Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0543–0581) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-Ro antibodies can be detected in 40% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and have been associated with various clinical manifestations of the disease as well as maternal-fetal complications. The aim of this study was to describe the frequency of anti-Ro antibodies in SLE patients and to assess their association with disease characteristics, maternal-fetal complications, treatment, morbidity and mortality.
Methods: Retrospective observational study. Data from SLE patients of the National Registry of the Argentine Society of Rheumatology (RELESSAR) were used. Sociodemographic data, comorbidities, disease characteristics, maternal-fetal complications, SLE morbidity and mortality, activity and damage scores were recorded.
Statistical analysis: Descriptive statistics. Appropriate tests (Chi2, Fisher, Student’s t-test or Wilcoxon), and univariate/multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify factors associated with presence of anti-Ro antibodies.
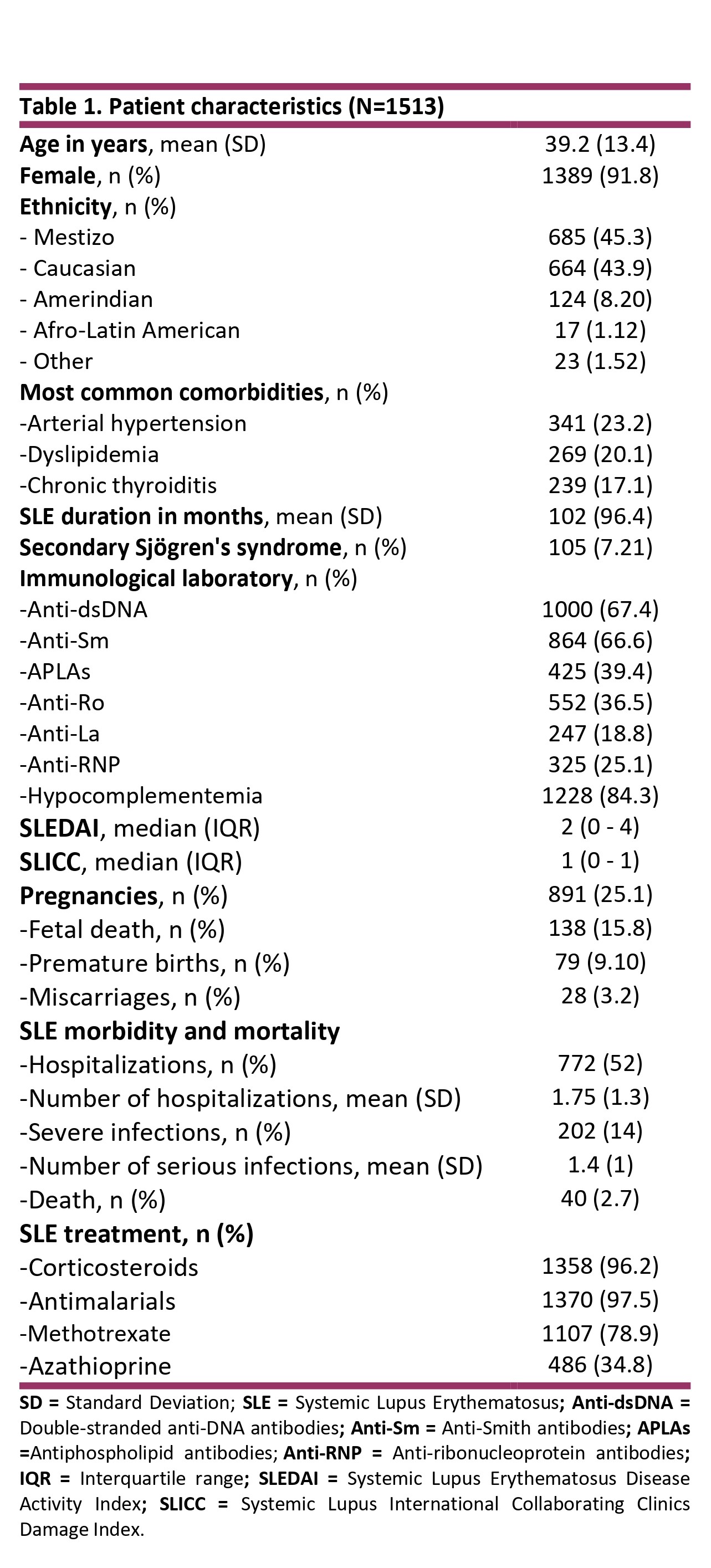
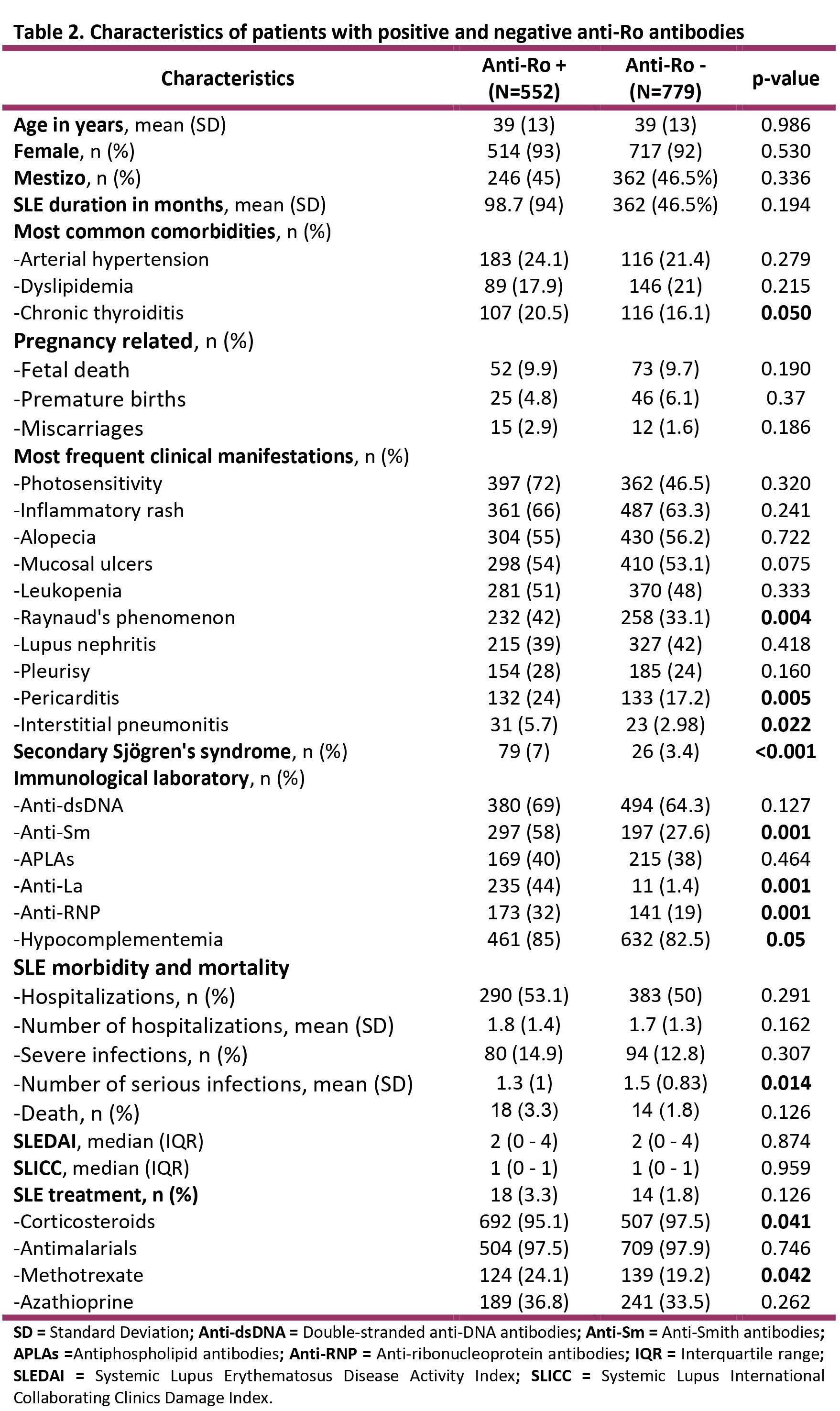
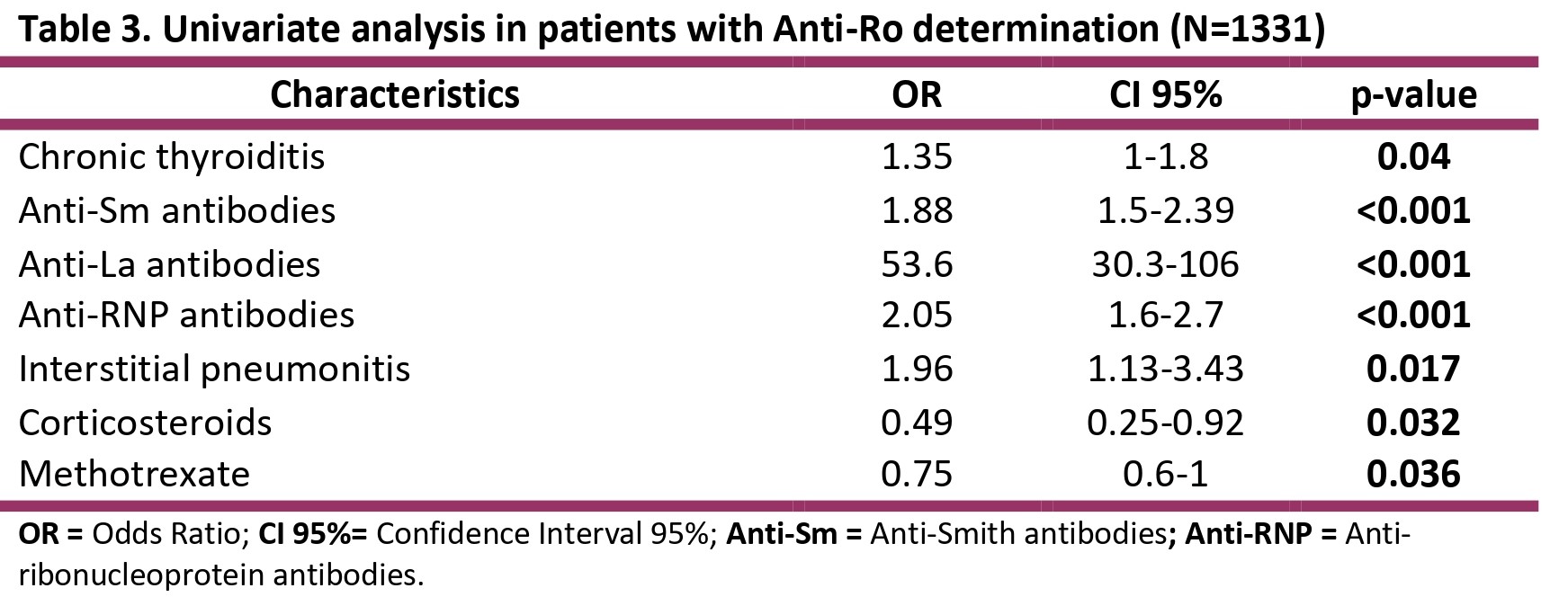
Results: A total of 1513 patients were included. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. Anti-Ro antibodies were requested in 88% (n=1331), of which 41% (n=552) were positive. Characteristics of patients with positive and negative Anti-Ro antibodies can be observed inTable 2. Anti-Ro antibodies were associated with hypocomplementemia (p< 0.05), anti-La antibodies (< 0.001), anti-Sm antibodies (p< 0.001), anti-RNP antibodies (p< 0.001) and Sjogren’s syndrome (p< 0.001). Also were associated with Raynaud’s phenomenon (p< 0.004), pericarditis (p< 0.005) and interstitial pneumonitis (p< 0.02). More infections (p< 0.01) and a greater use of corticosteroids (p< 0.04) and methotrexate (p< 0.04) were observed. Univariate analysis in patients with Anti-Ro determination is shown in table 3. In the multivariate model, the independent variables were anti-Sm antibodies (OR 1.9, 95% CI 1.4-2.5), anti-La antibodies (OR 48, 95%CI 26-99), chronic thyroiditis (OR 1.9, 95%CI 1.3-2.7) and the use of methotrexate (OR 0.66, 95%CI 0.5-0.9).
Conclusion: In this SLE patients, anti-Ro positivity was associated with the presence of other antibodies, chronic thyroiditis and methotrexate use, but not with any specific clinical profile, maternal-fetal complications or SLE-related morbidity and mortality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mendoza Martinez L, Dapeña J, Bande J, Medina M, Papasidero S, caracciolo J, Quintana R, Garcia L, Gobbi C, Sapag Durán S, Spindler A, Alvarez A, Pisoni C, Gomez C, Paniego R, Santa cruz M, Gonzalez Lucero L, Aguila Maldonado R, Gordon S, Romero J, Rausch G, Allievi A, Orden A, zacariaz hereter j, Baéz R, González A, Vandale J, Goñi M, Caputo V, Larroudé M, Gómez G, Marin J, Collado V, María Victoria G, Zelaya M, Sacnún M, Rojas Tessel R, Arias Saavedra M, Machado Escobar M, Astesana P, Paris U, Pons-Estel B, García M. Frequency of Anti-Ro Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: Insights from Multicenter and National Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-of-anti-ro-antibodies-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-insights-from-multicenter-and-national-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-of-anti-ro-antibodies-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-insights-from-multicenter-and-national-registry/