Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Treatment II: Non-Cellular Lupus Therapeutics
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) are hypoglycemic agents with well-established cardioprotective properties and emerging data for kidney-protective benefits in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). We sought to determine whether GLP-1RA use will improve cardiovascular (CV) and kidney outcomes among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis (LN).
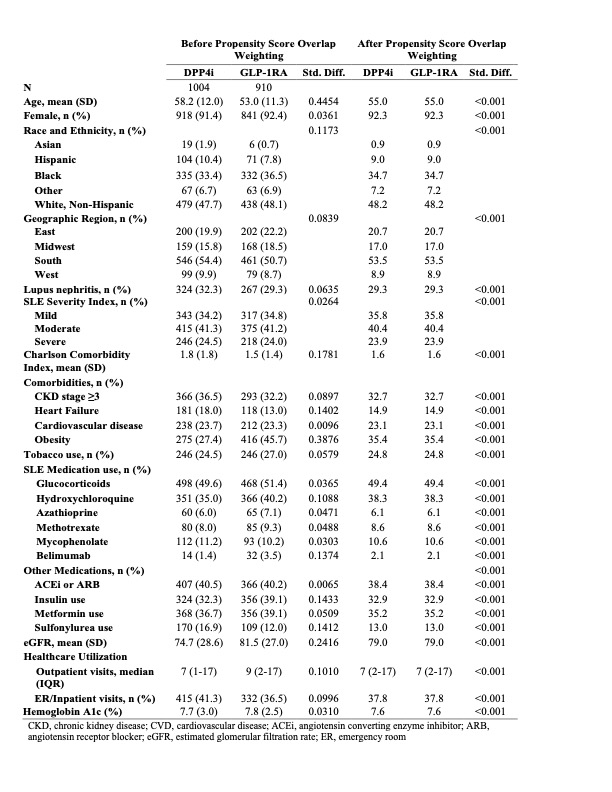
Methods: We specified and emulated a pragmatic target trial to evaluate the impact of GLP-1RA vs. a comparator class of hypoglycemic agents, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i), on CV and kidney outcomes among patients with SLE and T2D. We utilized a large, US multi-center electronic health record database, TriNetX, to identify patients with SLE (N= 96,511). We included all patients who met eligibility criteria of SLE, T2D, no prior end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), and no prior GLP-1RA or DPP4i use who initiated a GLP-1RA or DPP4i between 10/2006 and 8/2021. We used propensity score overlap weighting to emulate randomization between treatment groups. Covariates included demographics, LN, SLE severity index, medications for SLE and T2D, comorbidities, and healthcare utilization. CV outcomes included major adverse cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, and venous thrombosis (VTE). Kidney disease progression was defined as eGFR decline ≥ 30% or new-onset ESKD, and we assessed all-cause mortality. We also assessed the control outcome of genital infection, which was expected to be null. We used Cox regression to compare incidence rates for each outcome based on the weighted populations for a per-protocol analysis with censoring upon deviation from treatment strategy and a secondary intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis. We analyzed the subgroup with LN.
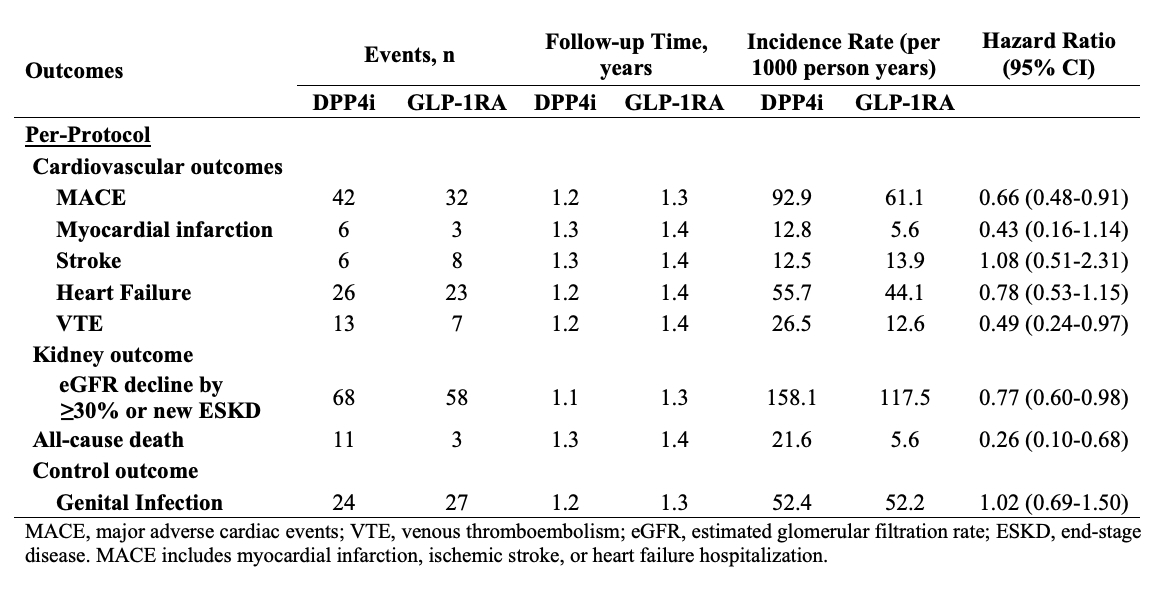
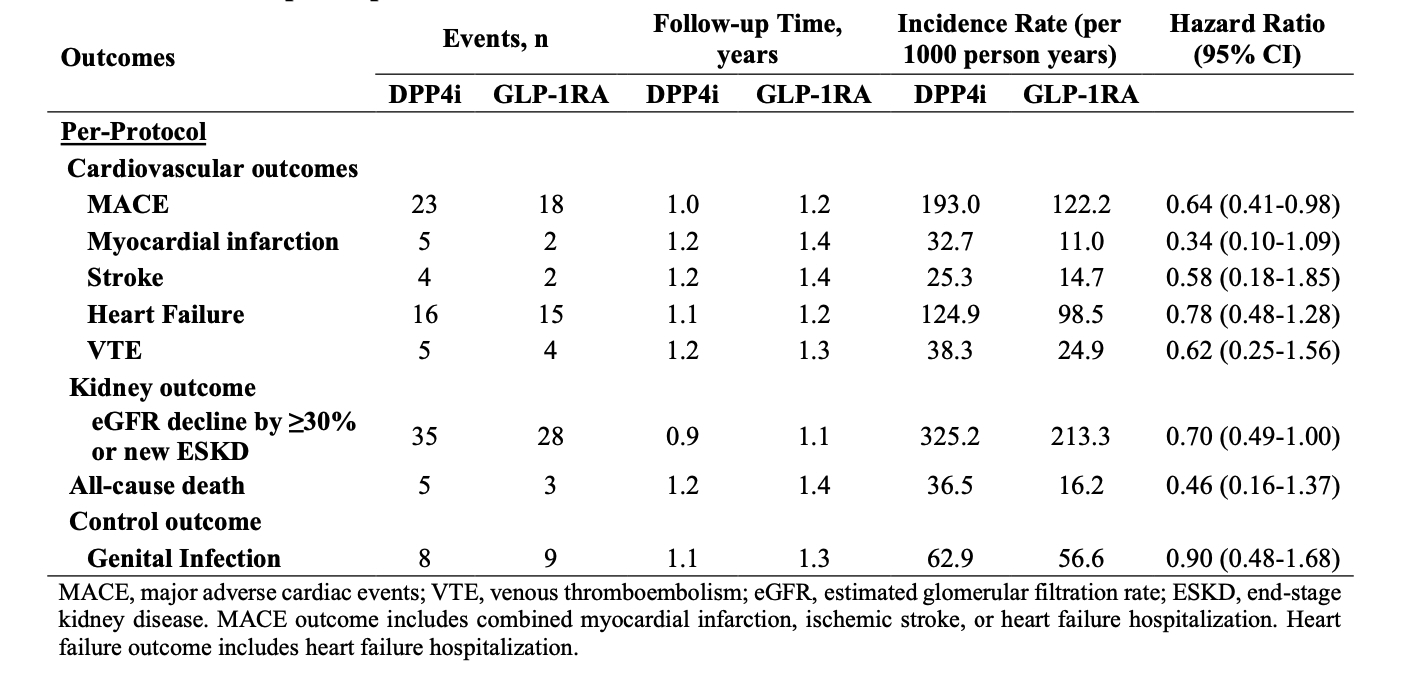
Results: There were 910 and 1004 initiators of GLP-1RA and DPP4i, respectively, with SLE and T2D; of these, 267 and 324 patients had LN, respectively. Baseline covariates were balanced after propensity score overlap weighting (Table 1). The mean age was 55 years, and 92% of patients were female; 48% were Non-Hispanic White, and 35% were Black. One-third had CKD ≥3. In the per-protocol analysis, the risks of MACE (HR 0.66 [95% CI 0.48-0.91]), VTE (HR 0.49 [0.24-0.97]), kidney disease progression (HR 0.77 [95% CI 0.60-0.98]), and all-cause death (HR 0.26 [95% CI 0.10-0.68]) were lower in the GLP-1RA users vs. DPP4i users (Table 2). In the ITT analysis, the HRs were 0.80 (95% CI 0.62-1.03) for MACE, 0.79 (95% CI 0.65-0.96) for kidney disease progression, and 0.42 (95% CI 0.25-0.73) for all-cause death. Within the LN subgroup, GLP-1RA use was similarly associated with lower risks of MACE and kidney disease progression (Table 3). There was no difference in the risk of the control outcome of genital infection (HR 1.02 [95% CI 0.69-1.50]).
Conclusion: In this study of patients with SLE and T2D, we found a lower risk of MACE, VTE, kidney disease progression, and all-cause mortality with use of GLP-1RA vs DPP4i. Our study is limited by a small sample size, and all SLE patients also had T2D as an indication for treatment. Overall, these findings support the potential benefits of GLP-1RA to reduce morbidity among patients with SLE and warrant further investigation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jorge A, Patel A, Zhou B, Zhang Y, Choi H. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Use and the Risk of Adverse Cardiac and Kidney Outcomes Among Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucagon-like-peptide-1-receptor-agonist-use-and-the-risk-of-adverse-cardiac-and-kidney-outcomes-among-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucagon-like-peptide-1-receptor-agonist-use-and-the-risk-of-adverse-cardiac-and-kidney-outcomes-among-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-lupus-nephritis/