Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: CD19-targeting CAR T cells showed remarkable improvements of modified Rodnan skin score in SSc patients within 6 months after treatment and stable reduction afterwards as reported previously. Histologically, we observed the partial recovery of papillary dermal structures and the reduced expression of Fibroblast activation protein upon CD19 CART treatment.
Objectives: To analyze transcriptomic changes that occur upon CD19.CART therapy, bulk-RNA Sequencing of skin biopsy samples was performed.
Methods: Skin biopsies were taken after cessation of previous immunosuppression before CD19.CART treatment (n=4) and one, six and twelve months after application of CD19.CART-therapy (n=5, respectively). RNA was isolated using Nucleo Spin Machery Nagel kit. Illumina Sequencing was performed. Quality control on the Illumina raw data was done using FastQC and trim_galore. The processed paired-end reads were then aligned to the reference human genome (GRCh38 release 111) using the aligner, STAR, and the mapping outputs were exported to transcriptome coordinates for quantitation with Salmon. Using the tximport R package, transcript level counts for each sample were read and converted to gene-level counts to produce a length-scaled counts matrix. Using the counts matrix and sample metadata, we performed differential expression (DEG) analysis using DESeq2. We also used variancePartition to assess potential factors contributing to technical variance and included them in the design matrix. For DEG analysis, we modelled patient and time to extract desired contrasts (post-treatment samples against the reference, before CAR treatment samples). Significant DEG were exported at an adjusted P-value cutoff < 0.05 for each comparison.
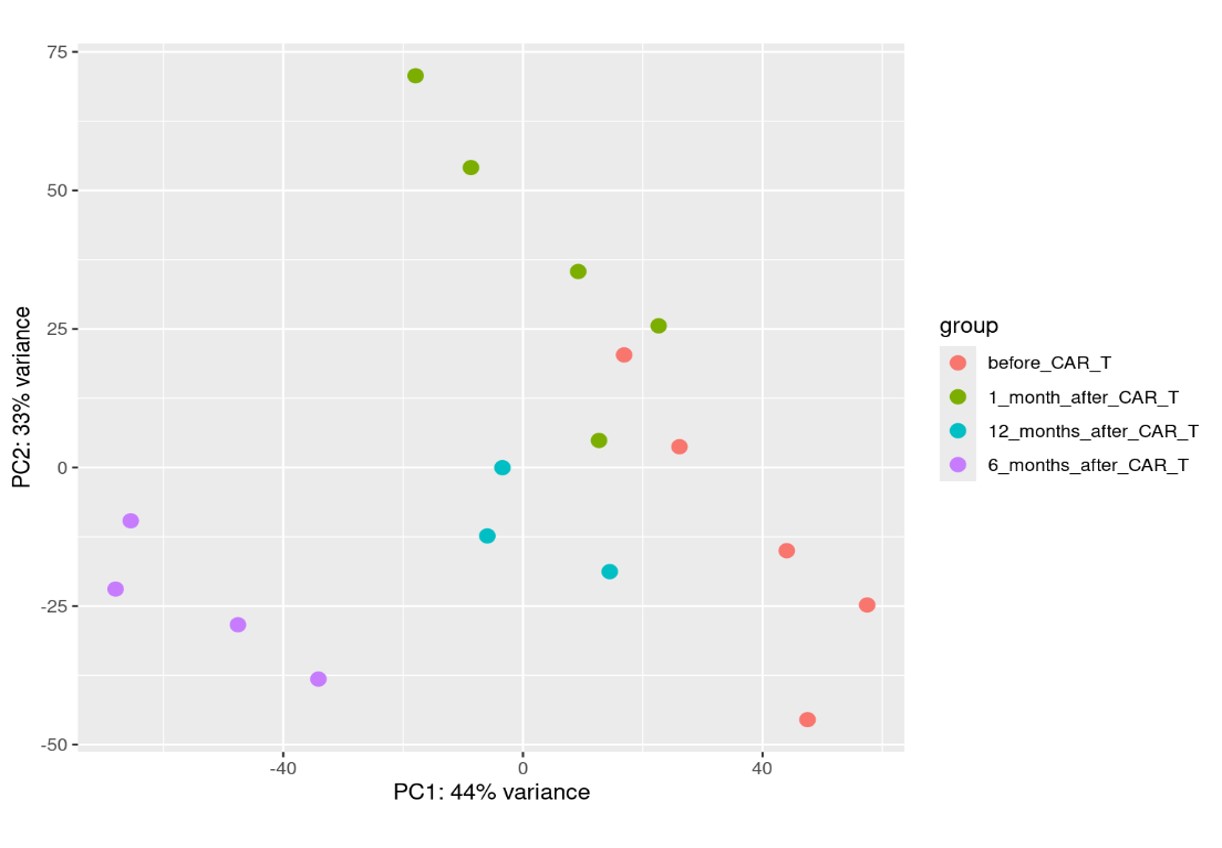
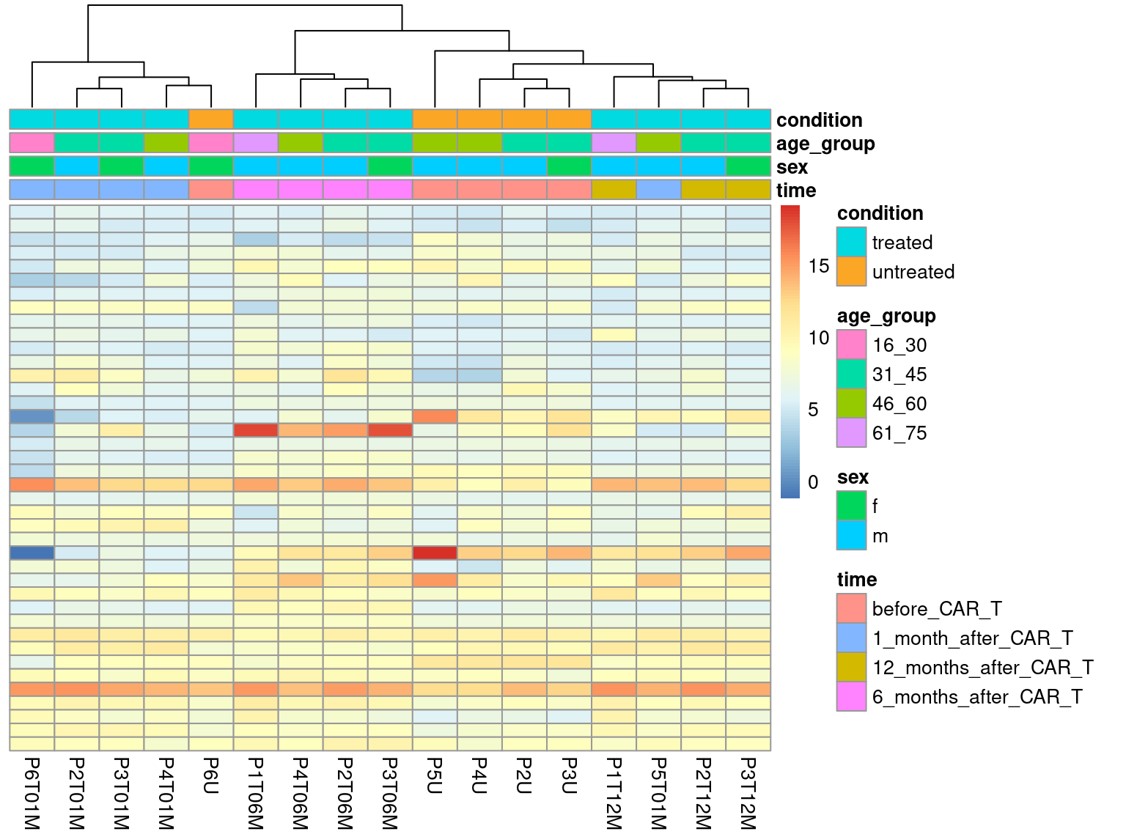
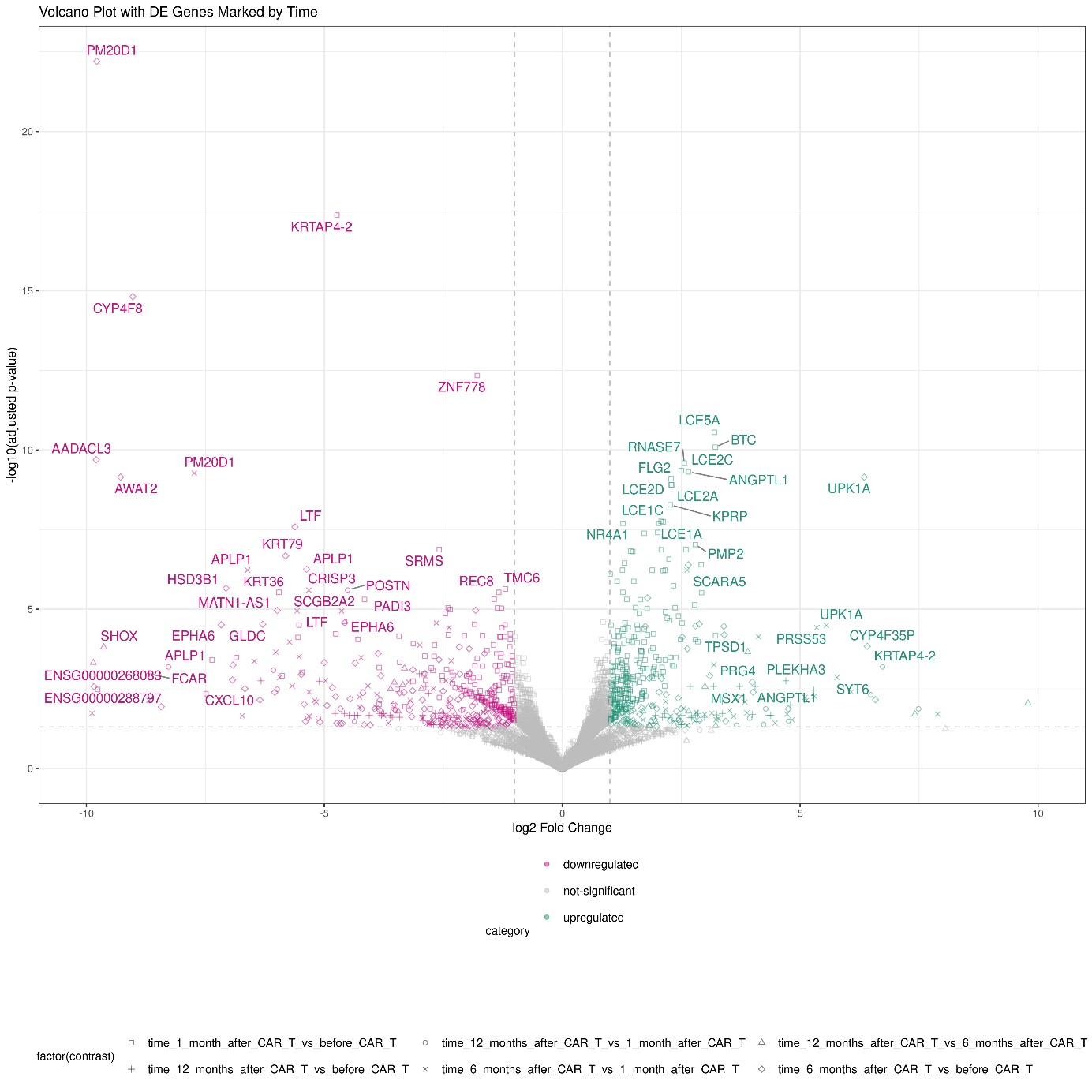
Results: After adjustment for experimental variances, the samples taken before CD19.CART therapy and after 1, 6 and 12 months clustered as demonstrated by Principal Component Analysis and displayed in figure 1. Differentially expressed genes in each group of samples are visualized in figure 2. Based on the significance level described above, 374 genes were significantly upregulated and 397 genes were significantly downregulated as visualized in the Vulcano plot in figure 3. The following comparisons were performed before CD19.CAR-T treatment and after 1,6,12 month respectively and in between the different time-points and analysis is ongoing. Finally, we performed functional enrichment using the significant genes using gProfiler2 in R. Interestingly, downregulation of genes associated with extracellular matrix and upregulation of genes associated with inhibition of inflammation driven tissue fibrosis was observed. Further validation analyses are ongoing.
Conclusion: Here, we first describe transcriptomic changes occurring in the skin upon CD19.CAR-T treatment as analyzed by bulk-RNA Sequencing. Samples cluster depending on the time point of analysis. DEG associated with reduction of extracellular matrix are detected. Further analyses are ongoing.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Auth J, Kumar Selvaraju M, Müller F, Gupta P, Ekici A, Tur C, Raimondo M, Distler J, Dees C, Chenguiti S, Hagen M, Wirsching A, Taubmann J, Kharboutli S, Spoerl S, Aigner M, Kretschmann S, Vasova I, MAckensen A, Schett G, Bergmann C. First Analyses of Transcriptomic Changes in the Skin of SSc Patients upon CD19-targeting CAR T Cell Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/first-analyses-of-transcriptomic-changes-in-the-skin-of-ssc-patients-upon-cd19-targeting-car-t-cell-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/first-analyses-of-transcriptomic-changes-in-the-skin-of-ssc-patients-upon-cd19-targeting-car-t-cell-therapy/