 13 (22.8%) to group 3, 19 (33.3%) to group 4 and 4 (7%) to group 5. The mean prednisone daily dose was 15.9±6.9 grm the median accumulated prednisone dose was 4,967.5 (IQR 3,195-6,670) gm, the mean maximum dose of prednisone was 39.3±14.2 gm, while the median number of days under prednisone treatment was 303.2 ± 103.9 days.
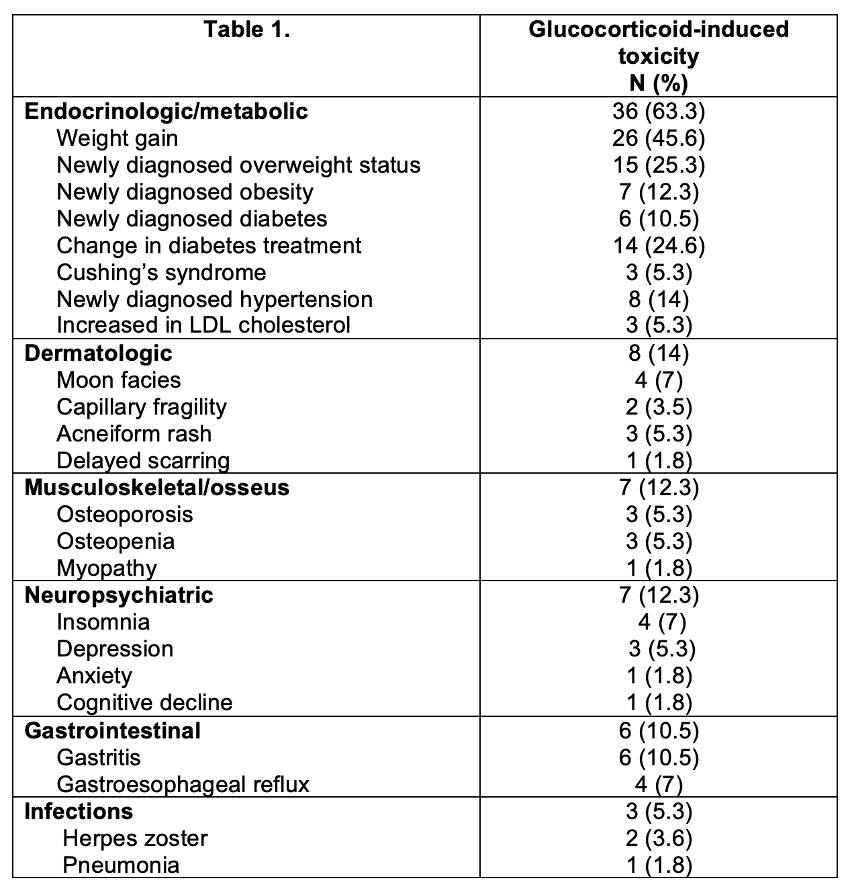
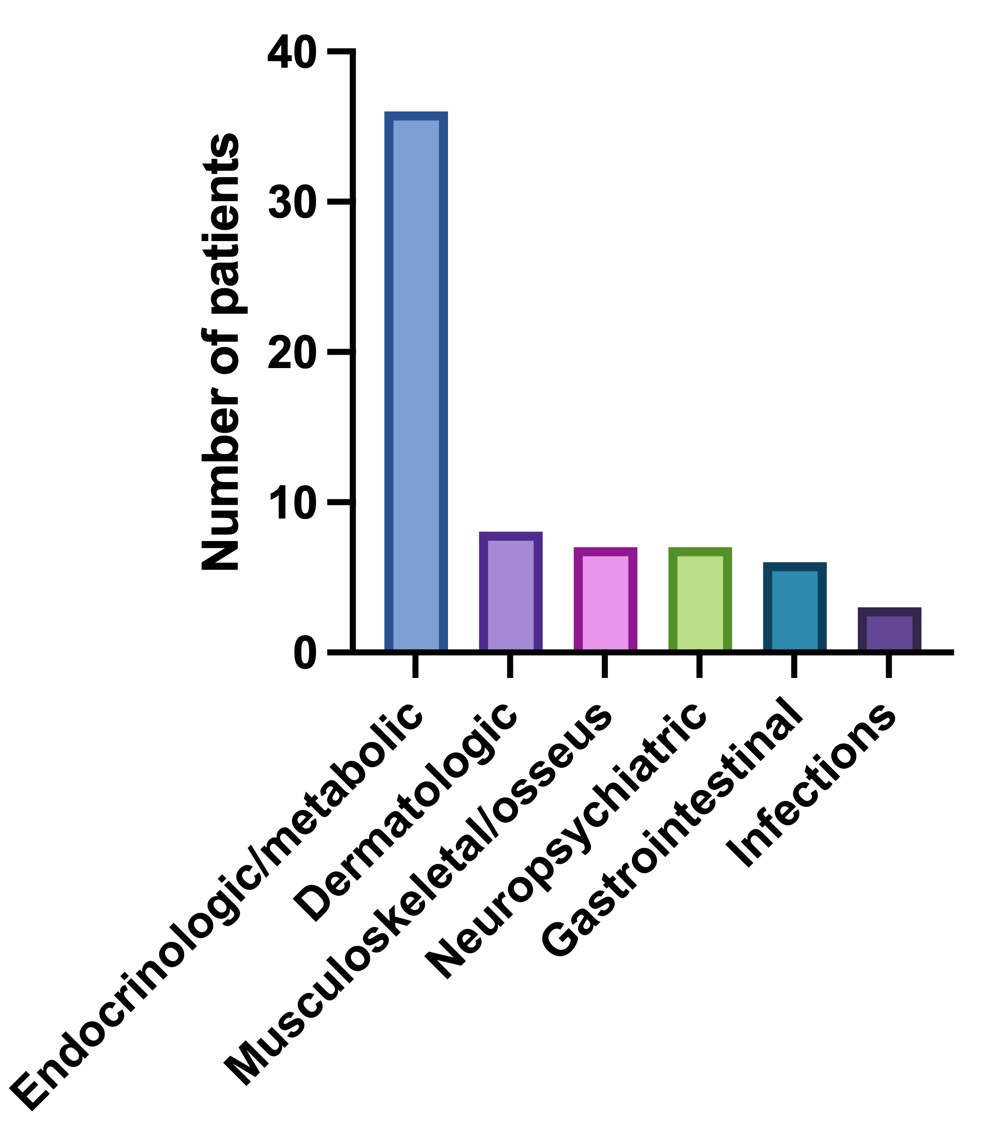
Forty-two (73.7%) patients developed one or more toxicities. The first toxicity was documented at a median of 64 (IQR 34.5-132) days. The median number of toxicities was 3 (IQR 1-4). The frequency and types of toxicities reported during the study period (non-mutually exclusive) are summarized in Figure and Table 1.
There were no differences in daily, accumulated, and maximum prednisone dose, or days with prednisone treatment, development of toxicities, days to first toxicity or number of toxicities according to sex or clinical phenotypes. Patients in group 3 and 4 presented more endocrinologic/metabolic toxicities compared to the other groups.
Patients who experienced toxicities had a higher accumulated prednisone dose (5,605 [IQR 4.215-7,015] vs. 3,400 gm [IQR 2,025-5,638], p=0.03), maximum prednisone dose (42.5±12.8 vs. 30.2±14.5 gm, p=0.003) and days of prednisone treatment (321.3±96.7 vs. 252.6±110, p=0.02) than patients without toxicities (Figure 2). Patients that used immunosuppressors did not present lower accumulated prednisone doses (5,335 [IQR 4,132-6,314] vs. 4,272.5 gm [IQR 2,100-7,427], p=0.41) or a lower incidence of toxicities (29 [74.4%] vs. 13 [72.2%], p=0.23).
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the high prevalence of glucocorticoid toxicity in patients with IgG4-RD undergoing glucocorticoid therapy, even within a relatively brief timeframe of one year. The presence of glucocorticoid toxicity was associated with higher doses and a longer use of prednisone.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mora-Rosas A, Hernandez-Molina G, Cortez-Domínguez E, Martin-Nares E. Glucocorticoid Toxicity in Patients with IgG4-Related Disease Within the First Year of Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucocorticoid-toxicity-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-within-the-first-year-of-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucocorticoid-toxicity-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-within-the-first-year-of-treatment/