Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder primarily affecting the axial skeleton and associated with HLA-B27. Non-HLA genes, including ERAP1 (Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 1), also play a role in pathogenesis by influencing peptide trimming and cytokine regulation. The rs27038 SNP in ERAP1 may affect antigen processing and inflammatory responses. IL-17, a key proinflammatory cytokine, is central to AS immunopathology. This study investigates the association of ERAP1 rs27038 SNP with AS susceptibility, IL-17 levels, and disease severity.There is limited data on ERAP1 gene polymorphisms and IL-17 levels in Indian patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis, despite genetic and immunological differences across populations. This study addresses the gap by exploring the association of ERAP1 rs27038 and IL-17 in South Indian AS patients, aiming to improve early diagnosis and guide population-specific therapeutic approaches.
Methods: A case-control study included 75 AS patients (modified New York criteria) and 25 age- and sex-matched healthy controls from a tertiary care centre in South India . Clinical parameters (BASDAI, ESR, hsCRP) were recorded. Genomic DNA was extracted, amplified using qPCR and rs27038 SNP genotyping was done via Sanger’s sequencing. Serum IL-17 was quantified by ELISA. Genotypic and allelic frequencies were compared using Chi-square test. IL-17 levels were compared using the ManWhithey U test. Correlations with disease activity were analyzed using Spearman’s rank correlation.
Results: Serum IL-17 levels were significantly elevated in AS patients (median 48.39 pg/mL) compared to controls (median 8.78 pg/mL, p=0.0002). The ERAP1 rs27038 polymorphism showed significant association with AS susceptibility, with the A allele being more frequent in cases than controls (22% vs. 8%, p=0.03, OR=3.15, 95% CI: 1.05-9.24). Serum IL-17 demonstrated good diagnostic performance (AUC=0.848, 95% CI: 0.755-0.917), comparable to hsCRP (AUC=0.843). Il-17 showed a significant correlation with hsCRP levels (rho=0.353, p=0.0009), but did not show association with BASDAI/ASDAS (rho=0.120, p=0.34; rho=0.13, p=0.31 respectively). Logistic regression identified HLA-B27 positivity (OR=38.25), elevated ESR (OR=1.095), and Patient Global Assessment (OR=1.94) as independent predictors of AS. However, no significant associations were found between rs27038 genotypes and IL-17 levels.
Conclusion: Our findings support the role of both IL-17-mediated inflammation and ERAP1 genetic variants in AS pathogenesis. Serum IL-17 could serve as a valuable biomarker for AS diagnosis, potentially enabling earlier detection and intervention. The ERAP1 rs27038 polymorphism contributes to AS susceptibility but appears to act through pathways independent of IL-17 regulation. These results provide insights into AS pathogenesis and suggest potential applications in diagnosis, risk assessment, and targeted therapies.
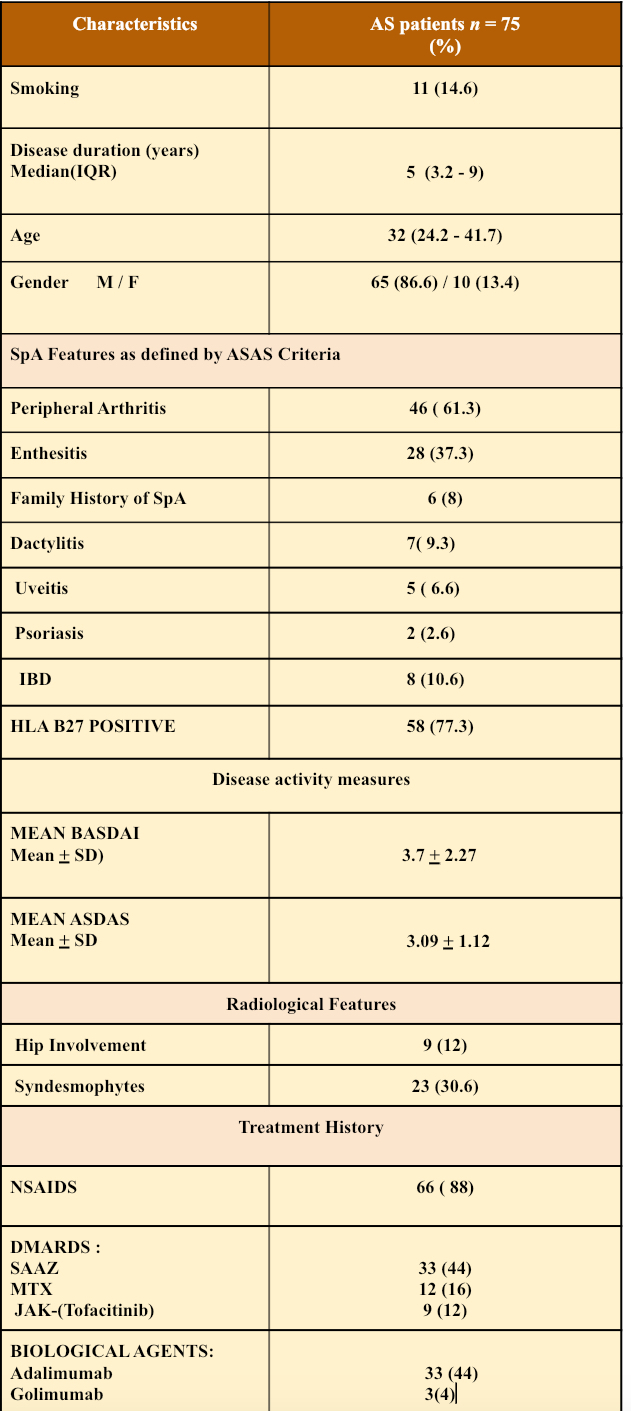 Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patients with ankylosing spondylitis
Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patients with ankylosing spondylitis
.jpg) Figure1: Serum IL-17(pg/mL) in Cases vs Controls (P = 0.0002)
Figure1: Serum IL-17(pg/mL) in Cases vs Controls (P = 0.0002)
.jpg) Table 2: Genotype distribution and allele frequency of rs27038 SNP in study population
Table 2: Genotype distribution and allele frequency of rs27038 SNP in study population
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gavali M, Fatima H, Sirivelu B, S N, M N. Genetic and Cytokine Correlates in Ankylosing Spondylitis: rs27038 polymorphism of ERAP1 gene and IL-17 Interactions : A Case-Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-and-cytokine-correlates-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-rs27038-polymorphism-of-erap1-gene-and-il-17-interactions-a-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-and-cytokine-correlates-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-rs27038-polymorphism-of-erap1-gene-and-il-17-interactions-a-case-control-study/
