Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
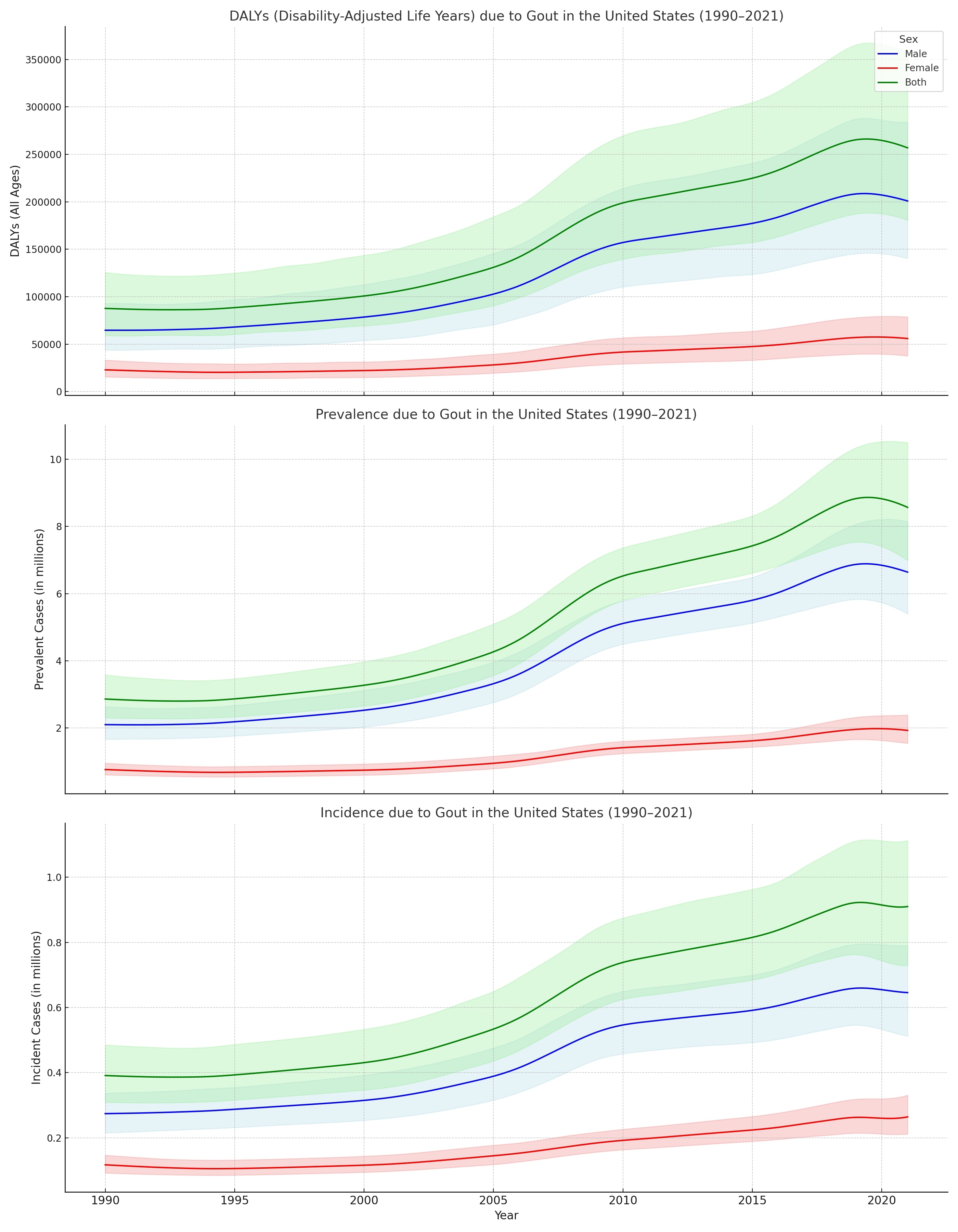
Background/Purpose: Gout, a chronic inflammatory arthritis driven by hyperuricemia, has become an increasingly significant cause of disability in the United States. Despite therapeutic advances, its rising burden and geographic disparities remain poorly understood. This study quantifies the long-term trends in gout-related prevalence, incidence, and years lived with disability (YLDs) across all 50 U.S. states from 1990 to 2021.
Methods: We utilized the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study framework to estimate gout-related prevalence, incidence, and years lived with disability (YLDs) across all U.S. states from 1990 to 2021. Data were stratified by sex and analyzed at the state level. To assess temporal trends, we calculated the annualized percentage change (APC).
Results: Nationally, from 1990 to 2021, the age-standardized prevalence rate of gout increased from 1,036 to 1,723 per 100,000, incidence rose from 140 to 230 per 100,000, and YLDs grew from 31.8 to 56.4 per 100,000. The corresponding national APCs were 1.61% for prevalence, 1.45% for incidence, and 1.87% for YLDs. State-level analysis revealed the highest APC in YLDs occurred in Mississippi (2.12%), Georgia (2.10%), and Hawaii (2.09%), while the lowest was observed in Minnesota (1.50%). For prevalence, Mississippi (2.17%) and Georgia (2.12%) again led, whereas Minnesota (1.55%) and Maine (1.58%) showed the slowest rise. Incidence rates saw the steepest increase in Wyoming (1.40%) and Mississippi (1.38%), with the smallest change in Minnesota (0.89%). Sex-specific analysis showed consistently higher rates and steeper increases in males compared to females across all measures.
Conclusion: The burden of gout has risen substantially across the U.S. over the past three decades, with marked geographic heterogeneity. Southern states like Mississippi and Georgia experienced the fastest growth across all indicators. These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted public health interventions and equitable access to preventive and therapeutic gout care in high-burden regions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kalra E, Gajbhiye D, Tummala C, Desai H. Geographic Trends in the Burden of Gout in the United States from 1990 to 2021: A State-Level Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, and Disability [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/geographic-trends-in-the-burden-of-gout-in-the-united-states-from-1990-to-2021-a-state-level-analysis-of-prevalence-incidence-and-disability/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/geographic-trends-in-the-burden-of-gout-in-the-united-states-from-1990-to-2021-a-state-level-analysis-of-prevalence-incidence-and-disability/

.jpg)
.jpg)