Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0543–0581) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most common and severe manifestation of SLE. Risk factors for lupus nephritis and renal function decline are not well understood. We completed a genome wide association study (GWAS) of LN in a multi-ethnic cohort of children and adults with SLE.
Methods: We included SLE patients from dedicated Lupus clinics and the SLICC cohort. All patients met ACR and/or SLICC SLE classification criteria and were genotyped on a multi-ethnic Illumina array. Ungenotyped SNPs were imputed to TopMed, and principal components for ancestral estimation were generated using both 1000 Genomes and GRAF-pop. LN was defined by SLE criteria and confirmed on kidney biopsy in 75%. Kidney function (estimated glomerular filtration rate, eGFR) was calculated using the Schwartz Bedside formula for measures < 18 years and CKD-EPI (without race) for >18 years of age and collected longitudinally over time. Wilcoxon rank sum or Chi-square tests were used to compare characteristics between LN and Non-LN patients. We completed GWAS of LN in marginal and multivariable adjusted regression models with principal components for ancestry, sex and cohort site.
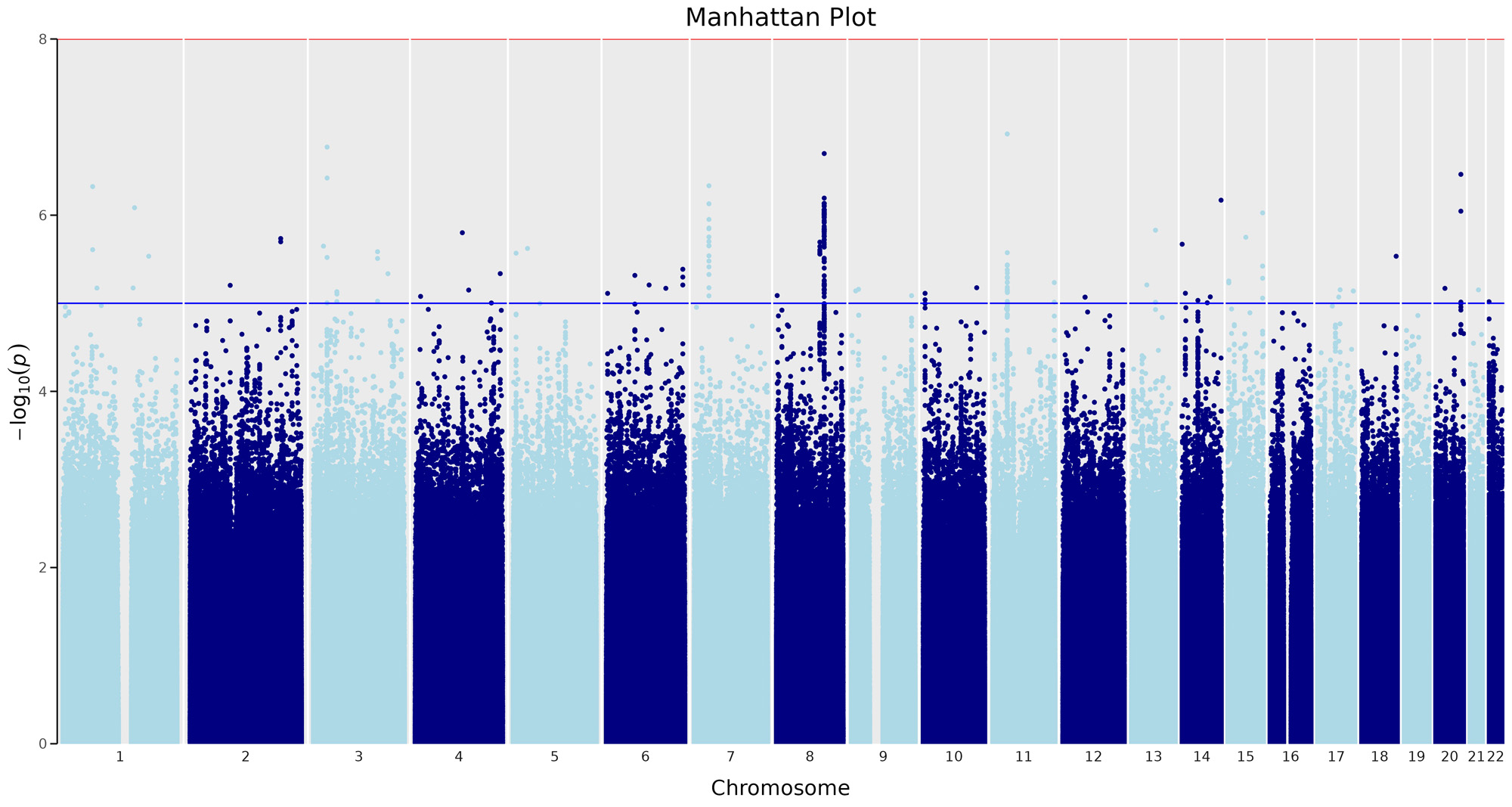
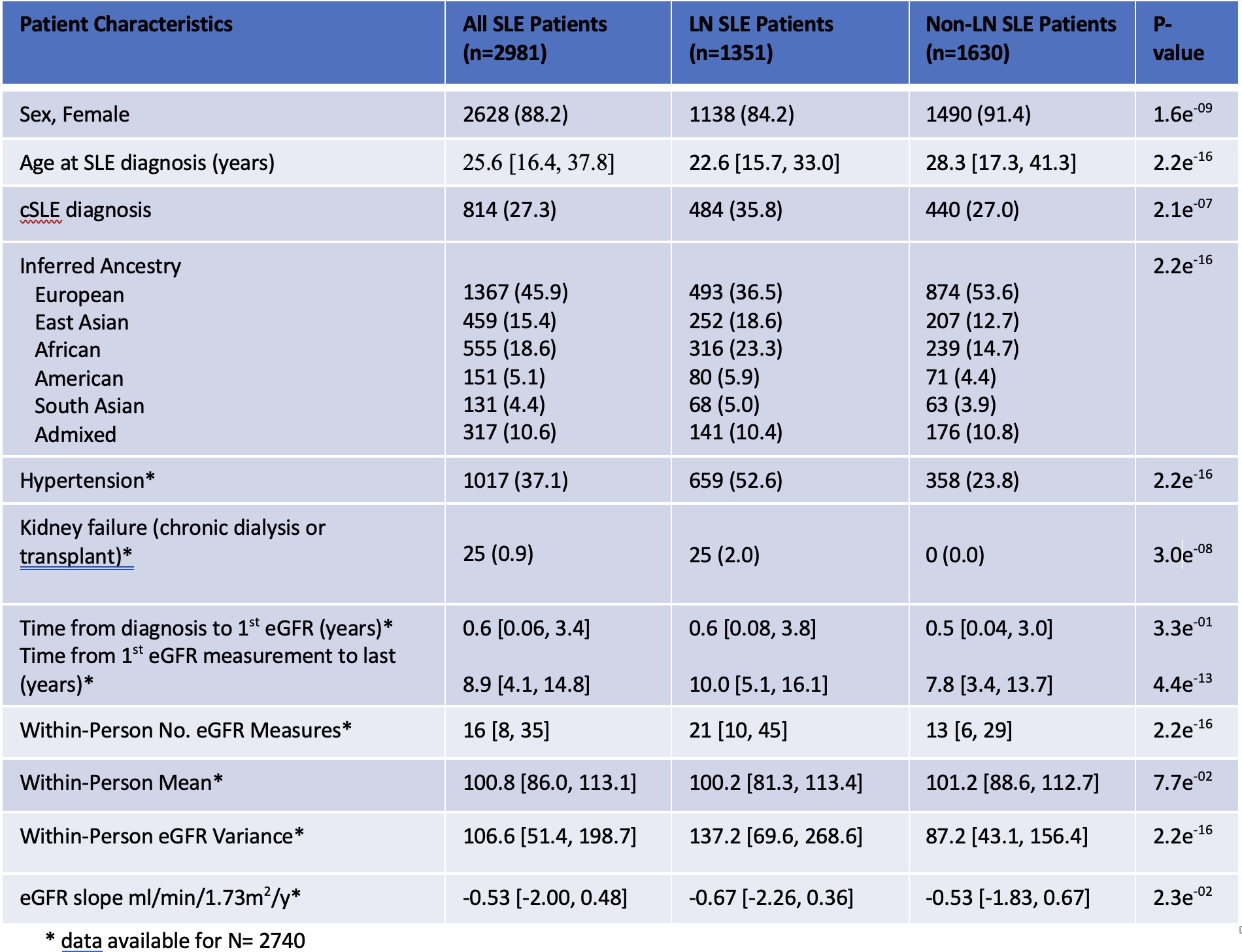
Results: The study included 2981 patients with SLE, 88% female, 46% of European ancestry and 27% childhood-onset SLE. LN was present in 45%. People with LN were younger at diagnosis, and more likely of African American or East Asian ancestry than those without LN. People with LN had significantly lower within-person mean eGFR, greater eGFR variability and slope over time compared to those without LN (Table). GWAS of LN demonstrated a peak on chromosome 8, intronic to ATP6V1C1, yet did not reach a genome-wide significance (p < 5×10-8).
Conclusion: A GWAS of LN in a multiethnic cohort of children and adults with SLE, did not identify a significant locus. The top signal was on chromosome 8, intronic to ATP6V1C1. We will complete GWAS of repeated eGFR measures, as it is a more informative outcome that we expect will improve power for detecting genetic loci for LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Riedl Khursigara M, Gold N, Tang T, Dominguez D, Klein-Gitelman M, Gladman D, Goldman D, Harvey E, Ishimori M, Jefferies C, Kamen D, Kamphuis S, Knight A, Lee C, Levy D, Noone D, Onel K, Peschken C, Petri M, Pope J, Pullenayegum E, Silverman E, Touma Z, Urowitz M, Wallace D, Wither J, Hiraki L. Genetic Determinants of Lupus Nephritis and Kidney Function in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-determinants-of-lupus-nephritis-and-kidney-function-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-determinants-of-lupus-nephritis-and-kidney-function-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/