Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: RFs are polyclonal autoantibodies which bind the Fc domain of IgGs. Patients with RA and high RF levels have poorer prognosis, more severe progressive disease, greater joint and bone destruction, and decreased response to certain biological DMARD (bDMARD) therapies. Post-hoc analysis of the EXXELERATE phase 4 trial (NCT01500278), showed that in the highest RF quartile patients ( >204 IU/ml), adalimumab (ADA) concentrations and treatment target achievement were reduced compared with the lower RF quartiles. By contrast, patients treated with the Fc-free PEGylated Fab, certolizumab pegol (CZP), maintained consistent drug concentrations and had similar clinical outcomes across all RF quartiles.1 In this study, we determine the molecular basis of RF binding to bDMARDS and the potential impact on bDMARD efficacy.
Methods: Monoclonal RFs (RF-AN, RF-61, RF-Yes8cT56K, SG22)2-5 and bDMARDs [ADA, infliximab (IFX), golimumab (GLM), etanercept (ETN), tocilizumab (TCZ), rituximab (RTX), and abatacept (ABT)] were based on published sequences and produced in mammalian cells. Certolizumab (CZ) Fab’ was produced in E. coli and PEGylated according to manufacturing guidelines. Human sera were obtained from Medix Biochemica. RF binding to bDMARDs was assessed by ELISAs and surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Modelling of RF:Fc complex and CZ used Protein Data Bank structures: 5WUV, 1ADQ. Protein complex formation was assessed by dynamic light scattering (DLS). Live cell imaging of primary human macrophages was performed with an Incucyte microscope (Sartorius).
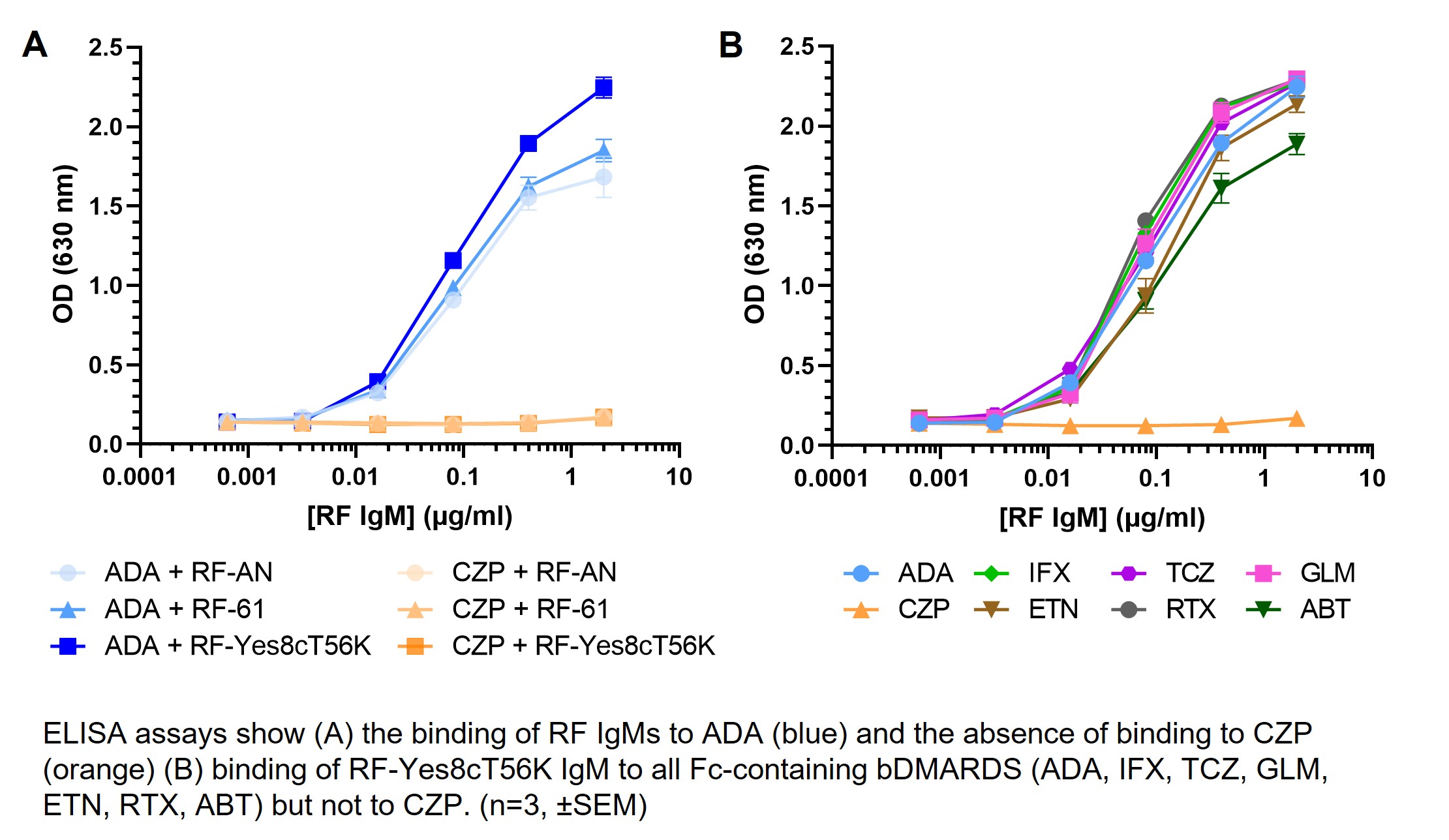
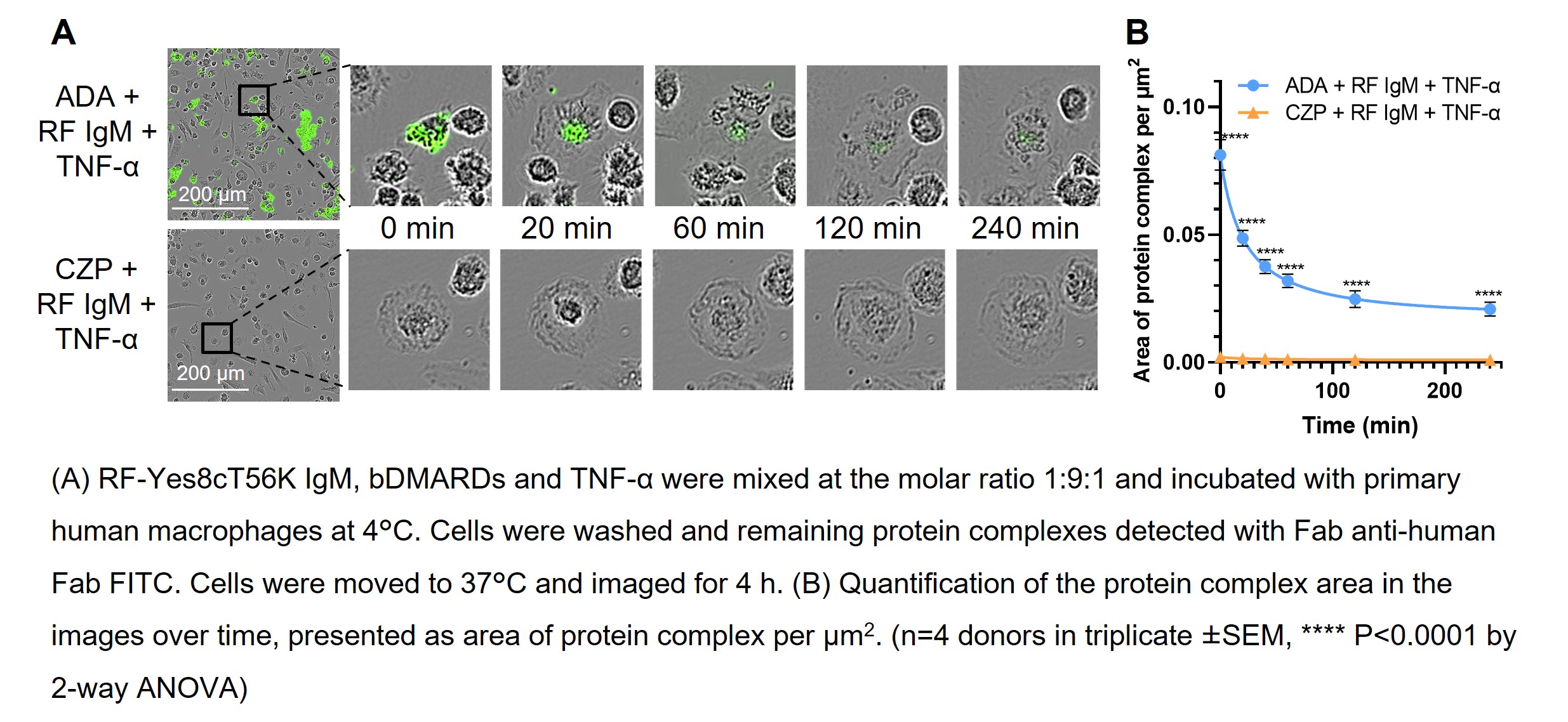
Results: Monoclonal RF IgMs bound to all Fc-containing bDMARDs tested both by ELISA and SPR. No binding to CZP could be detected (Figure 1). RF positive sera from RA patients showed similar characteristics. X-ray crystallography structures showed RF-AN IgM Fab binding to human IgG1 Fc. In contrast, the structure of CZ highlights that CZP has no Fc domain for RF interactions. DLS showed that ADA formed large protein complexes when mixed with IgM RFs and TNF-α, while CZP did not. ADA-TNF-α-RF protein complexes were cleared by primary human macrophages (Figure 2).
Conclusion: RFs bound to Fc-containing bDMARDs but not to Fc-free CZP. RF binding to ADA drove protein complex formation, which stimulated macrophage mediated protein complex clearance. These findings provide insights into why CZP efficacy is independent of patient RF level, while patients with RA and high RF levels, exhibit reduced serum drug concentrations and treatment outcomes when treated with Fc-containing bDMARDs, compared to those patients with lower RF levels.
References: 1. Smolen J. ACR Convergence 2023;2148; 2. Corper A. Nat Struct Biol 1997;4(5):374–81; 3. Duquerroy S. J Mol Biol. 2007;368(5):1321–31; 4. Shiroshi M. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(18):7008–16; 5. Bende R. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(4):1074-83.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bidgood S, Hopkin S, Malpas K, Kallenberg D, O’Neill J, Odede G, Lauwerys B, Ufuktepe B, Humphreys D. Fragment Crystallizable (Fc)-Free Certolizumab Pegol Is Not Bound by Rheumatoid Factors, While Fc Containing Biological DMARDsAre, Driving ImmuneComplex Formation and Cellular Clearance [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fragment-crystallizable-fc-free-certolizumab-pegol-is-not-bound-by-rheumatoid-factors-while-fc-containing-biological-dmardsare-driving-immunecomplex-formation-and-cellular-clearance/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fragment-crystallizable-fc-free-certolizumab-pegol-is-not-bound-by-rheumatoid-factors-while-fc-containing-biological-dmardsare-driving-immunecomplex-formation-and-cellular-clearance/